Web Stories
Latest Blogs
Blood-Brain Barrier: What It Is And Why It Matters
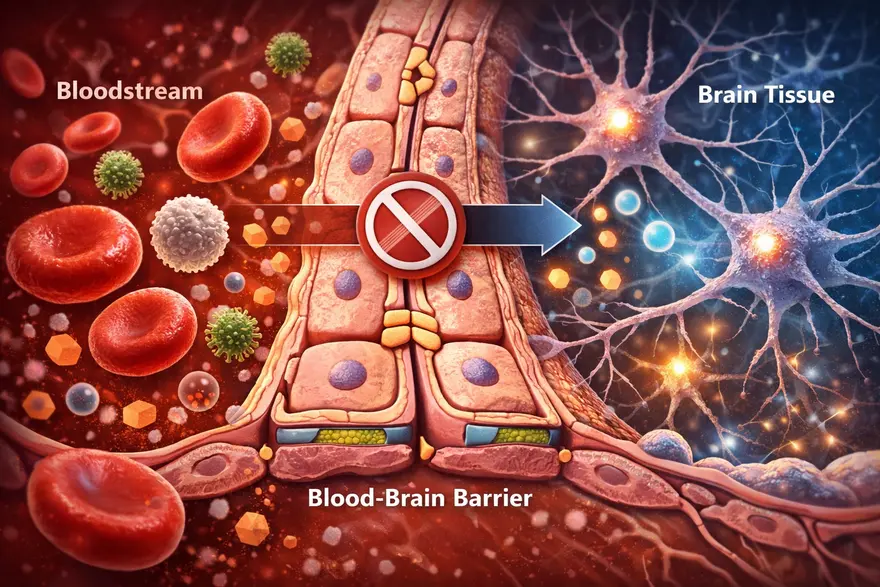
Your brain needs constant fuel from your blood, like oxygen, glucose, and other nutrients. But it also needs protection from germs, toxins, and sudden chemical shifts that could disrupt delicate brain signalling. That is where the blood-brain barrier (BBB) comes in. The BBB is a specialized “gatekeeper” built into the small blood vessels of the brain. It carefully controls what can enter and leave brain tissue, helping keep the brain’s internal environment stable. In this article, you will learn what the blood-brain barrier is, how it works, what can (and cannot) cross it, what happens when it is disrupted, and why it matters for neurological conditions and medicines. Medical note: This is educational information, not a substitute for medical advice. What Is The Blood-Brain Barrier? The blood-brain barrier is a highly selective filter formed by specialized cells lining the brain’s tiny blood vessels. It protects the brain by allowing essential nutrients in while blocking many harmful substances, germs, and toxins. Blood-brain barrier in one sentence: It is the brain’s security system, a tight, selective lining of blood vessels that controls what reaches brain tissue. Why Is The Blood-Brain Barrier So Important? The brain is extremely sensitive to changes in its chemical environment. Even small shifts in salts (electrolytes), hormones, or inflammatory molecules can affect how neurons communicate. The BBB helps by: Protecting the brain from pathogens and circulating toxins Maintaining stability (brain “homeostasis”) so neurons can function normally Controlling immune access, limiting unnecessary inflammation in brain tissue Influencing treatment, because many medicines cannot easily cross it In short, the BBB is one reason your brain can stay stable and functional even while your bloodstream changes with meals, exercise, stress, or illness. Blood-Brain Barrier Structure: What It’s Made Of The BBB is not one single wall. It is a set of structures working together in what scientists often call the neurovascular unit. The key components include: Endothelial Cells With Tight Junctions (The “Sealed Lining”) Brain capillaries are lined by endothelial cells that are packed unusually tight. The tight junctions between them act like sealant, preventing many substances from slipping between cells. Basement Membrane (The Support Layer) A thin structural layer supports the vessel wall and helps organize the barrier’s architecture. Pericytes (Stability And Regulation) Pericytes wrap around capillaries and help maintain vessel integrity, regulate permeability, and support repair. Astrocyte End-Feet (Barrier Support And Signalling) Astrocytes are support cells in the brain. Their “end-feet” surround blood vessels and help maintain BBB function through signalling and regulation. How The Blood-Brain Barrier Works Because the BBB is so selective, most substances cannot just drift into brain tissue. Entry is controlled mainly through specific routes: Passive diffusion (limited) Some small, non-charged, and fat-soluble (lipid-soluble) molecules can cross more easily by diffusion. Carrier transport (nutrients get VIP access) Essential molecules that the brain needs, but that are water-soluble, use transporters, such as: Glucose transporters (for the brain’s primary fuel) Amino acid transporters (for building blocks of proteins and neurotransmitters) Receptor-mediated transport (selective “escorts”) Certain larger molecules can cross via receptor-based mechanisms (think: a locked gate that opens for specific credentials). Efflux pumps (active “bouncers”) The BBB also has efflux transporters that pump certain substances out of brain tissue back into blood. This is a major reason many drugs struggle to reach effective levels in the brain. What Can Cross The Blood-Brain Barrier? A helpful way to think about BBB access is this: small + lipid-soluble + uncharged tends to cross more easily, while large + water-soluble + charged usually needs a transporter or cannot cross well. Common examples that may cross the BBB to some degree include: Oxygen and carbon dioxide Some anaesthetic agents Some psychiatric and anti-seizure medications Alcohol and caffeine (both can affect the brain partly because they can cross) Important note: Whether a specific medicine crosses the BBB depends on its chemical properties and how strongly it is pumped out by efflux transporters. This is why two drugs in the same category can behave differently. What Usually Cannot Cross The Blood-Brain Barrier? The BBB blocks many things that could harm the brain, including: Many bacteria and viruses (though some infections can still reach the brain through other mechanisms) Many toxins and large proteins Many antibiotics and chemotherapy agents (which is why treating brain infections and brain tumours can be challenging) What Happens When The Blood-Brain Barrier Is Disrupted? The BBB is strong, but it is not invincible. Inflammation, injury, reduced oxygen, and vascular damage can weaken barrier function. When that happens, substances that are usually kept out may leak into brain tissue, potentially triggering swelling, inflammation, and changes in brain signalling. Conditions Linked With BBB Dysfunction (High Level) BBB disruption has been associated with a range of conditions, including: Stroke (especially in the area around injured tissue) Traumatic brain injury (TBI) and concussion Meningitis and encephalitis (brain and brain-lining infections) Multiple sclerosis and other inflammatory conditions Some neurodegenerative diseases (research shows BBB changes may play a role in certain cases) Chronic metabolic and vascular stress (such as uncontrolled high blood pressure or high blood sugar, which can affect vessel health) This does not mean BBB dysfunction is the only cause of these conditions. It is better understood as one piece of a complex puzzle. BBB And Neurodegenerative Diseases BBB changes are increasingly discussed in research on neurodegenerative diseases, meaning conditions that involve progressive changes in the brain over time. In some studies, BBB dysfunction has been linked with: Reduced clearance of waste proteins from the brain Increased inflammation signalling within brain tissue Greater vulnerability of neurons to metabolic and vascular stress In practical terms, BBB dysfunction is considered a potential contributor in some cases, rather than a single “root cause.” Neurodegenerative diseases are complex, and most experts view BBB changes as one factor among genetics, immune activity, vascular health, and other brain processes. The Role Of The BBB In Cancer The BBB matters in cancer mainly because it influences how well treatments can reach brain tissue. This is relevant in two major situations: Primary brain tumours (tumours that start in the brain) Metastases (cancers that spread to the brain from elsewhere in the body) Key points clinicians and researchers consider: Drug delivery is challenging: Many chemotherapy drugs and large targeted therapies struggle to cross an intact BBB in effective amounts. The barrier can be abnormal in tumour regions: Tumours can disrupt the BBB locally, but the disruption is often uneven. Some areas may be leaky while others remain protected, which can lead to patchy drug penetration. The “blood-tumour barrier” concept: In tumours, the barrier environment may differ from normal BBB. It can still block drugs even when it appears more permeable, which complicates treatment strategies. This is why brain tumour treatment often requires carefully selected therapies and, in some cases, a combination of surgery, radiation, and drug approaches designed to improve access to the tumour. Does BBB Disruption Cause Symptoms On Its Own? Usually, BBB disruption is not something you can “feel” directly. Symptoms are more often caused by the underlying condition affecting the brain (like stroke, infection, or inflammation). However, depending on the cause and the brain areas involved, symptoms might include: Headache, fever, neck stiffness (more typical with infections) Confusion, drowsiness, or altered alertness New neurological symptoms such as weakness, speech difficulty, seizures, or severe imbalance (more concerning for urgent causes) When To Seek Urgent Medical Care Seek emergency care if someone develops sudden neurological symptoms such as: Sudden one-sided weakness or numbness Facial drooping Trouble speaking or understanding speech New seizure Severe sudden headache Severe confusion, fainting, or reduced consciousness Sudden vision loss or major balance problems These can indicate conditions like stroke, severe infection, or other time-sensitive emergencies. How Doctors Evaluate Conditions Involving The BBB Clinicians do not usually “test the BBB” as a standalone screening step. Instead, they evaluate the condition that may be affecting the brain and its vessels. History And Neurological Exam A clinician will focus on symptom timing (sudden vs gradual), triggers, fever or infection signs, medications, and risk factors (blood pressure, diabetes, immune conditions). A neurological exam checks strength, sensation, coordination, speech, eye movements, and reflexes. Imaging (Often Essential) Depending on symptoms, doctors may recommend: MRI brain: high-detail soft-tissue imaging; sometimes uses contrast to evaluate inflammation, tumours, or areas where the