Web Stories
Latest Blogs
Elbow Joints: How They Work & Common Problems
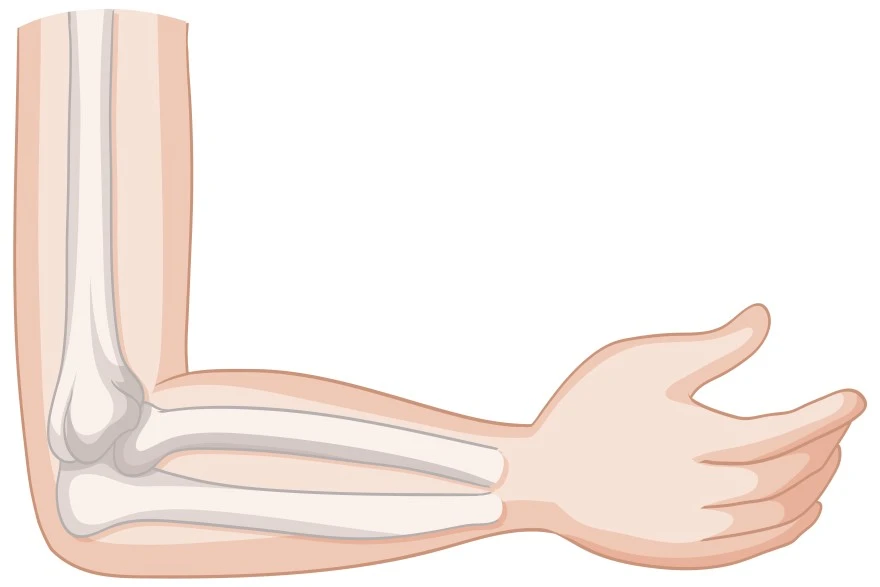
What Is the Elbow Joint? The elbow joint is a complex synovial hinge joint that connects the humerus (upper arm bone) to the two forearm bones, the radius and ulna. This remarkable joint provides both stability and mobility, allowing you to perform precise movements whilst protecting delicate nerves and blood vessels that pass through the area. Unlike single-function hinge joints such as the knee or ball-and-socket joints like the hip, the elbow joint contains three separate articulations within a single joint capsule, making it uniquely complex. The elbow joint works in coordination with your shoulder joint to position your hand in space, enabling you to reach, grasp, and manipulate objects effectively throughout your day. Anatomy of the Elbow Joint Understanding the elbow joint's anatomy helps explain how this remarkable structure functions. The key components include: Three bones: The humerus (upper arm), radius (thumb side of forearm), and ulna (pinky side of forearm) Three articulations: Humeroulnar joint (main hinge), humeroradial joint (supports bending), and proximal radioulnar joint (enables rotation) Joint capsule: A strong, fibrous membrane that encloses and stabilises the elbow joint Cartilage: Smooth hyaline cartilage that lines bone surfaces for friction-free movement Synovial fluid: Natural lubricant that nourishes cartilage and reduces friction The elbow joint ligaments provide crucial stability: Ulnar collateral ligament: Prevents excessive sideways movement on the inner side Radial collateral ligament: Stabilises the outer side of the joint Annular ligament: Encircles the radial head and keeps it aligned with the ulna during rotation Several bursae (fluid-filled sacs) around the elbow joint reduce friction between moving parts, whilst muscles like the biceps, triceps, and forearm muscles control elbow joint movement with remarkable precision. How the Elbow Joint Works The elbow joint functions primarily as a hinge, allowing your forearm to bend (flexion) and straighten (extension) through approximately About 145–150 degrees of motion. Additionally, the proximal radioulnar joint within the elbow enables forearm rotation, turning the forearm so the palm faces upward (supination) or downward (pronation). This dual functionality makes elbow joint movement essential for activities like turning door handles, using screwdrivers, or stirring food whilst cooking. The joint's stability comes from its unique bone architecture, where the ulna fits snugly into the humerus like a key in a lock, reinforced by strong elbow joint ligaments. Smooth cartilage surfaces and synovial fluid ensure effortless movement, whilst surrounding muscles provide the power and control needed for both delicate tasks and heavy lifting. Common Elbow Joint Problems Elbow Tendonitis (Tennis Elbow) Tennis elbow, or lateral epicondylitis, represents one of the most common causes of elbow joint pain. This condition occurs when tendons on the outside of your elbow become inflamed due to repetitive gripping or lifting motions. Despite its name, tennis elbow affects many people who don't play tennis: painters, carpenters, and office workers who use computers extensively often develop this condition. Symptoms include pain and tenderness on the outer elbow, weakness when gripping objects, and discomfort that worsens with wrist extension. According to findings summarised by the National Library of Medicine, healthcare professionals recommend rest, ice therapy, and anti-inflammatory medication as first-line treatment for elbow pain. Surgery is seldom required. Elbow Arthritis Elbow arthritis involves inflammation and degeneration within the joint, causing significant discomfort and functional limitations. Osteoarthritis, the most common type, results from wear and tear over time, whilst rheumatoid arthritis stems from autoimmune inflammation. Post-traumatic arthritis can develop following elbow injuries or fractures. Symptoms include morning stiffness, swelling, reduced range of motion, and persistent joint pain that may interfere with sleep and daily activities. An elbow joint x-ray often reveals characteristic changes such as joint space narrowing, bone spurs, or cartilage loss that help confirm the diagnosis. Elbow Fractures and Dislocations Elbow fractures and dislocations are serious injuries that require prompt medical evaluation and treatment Fractures commonly involve the radial head, olecranon (elbow tip), or distal humerus, often resulting from falls onto an outstretched hand. Elbow dislocations occur when the joint bones are forced out of alignment, typically due to trauma or sports injuries. These conditions cause severe elbow joint pain, visible swelling, inability to move the joint normally, and sometimes obvious deformity. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent permanent damage to the intricate elbow joint anatomy and surrounding structures. Tests Used to Diagnose Elbow Joint Disorders Healthcare providers use several diagnostic approaches to evaluate elbow problems: Physical examination: Assessing range of motion, stability, and pain patterns Elbow joint x-ray: Reveals fractures, dislocations, and arthritic changes MRI scans: Provide detailed images of soft tissues, including ligaments, tendons, and cartilage around the elbow Ultrasound: Detects tendon tears and inflammation CT scans: Offer additional detail for complex fractures Elbow Joint Treatment Options Effective elbow joint pain treatment varies depending on the specific condition and severity: Conservative management: Rest, ice, compression, elevation (RICE protocol) Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce pain and swelling Physical therapy: Targeted exercises to restore strength and mobility Bracing or splinting: Supports healing and prevents further injury Corticosteroid injections: Reduce persistent inflammation and pain when conservative measures fail Activity modification: Adjusting daily tasks to reduce joint stress Prevention of Elbow Injuries Use proper technique: Learn correct form for sports and repetitive activities Warm up thoroughly: Prepare muscles and joints before exercise Strengthen supporting muscles: Build forearm, bicep, and tricep strength Take regular breaks: Avoid prolonged repetitive motions Wear protective equipment: Use elbow pads during high-risk activities Rehabilitation After an Elbow Injury Initial rest and protection: Allow acute inflammation to settle Gentle range-of-motion exercises: Maintain joint flexibility Progressive strengthening: Gradually rebuild muscle strength Functional training: Practice daily activities and sports-specific movements Return to full activity: Resume normal activities with proper precautions Elbow Joint Surgery Surgical intervention may be necessary when conservative treatment for elbow pain fails or for severe injuries. Procedures may include arthroscopic cleaning, fracture repair, ligament reconstruction, or joint replacement in advanced arthritis cases. Modern surgical techniques often use minimally invasive approaches, reducing recovery time and improving outcomes. Post-surgical rehabilitation focuses on restoring elbow joint movement whilst protecting healing structures. How to Improve Elbow Joint Mobility Maintaining healthy elbow function requires consistent effort: Perform daily stretching: Gentle exercises maintain flexibility Strengthen regularly: Target all muscle groups around the joint Practice proper ergonomics: Adjust workstations to reduce strain Stay active: Regular movement prevents stiffness Listen to your body: Rest when you experience joint pain Conclusion Your elbow joint plays a vital role in daily function, and understanding its anatomy and common problems empowers you to maintain joint health. Whether you're experiencing joint pain or seeking prevention strategies, early intervention and proper care make a significant difference in outcomes. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of accurate diagnosis in managing elbow joint conditions. With our comprehensive portfolio of over 4,000 tests and profiles, including advanced imaging and inflammatory markers, we provide the precise diagnostics needed to guide effective treatment decisions. FAQs What are the most common elbow joint problems? The most frequent issues include tennis elbow (lateral epicondylitis), golfer's elbow (medial epicondylitis), osteoarthritis, and acute injuries like fractures or dislocations. How do I treat elbow pain at home? Initial home treatment involves rest, ice application for 15-20 minutes several times daily, over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications, and avoiding activities that worsen symptoms. Gentle stretching and strengthening exercises can help once acute pain subsides, but persistent symptoms require professional evaluation. When should I see a doctor for elbow pain? Seek medical attention if you experience severe pain, obvious deformity, inability to move your elbow, numbness or tingling in your hand, or if symptoms don't improve with home treatment within a few days. What are the causes of elbow arthritis? Elbow arthritis can result from normal wear and tear (osteoarthritis), autoimmune conditions (rheumatoid arthritis), previous injuries (post-traumatic arthritis), or genetic factors. Age, repetitive