BBB may be more permeable CT head: often used in emergencies because it is fast, especially for bleeding concerns Lab Tests (To Identify Contributors) Blood tests depend on the clinical scenario. A clinician may recommend tests such as: Complete Blood Count (CBC) Electrolytes (sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium) Blood glucose and or HbA1c Inflammation markers (for example, CRP, when relevant) Infection-related testing when clinically suspected In certain cases (especially suspected infection or inflammation), clinicians may recommend cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) testing via lumbar puncture, because CSF can provide important clues about inflammation and infection in and around the brain. Why The BBB Matters For Medicines The BBB is a major reason some brain conditions are hard to treat: many drugs cannot reach the brain in sufficient amounts. This shapes how medications are designed and how treatment plans are chosen. Researchers are exploring multiple strategies to improve brain drug delivery (for example, designing drugs that use existing transport systems or temporarily opening the barrier under controlled conditions). These approaches are active areas of medical research and are used only in specific settings under specialist care. How The BBB Affects Mental Health Mental health conditions are complex and involve brain circuits, neurotransmitters, hormones, immune signalling, life experience, and genetics. BBB research adds another layer: the barrier influences how inflammatory molecules, stress-related hormones, and certain signalling compounds interact with the brain. High-level ways BBB function may be relevant include: Inflammation signalling: When the BBB is disrupted, inflammatory molecules from the bloodstream may have more influence on brain tissue, which can affect mood and cognition in some contexts. Stress pathways: Chronic stress can change hormone levels and immune activity. Some research explores how stress-related signalling may interact with BBB regulation. Treatment effects: Some psychiatric medicines are effective partly because they can cross the BBB. Drug design and dosing also consider BBB transport and efflux pumps. Important note: BBB changes are not considered a standalone explanation for anxiety, depression, or other conditions. Instead, BBB research helps scientists explore why inflammation and systemic health can sometimes influence mood, sleep, and cognition. Current Breakthroughs In BBB Research BBB research is active and fast-moving. While many advances remain in specialist or research settings, several areas are shaping how scientists think about brain health and treatment: Better imaging of BBB permeability: Advanced MRI and other techniques are being used to study subtle BBB changes in living patients, helping researchers explore relationships with disease progression and symptoms. Targeted drug delivery systems: Work is ongoing on nanoparticles, engineered carriers, and “molecular Trojan horse” approaches that aim to transport medicines across the BBB more efficiently. Focus on transporters and efflux pumps: Researchers are studying how to use existing BBB transport mechanisms, or reduce drug “pumping out,” to improve medication effectiveness in the brain. Immune and vascular interactions: The neurovascular unit is being studied as a dynamic system, with attention to how immune signalling, vascular health, and BBB integrity influence brain outcomes. These advances do not mean new treatments are broadly available yet, but they explain why BBB science is a major focus in neurology and drug development. The Future Of BBB Treatments Future BBB-related treatments generally aim to do one of two things: protect the barrier when it is at risk, or safely deliver therapies across it when treating brain disease. Areas being explored include: Barrier protection strategies: Approaches that reduce inflammation, oxidative stress, or vascular injury to help preserve BBB integrity in conditions like stroke or chronic vascular disease. Controlled BBB opening: Techniques such as focused ultrasound with microbubbles are being studied to temporarily and locally open the BBB under controlled conditions to deliver medicines, especially in oncology and some neurodegenerative research contexts. Personalized drug selection: As knowledge grows about BBB transport and efflux activity, clinicians may increasingly use therapies chosen for their ability to reach brain tissue effectively. Combination approaches: In some conditions, the best results may come from combining systemic treatments, targeted delivery systems, and strategies that support vascular health. These are evolving areas of research and, in many settings, remain limited to specialized centres and clinical trials. Can You Protect Your Blood-Brain Barrier? There is no guaranteed way to “strengthen” the BBB with a supplement or quick fix. But supporting overall vascular and metabolic health helps protect the brain’s blood vessels, which indirectly supports BBB function. Practical habits include: Manage blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol if your clinician advises Treat infections promptly (especially severe or spreading infections) Use helmets and seatbelts to reduce head injury risk Avoid substance misuse and follow medication guidance Prioritize sleep and recovery, since brain repair systems work best with consistent rest FAQs What Is The Blood-Brain Barrier In Simple Words? It is a protective filter in the brain’s blood vessels that controls what can enter brain tissue from the bloodstream. What Is The Main Function Of The BBB? To protect the brain and keep its chemical environment stable by allowing needed nutrients in and blocking many harmful substances. What Cells Make Up The Blood-Brain Barrier? The BBB is built mainly from tightly sealed endothelial cells, supported by a basement membrane, pericytes, and astrocyte end-feet. What Can Cross The Blood-Brain Barrier? Small lipid-soluble molecules can cross more easily, while important nutrients like glucose use specialized transporters. Some medicines can cross, but many cannot. What Prevents Toxins And Germs From Reaching The Brain? Tight junctions limit leakage between cells, and transport systems plus efflux pumps control entry and actively remove certain compounds. What Happens If The Blood-Brain Barrier Is Damaged? It can become more permeable, allowing unwanted substances and inflammatory cells into brain tissue, which may worsen swelling or inflammation depending on the cause. Is BBB Disruption Linked To Multiple Sclerosis? BBB changes are associated with inflammatory activity in multiple sclerosis, and barrier dysfunction is considered part of the disease process in many cases. Why Is The BBB A Challenge For Treating Brain Diseases? Many drugs cannot cross the BBB effectively, making it harder to deliver treatment to brain tissue. Can A Blood Test Diagnose BBB Leakage? Not reliably as a simple screening test. Doctors usually rely on clinical evaluation, imaging, and condition-specific tests (and sometimes CSF studies) depending on symptoms. How Do Doctors Check BBB-Related Problems? They evaluate the underlying condition using history, neurological exam, imaging (CT or MRI), and targeted blood or CSF tests when indicated.
Chondroma Tumors: Causes, Symptoms & Treatment Options
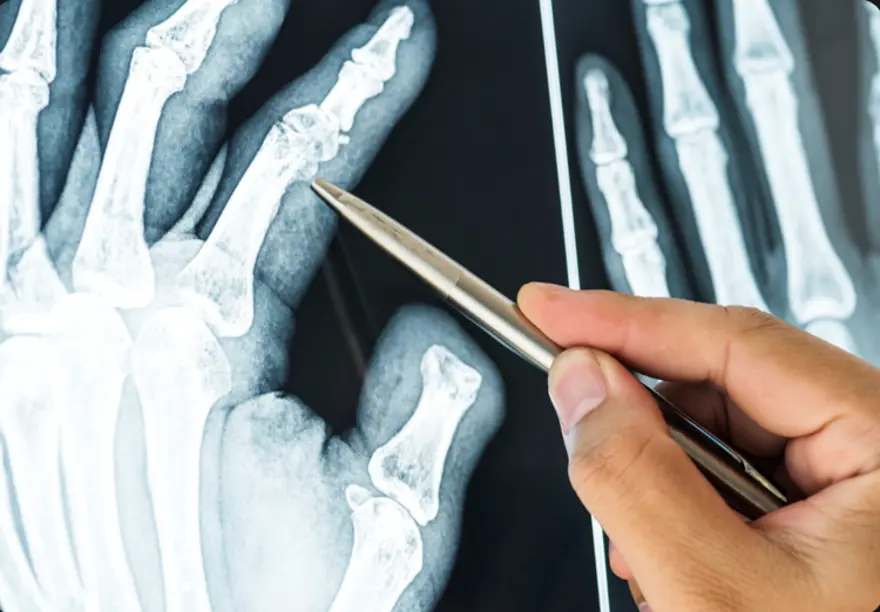
What is a Chondroma Tumour? A chondroma is a benign cartilaginous tumour composed of mature hyaline cartilage that develops within bone or soft tissue that develops within bones or soft tissues throughout the body. Grossly, they appear as bluish-white, glistening nodules, often with areas of calcification when examined directly. Chondromas most frequently involve the small tubular bones of the hands and feet, particularly the phalanges and metacarpals, though they can also develop in larger bones like the humerus (upper arm) or femur (thighbone). Unlike malignant Tumors, a chondroma grows slowly over months or years, often remaining undetected until symptoms appear or incidental discovery during unrelated medical examinations. Because chondromas are benign, they do not metastasize or invade adjacent soft tissues, though they can cause pressure-related symptoms to other body parts or invade vital organs. However, their growth can compress nearby structures, potentially causing significant symptoms depending on their location and size. According to a study published in Frontiers in Surgery, the age of onset for chondromas typically ranges from 20 to 60 years, with a peak incidence between 20 and 30 years. Types of Chondromas • Enchondroma: The most common type, developing within the bone marrow cavity • Periosteal chondromas: Tumors forming on the bone's outer surface or border • Juxtacortical chondromas: Another classification for surface-located Tumors • Soft tissue chondromas: Masses developing in soft tissues, particularly fingers, hands, toes, and feet • Cranial chondromas: Tumors occurring in skull base and paranasal sinuses • Pulmonary chondroma: A rare benign lung lesion sometimes associated with Carney triad (alongside gastric stromal Tumors and paragangliomas) Causes of Chondroma Tumors The exact causes of chondroma Tumors remain largely unknown to medical professionals. Unlike many other conditions where specific risk factors are well-established, chondromas appear to develop sporadically without clear predisposing factors. Most chondromas are sporadic; however, multiple lesions occur in syndromic forms such as Ollier disease (enchondromatosis) and Maffucci syndrome, which may carry a low risk of malignant transformation. They simply occur when cartilage cells begin abnormal growth patterns within bone tissue. However, certain genetic conditions like Ollier disease and Maffucci syndrome can increase the likelihood of developing multiple chondromas throughout the body. The slow-growing nature of chondromas means they may remain present for extended periods before becoming symptomatic or being discovered during unrelated medical procedures. This characteristic makes determining exact onset timing particularly challenging for doctors. Symptoms of Chondroma Tumors Chondromas often remain asymptomatic for considerable periods due to their gradual growth pattern. However, when symptoms do develop, they typically result from compression of surrounding structures. Common symptoms include: Visual disturbances or vision problems, most frequent in cranial chondromas Persistent headaches, common with skull base locations Palpable mass or noticeable bump, particularly evident in hand and foot chondromas Localised swelling around the tumour site Hearing difficulties may occur with skull base chondromas Dull, aching pain, more common in periosteal chondromas Weakness, numbness, or bowel/bladder dysfunction can occur rarely when spinal chondromas compress neural structures How is a Chondroma Diagnosed? Diagnosis begins with clinical evaluation and imaging. For cranial or spinal cases, neurological examination helps assess nerve involvement. This process helps assess cranial nerve function and overall neurological status, particularly important for skull-based Tumors. Because chondromas grow slowly and may exist asymptomatically for years, diagnosis often occurs incidentally during imaging performed for unrelated medical reasons. Your doctor will take a detailed medical history and conduct physical examinations to identify any palpable masses or neurological deficits. The combination of clinical presentation and imaging findings allows doctors to differentiate chondromas from other bone conditions and potential malignancies like chondrosarcoma. Diagnostic and Imaging Tests for Chondroma • X-rays: Reveal well-circumscribed, radiolucent lesions with possible chondroid calcifications (‘rings and arcs’ pattern), often surrounded by a thin sclerotic rim. • CT scan: Offers excellent bone detail and helps evaluate cortical integrity and matrix mineralization, bone involvement, and relationship to surrounding structures with excellent bone detail. • MRI scan: Demonstrates lobulated lesions with low-to-intermediate signal on T1 and high signal on T2, helping differentiate from chondrosarcoma, particularly valuable for assessing tumour extent and planning surgical approaches. • Bone Scans: Utilise radioactive tracers to evaluate bone metabolism and identify areas of increased activity associated with tumour growth. • Biopsy: Sometimes necessary for definitive diagnosis, involving tissue sample collection for microscopic examination to confirm chondroma characteristics. • Complete Blood Count (CBC): Routine blood tests help assess overall health status and identify any systemic conditions affecting treatment decisions. Treatment Options for Chondromas Treatment approaches vary significantly based on symptom severity, tumour location, and patient factors: • Surgical Removal: The primary treatment for symptomatic chondromas, offering potential cure through complete tumour excision. • Endoscopic endonasal approach (EEA): A minimally invasive surgical technique used for skull base chondromas, offering improved visualization and reduced morbidity, accessing through natural nasal corridors without external incisions. • Complete Excision: Traditional surgical removal through direct incision, particularly effective for accessible Tumors in hands and feet. • Watchful Waiting: Conservative monitoring approach for asymptomatic chondromas not threatening vital structures or causing functional problems. • Bone Grafting: May accompany tumour removal to replace missing bone tissue and restore structural integrity. Surgical Treatment for Chondromas Surgical removal represents the primary treatment for symptomatic chondromas. For skull base and paranasal sinus locations, specialists often prefer the endoscopic endonasal approach, a minimally invasive technique using nasal cavities as natural access corridors. This innovative approach offers significant advantages over traditional open surgery, including no external incisions, no facial disfigurement, and faster recovery times. For hand and foot lesions, intralesional curettage or excision under local or general anaesthesia is typically curative, which means scraping out the tumour under anaesthesia. After tumour removal, bone grafts may be required to replace missing bone and restore structural integrity. Non-Surgical Management of Chondromas For asymptomatic chondromas causing no functional problems, watchful waiting represents a reasonable approach. Your doctor may choose to monitor the tumour over time through periodic imaging studies, ensuring it's not growing or compressing nearby structures. This approach avoids surgical risks whilst maintaining vigilance for behavioural changes. Patients typically receive instructions to report new symptoms like pain, swelling, vision changes, or neurological symptoms, which would prompt reassessment and possible surgical intervention. Chondromas in Children vs. Adults • Age patterns: Soft tissue chondromas commonly develop during middle age, whilst periosteal types occur at any age • Location differences: Children may present with various bone locations; adults show more typical distribution patterns • Symptom recognition: Children might more readily notice palpable masses in hands and feet • Growth rates: Paediatric chondromas grow slowly over months or years • Treatment approaches: Surgical principles remain similar, though growth plate considerations may apply Prognosis for Chondroma Tumors The prognosis for chondroma Tumors is generally excellent, with most patients experiencing complete recovery after appropriate treatment. These benign Tumors rarely recur following complete surgical removal, and the risk of complications remains low when treated by experienced medical teams. Most people return to normal activities within weeks to months after surgery, depending on the tumour location and surgical approach. Long-term follow-up typically involves periodic imaging to ensure no recurrence, though this becomes less frequent over time as the risk diminishes. Chondromas and Cancer Risk Understanding chondroma cancer risk helps patients navigate their health journey with confidence. Unlike chondrosarcoma, which is malignant, chondromas remain benign throughout their existence. However, certain genetic conditions like Ollier disease and Maffucci syndrome may slightly increase the transformation risk to chondrosarcoma. The vast majority of chondromas never become cancerous, making the chondroma cancer connection relatively uncommon. Regular monitoring through clinical examinations and appropriate imaging studies helps detect any suspicious changes early, ensuring optimal outcomes for all patients. Conclusion Understanding chondroma Tumors empowers you to recognise symptoms, seek appropriate medical care, and make informed treatment decisions. While these benign cartilage Tumors can cause concerning symptoms, the prognosis remains excellent with proper diagnosis and treatment. Whether dealing with enchondroma in your hand or a cranial chondroma causing headaches, early medical consultation ensures the best outcomes. Remember that chondroma cancer transformation is rare, and most patients enjoy complete recovery after treatment. If you notice persistent lumps, unexplained pain, or neurological symptoms, don't hesitate to consult your doctor for proper evaluation. At Metropolis Healthcare, we support your diagnostic journey with comprehensive testing services. Our extensive network of over 220 laboratories and 4,600 service centres ensures accessible, accurate diagnostics when you need them most. From routine blood tests to specialised imaging support, our home sample collection service brings convenience to your doorstep across 10,000+ touchpoints nationwide. FAQs Can chondromas become cancerous? Malignant transformation of solitary chondromas is exceedingly rare; however, multiple enchondromas in Ollier disease or Maffucci syndrome carry up to a 30% risk of secondary chondrosarcoma. These benign Tumors typically remain non-cancerous throughout their existence, though regular monitoring helps detect any suspicious changes early. What are the main symptoms of a chondroma? Common symptoms include palpable masses, localised pain, swelling, and functional impairment. Cranial chondromas may cause vision problems, headaches, or hearing difficulties depending on location. How are chondromas treated? Treatment depends on symptoms and location. Symptomatic chondromas typically require surgical removal, whilst asymptomatic Tumors may be monitored through regular clinical examinations and imaging studies. Are chondromas hereditary? Chondromas aren't typically hereditary conditions. However, genetic syndromes like Ollier disease and Maffucci syndrome can increase the likelihood of developing multiple chondromas throughout the body.