use, and previous elbow injuries increase your risk of developing arthritis. Can elbow injuries lead to permanent damage? Yes, untreated or improperly managed elbow injuries can result in permanent stiffness, weakness, chronic joint pain, or reduced function. Complex fractures, severe ligament tears, and advanced arthritis may cause lasting limitations, emphasising the importance of proper treatment and rehabilitation. How long does it take to recover from an elbow injury? Recovery time varies significantly depending on injury severity and type. Minor strains may heal within weeks, whilst fractures or surgical repairs can take several months to a year. Consistent rehabilitation and following medical advice are crucial for optimal recovery and preventing re-injury. References • https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK431092/ • https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/elbow-joint • https://teachmeanatomy.info/upper-limb/joints/elbow-joint/ • https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/tennis-elbow/symptoms-causes/syc-20351987
What Are Endorphins? Understanding the Brain’s Natural Painkillers
What Are Endorphins? Endorphins are neuropeptides—natural chemicals produced by the brain and nervous system—that act primarily as neurotransmitters and neuromodulators. The meaning of endorphins stems from combining "endogenous" (produced within) and "morphine" (a powerful painkiller). When released, endorphins bind to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, blocking pain signals and producing sensations of relief, pleasure, and well-being. Endorphins are primarily synthesized in the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and other regions such as the periaqueductal gray area of the brain, two crucial brain regions responsible for hormone regulation and stress response. How Endorphins Work in the Brain Endorphins function by binding to opioid receptors in the brain and spinal cord, blocking pain signals and activating the brain’s reward centres. They act on the same opioid receptors as morphine or heroin but are naturally released in response to pain, stress, exercise, and pleasurable experiences, explaining the “euphoric” feeling after a workout or during intense situations. Types of Endorphins in the Body Your body produces several types of endorphins, each with specific roles. Endorphins are part of the endogenous opioid peptide family, which includes three main groups: Beta-endorphins: The most potent type, primarily responsible for pain relief and euphoric feelings Enkephalins: Found throughout your brain and spinal cord, helping regulate pain and emotional responses Dynorphins: Involved in pain modulation, stress response, and may contribute to mood dysregulation under chronic stress Role of Endorphins in Managing Pain Endorphins help manage pain by acting as natural painkillers. They’re released during injury, stress, or intense activity and work by blocking pain signals before they reach the brain. This built-in relief system can be powerful: athletes, for example, often feel less pain during high-intensity performance due to elevated endorphin levels. The Connection Between Endorphins and Emotions Beyond pain management, endorphins significantly impact your emotional wellbeing. These natural chemicals promote feelings of happiness, contentment, and euphoria. Understanding endorphins highlights their vital role in mental health—they help buffer against depression and anxiety while promoting positive emotions and resilience. When endorphin levels are adequate, you're more likely to experience stable moods, better stress tolerance, and overall emotional resilience. Endorphins and Stress Reduction Endorphins act as natural stress buffers, helping your body cope with challenging situations. During stressful periods, elevated endorphin levels can create feelings of calm and resilience. The endorphins function includes moderating your body's stress response, preventing excessive anxiety and promoting emotional stability. Regular endorphin release through healthy activities can help build long-term stress resilience. What Triggers Endorphin Release? Your body releases endorphins in response to various stimuli, both pleasant and challenging. Common triggers include: Intense physical exercise, particularly aerobic activities Laughter and social interaction Eating spicy foods or dark chocolate Listening to enjoyable music Meditation and deep breathing exercises Acupuncture treatments, which stimulate sensory nerves that may promote endorphin release Exercise-Induced Endorphins ("Runner's High") The phenomenon known as "runner's high" demonstrates how to release endorphins through physical