Cold Urticaria: What It Is, Why It Happens & How to Manage It
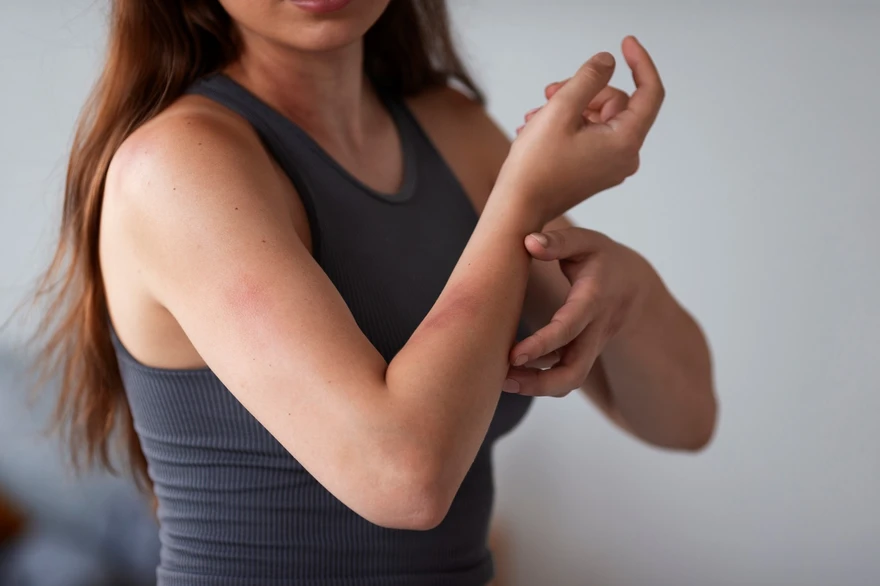
What is Cold Urticaria? Cold urticaria is a type of physical urticaria in which exposure to cold air, water, or objects triggers an allergic skin reaction, causing sudden hives, redness, and swelling within minutes. The immune system mistakenly treats cold exposure as a harmful stimulus, triggering mast cells in the skin to release histamine and other inflammatory mediators that dilate blood vessels and leak fluid into surrounding tissues. While most cases are mild and self-limiting, severe reactions may involve systemic symptoms and require immediate medical care. How Cold Urticaria Affects the Body Cold urticaria sets off an inflammatory cascade when the skin encounters cold. Mast cells release histamine and other mediators, causing small blood vessels to dilate and leak fluid into the skin, leading to raised, itchy hives that usually resolve while most cases are mild and self-limiting, severe reactions may involve systemic symptoms and require immediate medical care. In severe reactions, this process can involve the lungs and cardiovascular system, triggering breathing difficulty, low blood pressure, or even anaphylaxis, which requires urgent medical care. Types of Cold Urticaria Several forms of cold urticaria exist, each with distinct features: Primary acquired cold urticaria: Most common; triggered by direct cold exposure. Secondary cold urticaria: Linked to underlying conditions like infections or blood disorders. Familial Cold Autoinflammatory Syndrome (FCAS): A rare inherited autoinflammatory disorder that causes hives, fever, and joint pain after generalized cold exposure. Cold Urticaria Symptoms Recognising cold urticaria symptoms helps you identify when you're experiencing this condition. The primary manifestations include: Rapid appearance of hives or welts after cold exposure Itching, burning, or stinging sensation Swelling of hands, face, lips, or eyelids Redness or patches on exposed skin In severe cases: breathing difficulty, dizziness, or fainting after sudden cold exposure As per the National Organisation for Rare Disorders (NORD), cold urticaria accounts for a small subset of chronic inducible urticarias and can cause rapid hives and swelling within minutes of cold exposure, with some patients experiencing systemic reactions. NORD notes that both typical and atypical forms exist, and that the condition may be primary or secondary to other diseases, though its exact cause remains unclear. Common Triggers of Cold Urticaria Any sudden drop in temperature can trigger cold urticaria. Most reactions occur when the skin warms after exposure to cold. Some common triggers include: Cold water exposure (e.g., swimming, washing hands, or being caught in rain) Cold weather or wind Prolonged exposure to air-conditioned environments Holding cold objects (ice, frozen foods, metal cans) Cold drinks or ice cream contacting the lips. Sudden temperature change from warm to cold What Causes Cold Urticaria? The exact cause of cold urticaria is unclear, but it is thought to involve abnormal mast cell activation, where cold exposure triggers histamine release and inflammation. In some people, cold may provoke an IgE-mediated autoimmune response that makes mast cells overly sensitive, while secondary cold urticaria can be linked to infections, autoimmune diseases, or blood disorders. Cold Stimulation Test (Ice Cube Test) Doctors use a simple test to diagnose cold urticaria: An ice cube is placed inside a plastic bag. The bag is applied to the skin—usually the forearm—for 1–5 minutes. After removing the ice, the skin is observed for the development of a raised, itchy wheal. A raised, red welt confirms the diagnosis of cold urticaria. When Doctors Recommend the Test This test is recommended when a person develops unexplained hives or chronic hives after cold exposure or when there is a suspected severe reaction to cold water. Complications of Cold Urticaria While many people experience mild reactions, cold urticaria can lead to serious complications: Severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath after sudden full-body cold exposure Rapid drop in blood pressure Fainting episodes Swelling of the throat or tongue Danger during cold-water swimming or diving Cold Urticaria Treatment Options Effective cold urticaria treatment focuses on symptom management and prevention. Treatment approaches include: Antihistamines: The first-line treatment to reduce hives and itching. Leukotriene modifiers: For people who don’t respond to antihistamines. Omalizumab: Used in chronic or severe cases. Emergency epinephrine: For patients with a history of severe reactions. Avoiding known triggers and maintaining warmth: Key components of long-term management. Home Remedies & Self-Care Tips for Cold Urticaria Managing cold urticaria involves practical strategies to minimise exposure and reduce symptom severity. Daily Precautions Dress in layers during winter. Use gloves, scarves, and face coverings. Warm the car before stepping outside to reduce cold shock. Avoid sudden exposure to cold water. Lifestyle & Prevention Tips Test the water temperature with your hand before bathing. Avoid ice-cold drinks if lip swelling occurs. Carry prescribed antihistamines (and an epinephrine auto-injector if advised) when travelling. Inform swimming instructors or companions about your condition. When to See a Doctor? Seek medical help if symptoms occur frequently or if hives appear without clear triggers. Immediate care is needed if cold exposure leads to: Difficulty breathing Fainting Swelling of the throat Severe dizziness or low blood pressure How Cold Urticaria is Diagnosed Healthcare providers use a systematic approach to diagnose cold urticaria: Detailed medical history Ice cube test Physical examination Laboratory tests to rule out secondary causes Allergy evaluation, if needed Tests for Cold Urticaria ABPA Panel Test: Blood panel to assess allergy to Aspergillus in patients with asthma-like or respiratory symptoms. Alternaria Alternata (Specific IgG): Checks IgG antibodies to Alternaria mould linked with environmental allergy. Aspergillus fumigatus(Specific IgG): Measures IgG to A. fumigatus to assess possible mould-related allergy. Allergen, Individual-Microorganism Cladosporium Herbarum fungus: Evaluates IgE response to circulating allergen-specific IgE for Cladosporium herbarum (Fungus). Allergen, Individual-Microorganism Penicillium Notatum fungus (Penicillium chrysogenum): Screens for specific IgE antibodies to Penicillium mould as part of allergy workup. Medical History Evaluation Doctors ask about symptoms, exposure patterns, family history, and past allergic conditions. Physical Exam & Lab Tests During physical examination, your doctor assesses your skin condition, checks for signs of other allergic diseases, and evaluates your overall health status. Laboratory tests may include: CBC (Complete Blood Count) Test Thyroid Profile Test (TFT) Autoimmune screening (e.g., ANA test) to detect possible systemic causes Tests for infections with an Opportunistic Infection Panel Screening for chronic hives or associated disorders Cold Urticaria in Children: What Parents Should Know Cold urticaria can affect children, requiring special considerations for management and safety. Parents should watch for symptoms after cold exposure and teach children to recognise early warning signs. Children may experience more intense or unpredictable reactions to cold exposure. Swelling around the lips or hands after ice cream is common. Avoid swimming in cold water unless a doctor clears it. Keep emergency medication handy in case of severe reactions. Most children outgrow cold urticaria within a few years, though monitoring is advised. Cold Urticaria Outlook & Long-Term Management The outlook for cold urticaria differs from person to person. Many improve over time, and some go into complete remission within a few years, while others may have symptoms for longer and need ongoing management. With the right treatment, trigger avoidance, and regular medical follow-up, most people can maintain a good quality of life and continue normal activities with sensible precautions. Conclusion Cold urticaria can usually be well managed with proper diagnosis, preventive care, and ongoing treatment where needed. Recognising your triggers early and consulting a doctor if reactions are frequent or severe helps prevent complications and supports safer day-to-day living. As a trusted diagnostic partner, Metropolis Healthcare offers 4,000+ tests, full-body checkups, specialised allergy and immunology testing, and strong home sample collection across 10,000+ touchpoints, with quick turnaround and accurate results. You can book tests conveniently via website, app, WhatsApp, or phone, making it easier to get timely, reliable reports that support your doctor in managing cold urticaria effectively. FAQs What triggers cold urticaria the most? The most common triggers include sudden exposure to cold air, cold water, cold wind, and contact with cold objects. Swimming in cold water is among the strongest triggers due to the rapid temperature drop. Can cold urticaria be cured permanently? There is no permanent cure, but symptoms can be effectively controlled. Many people with primary cold urticaria improve over 5–10 years. Is cold urticaria a serious condition? It can be serious if it triggers whole-body reactions, such as fainting or breathing difficulties, especially after swimming. Most cases are mild but require caution. How long does a cold urticaria reaction last? Localised reactions usually last 1–2 hours. More severe reactions may last longer and require medical attention. Can you swim if you have cold urticaria? Swimming should be avoided in cold water. If approved by a doctor, warm-water swimming may be safe under supervision. What foods should be avoided with cold urticaria? Ice-cold drinks Ice cream, if it triggers lip swelling Frozen foods that require handling
Movement Disorders: Types, Symptoms & When to Seek Help
What are Movement Disorders? Movement disorders are a group of neurological conditions that affect your body's ability to produce and control normal movement patterns. These conditions originate in the nervous system, specifically disrupting the brain regions responsible for coordinating muscle activity and movement control. Movement disorders can manifest as either reduced movement (hypokinetic conditions like Parkinson's disease) or excessive, uncontrolled movement (hyperkinetic conditions such as essential tremor, chorea, or other involuntary movements). More than 30 different diseases are classified as movement disorders, with symptoms varying widely among individuals but often progressing over time. How the Nervous System Controls Movement Your nervous system orchestrates all voluntary and involuntary movements through an intricate network of neural pathways connecting your brain, spinal cord, and muscles. The brain sends precise signals through the spinal cord to peripheral nerves, instructing muscles when to contract and relax in coordinated patterns. Movement disorders occur when disruptions affect these neural communication pathways. The sensorimotor cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum play crucial roles in movement coordination. When damage or dysfunction occurs in these brain regions, it leads to the characteristic abnormal movement patterns seen in various movement disorders. This disruption can stem from genetic factors, neurodegeneration, or environmental influences affecting how your brain processes and executes movement commands. Types of Movement Disorders Understanding different movement disorder types helps recognise symptoms and seek appropriate treatment: Parkinson's disease: A progressive neurological condition causing tremors, muscle rigidity, slowness of movement, and balance problems. Essential tremor: Involuntary rhythmic shaking, primarily affecting hands and neck during voluntary movement. Dystonia: Sustained muscle contractions causing repetitive, twisting movements and abnormal postures. Huntington's disease: Inherited disorder characterised by chorea (irregular, dance-like movements) and cognitive decline. Tourette syndrome: A neurological condition involving repetitive movements and vocal sounds called tics. Ataxia: A degenerative disorder affecting coordination, balance, and speech. Myoclonus: Sudden, brief muscle jerks or twitches. Restless legs syndrome: Uncomfortable leg sensations creating an urge to move. Multiple system atrophy: A rare condition affecting movement, blood pressure, and bladder control. Progressive supranuclear palsy: A rare neurodegenerative disorder affecting walking, balance, and eye movement control. Common Symptoms of Movement Disorders Movement disorders' symptoms vary depending on the specific condition, but several key indicators warrant attention: Tremors or involuntary shaking movements, especially at rest or during activity. Muscle rigidity or stiffness that affects normal movement. Bradykinesia (abnormally slow movement). Difficulty walking or noticeable changes in gait patterns. Loss of balance and coordination problems. Involuntary muscle contractions or spasms. Jerky, irregular movements affecting arms, legs, or the entire body. Speech difficulties or voice changes. Excessive fidgeting or inability to remain still. Facial grimacing or unusual expressions. Problems with fine motor skills, like writing or buttoning clothes. Are you experiencing unusual movements that interfere with daily activities? Early recognition of movement disorder symptoms can lead to timely intervention and better outcomes. What Causes Movement Disorders? Movement disorders' causes are diverse and often complex, involving multiple factors: Genetic mutations: Inherited conditions like Huntington's disease result from specific gene defects. Neurodegeneration: Progressive damage to brain cells, particularly in areas controlling movement. Neurotransmitter imbalances: Disruption in chemical communication between brain cells. Environmental toxins: Exposure to certain chemicals or heavy metals. Brain injuries: Trauma affecting movement-controlling brain regions. Infections: Viral or bacterial infections affecting the nervous system. Medication side effects: Certain drugs can trigger movement abnormalities. Autoimmune conditions: Immune system attacks on components of the nervous system. Risk Factors You Should Know Understanding movement disorders causes helps healthcare providers develop targeted treatment approaches and may inform prevention strategies for at-risk individuals. Several factors can increase your likelihood of developing movement disorders: Age: Many movement disorders become more common with advancing age, particularly after 60. Family history: A genetic predisposition significantly increases the risk of inherited conditions. Gender: Some conditions show gender preferences; for example, men develop Parkinson's disease more frequently. Environmental exposure: Occupational or residential exposure to pesticides, heavy metals, or industrial solvents. Previous head injuries: Traumatic brain injuries may increase susceptibility to certain movement disorders. Medication history: Long-term use of certain psychiatric or antiemetic medications. Possible Complications Without proper management, movement disorders can lead to serious complications: Progressive decline in mobility and independence Increased fall risk and potential injuries Speech and swallowing difficulties (dysarthria and dysphagia) Cognitive impairment and dementia Depression and anxiety disorders Social withdrawal and isolation Sleep disturbances, including insomnia or excessive daytime sleepiness Nutritional problems due to eating difficulties Respiratory complications from swallowing issues Reduced quality of life for patients and families How Movement Disorders Are Diagnosed Healthcare providers use a systematic approach to diagnose movement disorders: Comprehensive medical history: A detailed discussion of symptoms, family history, medications, and potential environmental exposures. Neurological examination: Assessment of reflexes, muscle strength, coordination, gait, and movement patterns. Symptom observation: Careful evaluation of abnormal movements during rest and activity. Cognitive assessment: Testing memory, thinking skills, and mental function. Differential diagnosis: Ruling out other conditions that might mimic movement disorders. Tests for Movement Disorders Diagnostic testing helps confirm movement disorders and guide treatment decisions: Brain imaging: MRI or CT scans to identify structural abnormalities. Blood tests: Comprehensive metabolic panel to assess overall health. Autoimmune Parkinsonian Profile: Specialised testing for immune-related movement disorders. Huntington disease mutation analysis: Specific genetic test for Huntington's disease. Gene panels: Genetic screening for various dystonia types or specific conditions, such as the Early-Onset Juvenile Parkinsonism Gene Panel. Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: Examination of spinal fluid when indicated, with tests like the Bacterial Meningitis Panel, CSF. Electromyography (EMG): Testing muscle and nerve function. Treatment Options for Movement Disorders Movement disorders treatment varies based on the specific condition and severity: Medications: Dopamine replacement therapy, muscle relaxants, anticonvulsants, and botulinum toxin injections. Deep brain stimulation: Surgical implantation of electrodes to regulate abnormal brain activity. Physical therapy: Exercises to improve strength, flexibility, balance, and coordination. Occupational therapy: Strategies to maintain independence in daily activities. Speech therapy: Techniques to address communication and swallowing difficulties. Lifestyle modifications: Regular exercise, stress management, and adequate sleep. Support groups: Peer support and education for patients and families. Lifestyle Tips to Manage Movement Disorders Daily management strategies can significantly improve quality of life: Maintain regular exercise routines appropriate for your condition. Follow a balanced, nutritious diet rich in antioxidants. Establish consistent sleep schedules and good sleep hygiene. Practice stress-reduction techniques such as meditation or yoga. Use assistive devices when needed for safety and independence. Stay socially connected with family and friends. Attend regular medical appointments and follow treatment plans. Keep a symptom diary to track changes and medication effects. When to Seek Medical Help Recognising when to consult healthcare providers is crucial for optimal outcomes. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience a sudden onset of involuntary movements, severe muscle spasms, difficulty swallowing, or significant changes in existing symptoms. Early consultation allows for prompt diagnosis and treatment initiation, potentially slowing disease progression and improving long-term prognosis. Don’t wait—if movement symptoms interfere with daily activities, affect your safety, or cause emotional distress, seek evaluation promptly. Healthcare providers can offer comprehensive evaluations and develop personalised treatment plans that address your specific needs and concerns. Living With Movement Disorders: Coping & Support Living with movement disorders requires ongoing adaptation and support from healthcare teams, family, and community resources. Focus on maintaining realistic goals, celebrating small achievements, and adapting activities to accommodate changing abilities. Join support groups to connect with others facing similar challenges, share experiences, and learn practical coping strategies. Remember that movement disorders affect each person differently, and treatment responses vary. Work closely with your healthcare team to optimise treatment approaches, manage symptoms effectively, and maintain the best possible quality of life throughout your journey. Conclusion The Movement disorder treatment focuses on controlling symptoms in the past 25 years, underscoring how movement disorders as a whole are becoming an increasingly important public health concern. While these conditions can be challenging, many are manageable with timely diagnosis, appropriate medical care, lifestyle changes, and the right support systems. Recognizing early signs—such as tremors, stiffness, slowed movements, or other unusual motor symptoms—can lead to earlier intervention and improved outcomes. Whether you’re trying to understand the causes, exploring treatment options, or supporting a loved one, comprehensive and coordinated care plays a crucial role. At Metropolis Healthcare, we are committed to supporting your diagnostic journey with more than 4,000 tests, including specialised panels designed for autoimmune conditions. With 220+ laboratories and over 10,000 touchpoints across India, we ensure reliable and accessible testing whenever you need it. From genetic assessments to advanced metabolic panels, our home sample collection service delivers trusted diagnostics and convenience right to your doorstep. FAQs What are the early signs of a movement disorder? Early movement disorder symptoms often include subtle tremors, slight stiffness, balance problems, or changes in handwriting. You might notice difficulty with fine motor tasks, occasional muscle spasms, or mild coordination problems. These symptoms typically develop gradually and may initially be dismissed as normal ageing or stress-related issues. Can movement disorders be cured? Currently, most movement disorders cannot be completely cured, but many can be effectively managed with appropriate treatment. Movement disorder treatment focuses on controlling symptoms, slowing progression, and maintaining quality of life through medications, therapies, and lifestyle modifications. Early intervention often leads to better long-term outcomes. What is the most common movement disorder? Essential tremor is the most common movement disorder, affecting approximately 1% of the population worldwide. Parkinson's disease is the second most common, with over 8.5 million people affected globally according to WHO estimates. Both conditions significantly impact daily functioning but respond well to appropriate treatment approaches. Are movement disorders hereditary? Some movement disorders have genetic components, particularly Huntington's disease, certain types of dystonia, and some forms of Parkinson's disease. However, many movement disorders result from complex interactions between genetic predisposition and environmental factors. Genetic counselling can help assess your risk if you have a family history of these neurological conditions. Is Parkinson's a movement disorder? Yes, Parkinson's disease is one of the most well-known movement disorder types. It affects the brain's ability to produce dopamine, leading to characteristic symptoms, including tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and balance problems. The WHO reports that Parkinson's disease prevalence has doubled in the past 25 years, emphasising the importance of awareness and early detection. How do doctors diagnose movement disorders? Healthcare providers diagnose movement disorders through comprehensive neurological examinations, detailed medical histories, and observation of movement patterns. Diagnostic testing may include brain imaging, genetic analysis, blood tests, and specialised panels. The diagnostic process requires careful evaluation to distinguish between different movement disorder types and develop appropriate treatment plans. Can stress cause involuntary movements? Stress can trigger or worsen certain types of involuntary movements, including tics, tremors, and muscle spasms. However, stress alone rarely causes primary movement disorders. Chronic stress may exacerbate existing neurological conditions or contribute to functional movement disorders. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, and adequate sleep can help reduce symptom severity. Which doctor should I consult for movement disorders? Start with your primary care physician, who can perform initial assessments and provide referrals to neurologists specialising in movement disorders. Movement disorder specialists have additional training in diagnosing and treating these complex neurological conditions. They can offer comprehensive evaluation, advanced treatment options, and ongoing management strategies tailored to your specific condition.