activity. During sustained, intense exercise, your body releases significant amounts of Beta-endorphins, which produce euphoria and diminish pain perception by activating μ-opioid receptors. This natural high can last for hours after exercise completion, contributing to improved mood and wellbeing. How Food Impacts Endorphin Production Spicy foods: Capsaicin in chilli peppers triggers endorphin release as your body responds to the "heat" Dark chocolate: Contains compounds that encourage endorphin production whilst providing antioxidants Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids: Support overall brain health and may enhance endorphin receptor sensitivity Endorphins and Mental Health Endorphins play a key role in mental health by supporting a positive mood, emotional balance, and resilience against stress, depression, and anxiety. Low or altered endorphin activity is linked to mood disorders, which is why exercise, laughter, and other endorphin-boosting habits are often used alongside treatment to improve mental well-being. Endorphins vs. Dopamine Feature Endorphins Dopamine Primary Function Pain relief, euphoria, stress reduction Reward, motivation, motor control, mood Chemical Type Opioid peptides Neurotransmitter Duration Short-lived, rapid action Short-lived, with complex reuptake mechanisms Main Triggers Pain, exercise, stress Rewards, anticipation, novelty, pleasure Clinical Relevance Target for pain management; implicated in addiction Implicated in Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, addiction How Endorphins vs. Dopamine Affect Motivation Whilst dopamine drives motivation by creating reward-seeking behaviour, endorphins provide immediate pleasure and pain relief. Understanding endorphins vs. dopamine helps clarify their different roles: dopamine motivates you to pursue activities, whilst endorphins reward you during and after those activities. Symptoms of Low Endorphins vs Low Dopamine Low Endorphins: Increased pain sensitivity Persistent low mood Poor stress tolerance Anxiety and irritability Low Dopamine: Lack of motivation Difficulty concentrating Apathy towards previously enjoyable activities Movement difficulties Endorphins vs. Dopamine in Addiction Pathways Both endorphins and dopamine play roles in addiction, but differently. Dopamine creates the craving and seeking behaviour, whilst endorphins provide the immediate pleasure or relief. Many addictive substances manipulate both systems, but dopamine is more central to maintaining addictive patterns. Endorphins vs. Dopamine, Serotonin, and Oxytocin Chemical Type Main Function Release Triggers Key Effects Endorphins Neurotransmitter/Hormone Pain relief, pleasure Exercise, stress, laughter Blocks pain, creates euphoria Dopamine Neurotransmitter Motivation, reward Goal achievement, anticipation Drives motivation, reinforces behaviour Serotonin Neurotransmitter Mood regulation Sunlight, exercise Promotes stability and calm Oxytocin Hormone Social bonding Touch, social interaction Increases trust and empathy How Endorphins Support Immune Function Endorphins support immune function by lowering stress and inflammation. They reduce cortisol levels, helping prevent stress-related weakening of immunity. Endorphins may influence immune cell activity and reduce inflammation, though evidence remains primarily from experimental and animal studies, one reason regular exercisers often get sick less and recover faster. Low Endorphin Levels: Signs and Symptoms How can you tell if your endorphin levels might be low? Several signs may indicate insufficient endorphin production: Increased sensitivity to pain Frequent feelings of sadness or depression Persistent trouble sleeping Chronic fatigue and low energy Difficulty experiencing pleasure (anhedonia) Frequent mood swings Heightened stress or anxiety responses Increased cravings for comfort foods What Causes Low Endorphin Levels? Low endorphin levels can result from chronic stress, lack of exercise, poor diet, and substance abuse. Medical conditions, chronic pain, long-term illness, and ongoing inflammation can also interfere with endorphin production. Genetics and natural age-related decline further reduce these “feel-good” chemicals. Ways to Naturally Increase Endorphins Engage in regular aerobic exercise such as running, cycling, or swimming Laugh frequently by watching comedies or spending time with amusing friends Eat endorphin-boosting foods like dark chocolate or spicy dishes Listen to uplifting music that resonates with your emotions Practice mindfulness meditation or gentle yoga Spend time in sunlight and natural environments Participate in creative activities like art, dance, or music Volunteer or help others through