Astrocytomas Explained: Types, Diagnosis & Management
What Are Astrocytomas? An astrocytoma is a type of primary brain tumor that develops from astrocytes—supportive glial cells that help nourish and protect neurons. These are among the most common primary brain tumours, accounting for approximately 60% of primary adult brain tumors, and unlike secondary tumours, they originate within brain tissue itself. Astrocytes normally regulate the blood-brain barrier, neurotransmitters, and nutrient flow, but when they become cancerous, they form tumours that disrupt normal brain function. Their behaviour varies according to tumour grade and molecular features. Modern WHO classification integrates histopathological findings with molecular profiling, enabling more accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment. Astrocytomas can develop anywhere in the brain or spinal cord, but most often appear in the cerebral hemispheres, brainstem, or cerebellum, influencing both symptoms and treatment choices. Types of Astrocytomas Astrocytoma grading follows the World Health Organization (WHO) classification system, which categorises these brain tumours into four distinct grades based on their appearance under a microscope and growth characteristics: Grade 1 Astrocytomas (Pilocytic Astrocytoma): These slow-growing, benign tumours typically occur in children and young adults. Pilocytic astrocytomas are typically localized and seldom infiltrate surrounding brain tissue, making them the most treatable form. Grade 2 Astrocytomas (Low-grade Diffuse Astrocytomas): These tumours grow slowly but tend to infiltrate surrounding brain tissue. They commonly affect adults between the ages of 20 and 50 and may progress to higher grades over time if left untreated. Grade 3 Astrocytomas (Anaplastic Astrocytomas): These intermediate-grade tumours grow more rapidly and spread aggressively through brain tissue. They account for roughly 2% of all primary brain tumors and typically occur in adults aged 30–50. Grade 4 Astrocytomas (Glioblastoma): The most aggressive form, glioblastoma grows rapidly and spreads extensively throughout brain tissue. Glioblastomas comprise about 60% of all astrocytomas and may evolve from lower-grade tumors (secondary glioblastoma) or arise de novo (primary glioblastoma). Causes and Risk Factors for Astrocytomas The exact causes of astrocytomas remain largely unknown, as most cases develop spontaneously without identifiable triggers. Unlike many other cancers, astrocytomas lack well-established preventable risk factors, making prevention strategies limited. However, researchers have identified several potential contributing factors that may increase your risk of developing these astrocytoma brain tumours. Age represents one of the most significant risk factors, with different astrocytoma types affecting specific age groups. While pilocytic astrocytomas predominantly occur in children and young adults, higher-grade astrocytomas typically develop in older adults. Gender also plays a role, with men having a slightly higher risk of developing certain types of astrocytomas than women. As per a 2024 StatPearls review, astrocytomas are the most common gliomas and part of the glial tumours that constitute about 60% of all brain tumours, with Ionizing radiation remains the only well-established environmental risk factor for their development. Radiation Exposure and Astrocytomas Radiation can influence the risk of developing astrocytomas, but the level of risk depends on the dose, duration, and context of exposure: Previous head or neck radiation, especially in childhood, can increase the risk of secondary astrocytomas years later. Occupational exposure to ionising radiation may play a role, but evidence is still inconclusive. Medical imaging that uses radiation carries minimal risk when used appropriately. Atomic bomb survivors and nuclear accident victims show higher rates of brain tumour development. Genetics and Astrocytomas • Hereditary syndromes: Certain genetic conditions like Inherited syndromes such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome, Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1), and Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) significantly increase astrocytoma risk. • Family history: Having a first-degree relative with a brain tumour slightly increases your risk, though most astrocytomas occur without family history. • Molecular markers: Such as IDH1/IDH2 mutations, CDKN2A/B deletions, and TERT promoter mutations are key determinants in diagnosis, classification, and prognosis in astrocytoma development and classification. • Chromosomal abnormalities: Specific genetic changes like EGFR amplification and chromosome alterations contribute to tumour formation. • DNA repair defects: Inherited problems with DNA repair mechanisms may predispose individuals to developing astrocytomas. Symptoms of Astrocytomas Astrocytoma symptoms vary considerably depending on the tumour's size, location, and growth rate. Many people initially dismiss early symptoms as stress, fatigue, or normal ageing, which can delay diagnosis. Recognising these warning signs early enables prompt medical evaluation and treatment. The symptoms typically develop gradually as the tumour grows and increases pressure within your skull or affects specific brain regions. Here are the most common astrocytoma symptoms to watch for: Persistent headaches that worsen over time, especially morning headaches that improve throughout the day. Seizures or convulsions that occur for the first time in adults without a previous seizure history. Vision problems, including blurred vision, double vision, or loss of peripheral vision. Nausea and vomiting that occur without other illness, particularly morning vomiting. Balance and coordination difficulties leading to falls or clumsiness. Weakness or numbness in arms, legs, or face, often affecting one side of the body. Speech difficulties, including trouble finding words, slurred speech, or language comprehension problems. Memory problems and difficulty concentrating or making decisions. Personality changes, including mood swings, irritability, or behavioural alterations. Fatigue and drowsiness that don't improve with rest. How Astrocytomas Are Diagnosed Diagnosing astrocytomas requires a comprehensive approach combining clinical evaluation, advanced imaging, and tissue analysis. The diagnostic process typically begins when you or your doctor notices concerning symptoms that warrant further investigation. Your healthcare team will conduct a thorough neurological examination to assess cognitive function, motor skills, sensory perception, and reflexes. The diagnostic journey can feel daunting, but understanding each step helps reduce anxiety and ensures you're prepared for what lies ahead. Your doctor will review your medical history, including any previous radiation exposure, family history of brain tumours, or genetic conditions like Li-Fraumeni syndrome that might increase your risk. Modern astrocytoma diagnosis relies heavily on molecular testing to determine specific genetic characteristics that influence treatment decisions and prognosis. This personalised approach ensures you receive the most appropriate therapy based on your tumour's unique biological features rather than appearance alone. The integration of clinical findings, imaging results, and molecular diagnostics provides a complete picture that guides your treatment team in developing an optimal care plan tailored to your specific situation. Diagnostic and Imaging Methods for Detecting Astrocytomas Several sophisticated diagnostic tools help doctors detect and characterise astrocytomas accurately. Each method provides unique information that contributes to a comprehensive diagnosis: MRI Scan: Gold standard for brain tumour imaging, showing precise tumour size, location, and spread. CT Scan: Often used first in emergencies to detect mass effect, bleeding, or calcifications. PET Scan: Evaluates tumor metabolism to differentiate active tumor from post-treatment changes or necrosis. Biopsy procedures: Provide definitive diagnosis via tissue analysis, e.g. Histopathological examination (via stereotactic or open biopsy), with possible core or intraoperative (‘rush’) analysis, and selected molecular or microbiology tests on biopsy tissue. Lumbar puncture (Spinal Tap): Occasionally used to study cerebrospinal fluid when spinal or leptomeningeal spread is suspected. Neuropsychological testing: Evaluates memory, speech, and thinking to map the functional impact of the tumour. Treatment Options for Astrocytomas Treatment for astrocytomas requires a multidisciplinary approach tailored to your specific tumour type, grade, location, and overall health status. Your treatment team typically includes neurosurgeons, neuro-oncologists, radiation oncologists, and supportive care specialists working together to optimise your outcomes. • Surgical resection: The primary treatment for most astrocytomas, aiming to remove as much tumour tissue as possible while preserving neurological function. • Radiation therapy: External beam radiation targets residual tumor cells after surgery to reduce recurrence risk and reduces recurrence risk, particularly important for higher-grade tumours. • Chemotherapy: Temozolomide, the most commonly used chemotherapy for astrocytomas, is often combined with radiation therapy for Grade III and IV tumors for optimal results. • Targeted therapy: Targeted therapies that act on specific molecular pathways within tumor cells, such as EGFR or BRAF alterations, offering hope for more effective and less toxic treatments. • Clinical trials: Experimental treatments, including immunotherapy and novel drug combinations, may be available for eligible patients. • Supportive care: Medications to control seizures, reduce brain swelling, and manage symptoms improve quality of life throughout treatment. Managing Life with an Astrocytoma Diagnosis Living with an astrocytoma means adjusting to a new reality while focusing on quality of life and hope. Many people manage their condition for years with the right treatment and support. Strong coping strategies, a reliable support system, and active involvement in care decisions are crucial. Regular follow-ups with MRI scans become routine to monitor tumour changes or recurrence. Though scan days can be stressful, early detection makes treatment more effective, and managing “scanxiety” through relaxation, counselling, or support groups can help. Rehabilitation services, such as cognitive therapy for memory or attention problems, and physical or occupational therapy for mobility and daily activities, often improve functioning. Gentle, regular exercise within your limits can also boost mood and energy. Work life may need adjustment; some continue working with reasonable accommodations, while others require time off or disability support. Honest communication with employers usually helps find practical solutions. Prognosis and Survival Rates for Astrocytomas Understanding prognosis can guide treatment and life planning, but outcomes vary widely between individuals. Survival depends mainly on tumour grade, age, molecular profile, and how much of the tumour can be safely removed. Broadly, Grade 1 pilocytic astrocytomas have excellent long-term survival after complete surgery. Grade 2 astrocytomas often have a median survival is approximately 6–8 years for Grade II, 2–3 years for Grade III, and 12–15 months for Grade IV (glioblastoma) Younger patients and those with favorable molecular profiles (such as IDH-mutant or MGMT-methylated tumors) and more complete surgical resection are all linked with better outcomes. Modern molecular testing help personalize both prognosis and treatment, marking a shift toward precision neuro-oncology. Conclusion Astrocytomas are complex brain tumours that demand early diagnosis, personalised treatment, and regular follow-up. Prognosis depends on tumour grade, age, molecular markers, and how much of the tumour can be safely removed. However, advances in neuro-oncology and molecular testing are steadily improving outcomes and quality of life. Staying informed about your tumour type and closely engaging with your care team are key to making confident decisions. For accurate and reliable diagnostics, Metropolis Healthcare offers 4,000+ tests, including advanced molecular and speciality panels, along with comprehensive full body checkups. Patients benefit from home sample collection backed by 10,000+ touchpoints, quick turnaround times, and strict quality controls. Booking is simple and convenient via website, app, WhatsApp, or phone, ensuring you get timely, high-quality reports that support effective management of conditions like astrocytomas. FAQs What are the causes of astrocytomas? Astrocytomas develop from mutations in astrocyte DNA, influenced by genetic conditions such as Li-Fraumeni syndrome, radiation exposure, and environmental factors. In some cases, no clear cause is identified. What are the symptoms of an astrocytoma? Symptoms include persistent headaches, seizures, vision changes, memory problems, and loss of coordination. These symptoms occur due to pressure on specific brain regions. How is an astrocytoma diagnosed? Diagnosis involves neurological exams, an MRI scan, a CT scan, and biopsies to determine tumour type and grade. Astrocytoma radiology imaging helps identify tumour boundaries and structure. Can astrocytomas be treated successfully? Yes, treatments like surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy can effectively manage many types of astrocytomas. Early diagnosis improves outcomes significantly. Are astrocytomas hereditary? Most astrocytomas are not hereditary, but genetic conditions like Li-Fraumeni syndrome and neurofibromatosis can increase risk. What is the life expectancy for astrocytoma patients? Life expectancy varies by tumour grade. Pilocytic astrocytoma has excellent survival, while glioblastoma has a significantly lower prognosis. Early intervention improves outcomes. References https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17863-astrocytoma https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/astrocytoma/symptoms-causes/syc-20576675 https://www.aans.org/patients/conditions-treatments/astrocytoma-tumors/ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559042/
A Guide To Ependymomas: What Patients Should Know
What Are Ependymomas? Ependymomas are rare brain and spinal cord tumors that develop from ependymal cells — the specialized cells lining the ventricles and central canal, which help produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). They account for approximately 2–3% of all primary brain tumors and are less common than astrocytomas or the more aggressive medulloblastomas. While medulloblastoma vs. ependymoma comparisons show that both can affect similar regions, ependymomas usually grow more slowly and respond differently to treatment. Unlike syringomyelia, which involves fluid-filled cavities, ependymomas form solid masses that can obstruct CSF flow and disrupt normal brain or spinal cord function. Symptoms of Ependymomas Recognising ependymoma symptoms early is crucial for timely intervention. The symptoms vary significantly depending on whether you're dealing with a brain tumour or a spinal cord tumour. Brain-based ependymoma symptoms include: • Persistent headaches, often worse in the morning • Nausea and vomiting, particularly upon waking • Vision problems, including blurred or double vision • Seizures (abnormal electrical activity in the brain) • Balance difficulties and coordination problems • Confusion or personality changes Spinal cord ependymoma symptoms present differently: • Chronic back or neck pain lasting months • Numbness or tingling in arms or legs • Progressive weakness affecting mobility • Loss of bladder or bowel control • Difficulty walking or maintaining balance Causes and Risk Factors The exact causes of ependymomas are largely unknown, unlike syringomyelia, which can result from trauma or congenital abnormalities. Genetic factors may contribute, especially in hereditary conditions such as neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2). However, most ependymomas occur sporadically, without identifiable environmental triggers. The risk follows a bimodal distribution — peaking in children under 5 years and again in adults aged 30–40 years, and prior head or spine radiation may slightly increase risk. When comparing medulloblastoma vs. ependymoma, some risk features overlap, but they tend to affect different age groups. According to the National Cancer Institute reports, ependymomas occur across all ages, with posterior fossa tumours more common in children and spinal ependymomas more common in adults, reflecting a strong age- and location-based pattern in disease presentation. Types of Ependymomas Understanding different ependymoma types helps clarify treatment approaches and prognosis. The World Health Organization (WHO) classifies ependymomas into three main grades: Grade I Ependymomas: • Myxopapillary ependymomas (typically spinal) • Subependymomas (usually brain-based) • Slow-growing with better outcomes Grade II Ependymomas: • Classic ependymomas affecting the brain and spine • Moderate growth rate requiring careful monitoring • Most common type in children Grade III Ependymomas: • Characterized by rapid growth • Increased recurrence risk • The need for aggressive multimodal therapy (surgery plus radiation) Diagnosing Ependymomas Diagnosing ependymomas requires a systematic approach combining clinical evaluation with advanced imaging techniques: Initial neurological examination assessing reflexes, coordination, and cognitive function. Detailed symptom history documenting ependymoma symptom progression. Advanced imaging studies, including an MRI scan and potentially a CT scan. Tissue sampling through biopsy for definitive ependymoma histology confirmation. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis to check for tumor cells or biochemical markers of spread. Additional staging studies are determining the extent and spread. Imaging and Diagnostic Methods for Detecting Ependymomas Modern ependymoma radiology relies heavily on sophisticated imaging techniques that provide detailed visualisation of these complex tumours: MRI Scan capabilities • Superior soft tissue contrast for brain tumour detection • Detailed ependymoma histology correlation through imaging • Assessment of cerebrospinal fluid flow patterns • Differentiation from conditions like syringomyelia CT Scan applications: • Initial emergency evaluation for acute symptoms • Assessment of calcifications within tumours • Post-surgical monitoring and follow-up imaging Specialised imaging techniques: • Functional MRI (fMRI) for mapping eloquent brain regions • Diffusion tensor imaging evaluating white matter tracts • Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) provides metabolic data that can help differentiate tumor grade or recurrence Treatment Options for Ependymomas Treatment for ependymomas differs from that for astrocytoma or medulloblastoma and needs specialised, individualised planning. Surgery is the primary treatment, aiming for complete tumour removal while preserving neurological function, usually followed by radiation therapy, especially for incomplete resections or higher-grade tumours. Unlike syringomyelia, which is treated with drainage procedures, ependymomas require oncological management. Chemotherapy has a limited role in standard ependymoma treatment protocols compared with medulloblastoma, though ongoing trials are evaluating its benefit in recurrent cases, but newer targeted therapies may help in recurrent cases, guided by a multidisciplinary team. Ependymoma Prognosis Prognosis for ependymomas depends on tumour grade, location, patient age, and how much of the tumour can be removed. Complete surgical removal offers the best outlook, with five-year survival rates typically range between 65% and 85%, depending on tumor grade and extent of resection. Spinal cord ependymomas usually have a better prognosis than brain tumours because they’re easier to access surgically, and many ependymomas grow slowly compared with high-grade astrocytomas. Regular follow-up with MRI scans is essential to detect any recurrence early and tailor ongoing care to your individual risk and treatment response. Managing Ependymomas in Children Pediatric ependymomas require specialized care that balances tumor control with preservation of neurological, endocrine, and developmental function. Children may present differently, sometimes showing developmental delays, irritability, or regression rather than typical adult symptoms. Treatment often adapts radiation dose and timing to reduce long-term harm, and unlike adult astrocytoma or syringomyelia care, paediatric management must involve developmental specialists, school support, and family counselling. Lifelong follow-up with developmental, endocrine, and cognitive assessments is essential to detect and manage late treatment effects early. Coping with Ependymomas Living with an ependymoma diagnosis affects not only patients but entire families, requiring comprehensive support strategies: Emotional support strategies: • Connect with ependymoma support groups and online communities. • Seek professional counseling or psychological support to manage anxiety, depression, or adjustment challenges. • Maintain open communication with family and friends about your needs. Practical management approaches: • Organise medical appointments and maintain treatment records. • Prepare questions before healthcare visits to maximise consultation time. • Establish relationships with your multidisciplinary care team members. Lifestyle modifications: • Prioritise adequate rest and stress management techniques. • Maintain physical activity as tolerated and medically appropriate. • Focus on nutrition to support overall health during treatment. Conclusion Ependymomas require early diagnosis, multidisciplinary evaluation, and long-term follow-up to achieve the best possible outcomes. Understanding the tumour’s grade, location, and behaviour helps guide treatment choices and long-term monitoring, making accurate testing and regular imaging essential throughout the patient’s care journey. Metropolis Healthcare supports this process with 4,000+ tests, full body checkups, and advanced speciality diagnostics, all backed by 10,000+ home collection touchpoints for unmatched convenience. With quick, accurate results and easy booking through the website, Metropolis ensures patients receive reliable, seamless diagnostic support at every stage. FAQs What are the early signs of ependymomas? Early signs include persistent headaches, nausea, balance issues, back pain, or unexplained weakness. In children, early symptoms may include developmental delays or irritability. Can ependymomas be treated without surgery? Surgery is the primary treatment. In rare cases where surgery is unsafe, radiation therapy or targeted treatments may be considered. Observation is an option for small, asymptomatic tumours. How long do ependymoma patients survive? Survival depends on tumour grade and treatment success. Many patients with low-grade ependymomas live for years or even decades with proper treatment and monitoring. What are the side effects of ependymoma treatment? Several side effects of ependymomas include: Fatigue Hair loss (from radiation) Memory or concentration issues Balance problems Nausea or appetite changes References https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/brain-tumours/ https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/brain-tumours/types https://www.cancer.gov/rare-brain-spine-tumor/tumors/ependymoma https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23147-ependymoma https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/ependymoma/symptoms-causes/syc-20580744
Schwannoma: Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis & Treatment Options
What Is a Schwannoma? A schwannoma is a benign nerve sheath tumor that arises from Schwann cells — the cells responsible for producing myelin, the insulating material around peripheral nerve fibers. These tumours typically remain encapsulated and push nerves aside rather than invading them, making surgical removal often successful. Schwannomas can develop anywhere in your body where nerves exist. The most common type is vestibular schwannoma (previously called acoustic neuroma), which affects the vestibulocochlear nerve connecting the inner ear to the brain, which affects the nerve connecting your inner ear to your brain. Spinal schwannomas are also common and may compress spinal nerves, leading to pain, weakness, or sensory changes. Histologically, schwannomas display characteristic Antoni A and Antoni B patterns, often with Verocay bodies and strong S-100 protein positivity, including spindle-shaped cells arranged in specific patterns. These tumours are typically S-100 protein positive, which helps pathologists confirm the diagnosis during biopsy. Causes and Risk Factors of Schwannoma Several factors contribute to schwannoma development: • Genetic mutations: Loss-of-function mutations in the NF2 gene, which encodes the merlin protein, increase schwannoma susceptibility. • Hereditary conditions: Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2), schwannomatosis, and Carney complex are genetic syndromes that predispose individuals to multiple schwannomas. • Age factors: Most schwannomas occur in people aged 50-60, though they can develop at any age. • Spontaneous occurrence: Approximately 90% of schwannomas develop randomly without known genetic predisposition. • Gender considerations: Some types, like vestibular schwannoma, show a slight female predominance. Common Symptoms of Schwannoma Schwannoma symptoms vary depending on the tumour's location and size. Here are the most frequently reported symptoms: Localized pain: Often the first symptom, varying from mild discomfort to severe, persistent pain along the affected nerve pathway. Numbness and tingling: Loss of sensation or pins-and-needles feeling in the nerve distribution area. Muscle weakness: Progressive weakness in muscles supplied by the affected nerve. Balance problems: Particularly common with vestibular schwannoma affecting inner ear nerves. Hearing changes: Gradual hearing loss, tinnitus, or ear fullness with acoustic schwannoma. Visible lumps: Palpable masses, especially in superficial locations like arms or legs. Functional impairment: Difficulty with specific movements or activities, depending on nerve involvement. As per the National Cancer Institute, schwannoma can occur at any age and often presents with hearing loss, dizziness, pain, or numbness depending on its location. MRI and CT scans are key diagnostic tools, with biopsy reserved for atypical or uncertain cases. Diagnosis of Schwannoma Diagnosing schwannoma begins with a thorough clinical evaluation where your doctor assesses symptoms, performs a physical examination, and reviews your medical history. They'll look for characteristic signs like localised tenderness, sensory changes, or muscle weakness patterns. Your healthcare provider will enquire about symptom onset, progression, and any family history of genetic conditions like neurofibromatosis. Physical examination focuses on identifying lumps, testing nerve function, and assessing muscle strength in affected areas. Given that schwannoma symptoms can mimic other conditions, imaging studies become crucial for accurate diagnosis. The combination of clinical findings and imaging results helps doctors differentiate schwannomas from other nerve tumours or masses. Diagnostic and Imaging Methods for Detecting Schwannoma Several diagnostic tools help confirm a schwannoma diagnosis: • MRI scan: The gold-standard imaging technique for soft tissue visualization and assessing nerve involvement. • CT scan: Useful for assessing bone involvement and structural relationships, particularly when bony compression is suspected. • Ultrasound examination: Initial screening tool for superficial schwannomas in accessible locations. • Nerve conduction studies: Electrophysiological tests measuring nerve function and identifying areas of compression. • Biopsy analysis: Tissue sampling for microscopic examination and definitive histological confirmation. • Clinical examination: Comprehensive neurological assessment evaluating sensory, motor, and reflex functions. Treatment Options for Schwannoma Schwannoma treatment depends on tumour size, location, symptoms, and patient factors: • Surgical resection: The primary curative treatment, aiming to completely remove the tumor while preserving nerve integrity. • Observation strategy: Active surveillance with regular imaging for asymptomatic or slowly growing tumours. • Radiation therapy: A focused treatment option, often reserved for patients who are not surgical candidates or for residual/recurrent tumors. • Stereotactic radiosurgery: Precise radiation delivery targeting specific tumour areas, minimising healthy tissue exposure. • Symptom management: Medications and supportive therapies addressing pain, numbness, or functional limitations. • Multimodal approaches: Combination treatments tailored to individual patient needs and tumour characteristics. When Is Surgery Necessary for Schwannoma? Surgery becomes necessary when schwannomas cause progressive symptoms that significantly impact your quality of life. Key indications include worsening pain unresponsive to conservative management, progressive numbness or weakness affecting daily activities, and balance problems from vestibular schwannoma. Healthcare providers also recommend surgery when imaging shows rapid tumour growth threatening vital structures or nerve function. For example, a schwannoma spine location causing spinal cord compression requires prompt surgical intervention to prevent permanent neurological damage. The timing of surgery depends on symptom severity, tumour growth rate, and your personal preferences regarding intervention versus observation. Modern microsurgical and neuronavigation techniques aim for complete tumor removal while preserving nerve function whenever possible. Non-Surgical Treatment Options Several non-surgical approaches effectively manage schwannomas: • Active surveillance: Regular monitoring with periodic imaging and clinical assessments. • Pain management: Pharmacological interventions, including nerve pain medications and anti-inflammatory drugs. • Physical therapy: Exercises maintain strength, flexibility, and function in affected areas. • Radiation therapy: External beam radiation or stereotactic techniques controlling tumour growth. • Supportive devices: Assistive equipment helps manage functional limitations. • Lifestyle modifications: Adaptive strategies accommodating symptoms while maintaining independence. What Is the Prognosis for Schwannoma? The prognosis for schwannoma patients is generally excellent, with most experiencing successful outcomes following appropriate treatment. These benign nerve sheath tumors rarely undergo malignant transformation (less than 1% of cases)., with less than 1% showing cancerous transformation throughout a patient's lifetime. Surgical removal typically provides a complete cure, particularly when tumours are well encapsulated and haven't caused significant nerve damage. Most patients experience substantial symptom improvement or complete resolution following successful treatment. However, prognosis varies based on tumour location, size at diagnosis, and timing of intervention. Patients with genetic conditions like neurofibromatosis may develop multiple schwannomas requiring ongoing monitoring and management. Early detection and treatment generally lead to better functional outcomes and reduced risk of complications. Prevention and Managing Schwannoma Risk While most schwannomas occur sporadically, individuals with hereditary risk can take preventive measures and regular screening steps: • Genetic counselling: Essential for individuals with a family history of neurofibromatosis or related conditions. • Regular screening: Periodic imaging and clinical evaluations for those at increased genetic risk. • Symptom awareness: Understanding early warning signs enables prompt medical evaluation and intervention. • Family communication: Informing relatives about genetic conditions allows appropriate screening and monitoring. • Lifestyle considerations: Maintaining overall health supports optimal outcomes if treatment becomes necessary. Conclusion Schwannomas are usually slow-growing and benign, but they can still cause pain, numbness, hearing issues, or weakness if they press on nearby nerves. Early evaluation with imaging — particularly MRI, which is the preferred modality — enables accurate diagnosis and treatment planning, followed by appropriate treatment and regular follow-up, helps prevent complications and supports good long-term outcomes. During diagnosis and monitoring, Metropolis Healthcare supports you with 4,000+ tests, customised full body checkups, and speciality testing, backed by accurate results with quick turnaround times. A strong home sample collection network with 10,000+ touchpoints across India makes testing convenient, and you can easily book through the website or app. With experienced teams and trusted quality, Metropolis is your trusted partner for comprehensive diagnostics supporting schwannoma detection, monitoring, and overall health management. FAQs What is a schwannoma, and how is it diagnosed? A schwannoma is a benign nerve sheath tumour arising from Schwann cells. It is diagnosed using imaging tests such as MRI scans, CT scans, and neurological evaluations. In selected cases, a biopsy may be required to confirm the tumour type or rule out malignancy. What are the treatment options for schwannoma? Some of the treatment options for schwannoma include: Surgical removal Stereotactic radiosurgery Fractionated radiation therapy Observation for small, stable tumours Rehabilitation and pain management Can a schwannoma lead to complications? Yes. Large or untreated schwannomas can compress nerves, leading to pain, numbness, muscle weakness, or hearing loss. In rare instances, a spinal schwannoma can mimic symptoms of a spinal cord tumour, causing mobility issues. Malignant transformation is possible but extremely rare. Is a schwannoma cancerous? Most schwannomas are benign and do not spread to other parts of the body. A very small percentage may become cancerous, forming a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumour. Regular monitoring helps detect changes early. How is a schwannoma different from a neurofibroma? A schwannoma grows on the outer surface of a nerve and remains well-encapsulated, while a neurofibroma tends to grow within and around the nerve, making surgical removal more complex. Schwannomas are usually solitary, whereas neurofibromas may occur in clusters in genetic conditions. References https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17877-schwannoma https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/schwannoma/cdc-20352974 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559312/ https://www.cancer.gov/pediatric-adult-rare-tumor/rare-tumors/rare-soft-tissue-tumors/schwannoma