acts of kindness Endorphins and Sleep Quality Endorphins support good sleep by reducing stress and pain and working with neurotransmitters like serotonin that regulate sleep-wake cycles. Low endorphin levels can contribute to insomnia or restless sleep, while boosting them through exercise and other natural habits can improve sleep quality. Endorphins During Pregnancy and Childbirth Endorphin levels rise sharply during pregnancy and childbirth, helping the body cope with labour pain and promoting a sense of well-being. These natural chemicals also support early bonding by lowering stress and enhancing feelings of comfort and connection. This surge shows how the body prepares for the physical and emotional demands of birth. Endorphins and Chronic Pain Conditions Chronic pain disorders like fibromyalgia, arthritis, and migraines often involve disrupted endorphin activity, leading to increased pain sensitivity. Treatments such as exercise, acupuncture, and mind-body therapies aim to boost natural endorphin release and can complement medical care without added side effects. Endorphins and Addiction Recovery Substance abuse interferes with natural endorphin production, making withdrawal more painful and emotionally challenging. Recovery programs use endorphin-boosting activities, like exercise and meditation, to improve mood, reduce cravings, and support long-term healing alongside medical treatment. Can You Measure Endorphin Levels? Beta-endorphin levels can be measured in plasma or cerebrospinal fluid using specialized immunoassays, but such tests are mainly used in research rather than clinical practice. However, these measurements are primarily used in research settings rather than routine clinical practice. Typical plasma beta-endorphin levels are under 3 pmol/L, though reference ranges vary by assay method and laboratory standards, though reference ranges may vary between laboratories. Endorphin Myths vs. Facts Myth: Only exercise increases endorphins Fact: Many activities including eating, laughing, and socialising boost endorphin levels Myth: Endorphins are identical to dopamine Fact: These are distinct chemicals with different functions—endorphins focus on pain relief whilst dopamine drives motivation Myth: Simple blood tests easily measure endorphin levels Fact: Measuring brain endorphin activity is complex and not routinely available through standard blood tests Myth: Opioid medications work identically to natural endorphins Fact: While both bind to opioid receptors, medications can cause addiction and side effects that natural endorphin release doesn't produce How Endorphins Affect Social Bonding Endorphins enhance social connections by promoting feelings of trust, attachment, and pleasure during group interactions. Activities like laughing together, singing in groups, or participating in team sports trigger endorphin release, strengthening social bonds and improving overall well-being. Endorphins and Sexual Health Sexual activity powerfully triggers endorphin release, leading to reduced pain perception, heightened pleasure, stress relief, and increased emotional intimacy between partners. Endorphins, working alongside oxytocin, strengthen both emotional and physical bonds formed through intimate experiences, contributing to relationship satisfaction and overall well-being. Endorphins in Children and Adolescents Children and adolescents generally show higher baseline endorphin activity, which supports emotional regulation and resilience, supporting emotional regulation, resilience, and healthy social development. Activities like play, sports, and creative engagement boost endorphins in young people, contributing to positive moods and healthy coping mechanisms. Age-Related Changes in Endorphin Production Endorphin production and receptor responsiveness tend to decline with age, contributing to altered pain perception and mood regulation, potentially contributing to increased pain sensitivity, reduced stress tolerance, and mood changes in older adults. However, maintaining an active lifestyle throughout life can help counteract these natural changes, supporting continued well-being and emotional resilience as you age. Endorphin-Boosting Lifestyle Tips Maintain regular physical activity suited to your fitness level Prioritise laughter and enjoyable activities in your daily routine Foster meaningful social connections and relationships Engage with music, art, and creative pursuits Practice mindfulness, meditation, or relaxation techniques Spend regular time outdoors in natural settings Maintain a balanced, nutritious diet with occasional treats Participate in volunteer work or acts of kindness towards others When to See a Doctor About Endorphin-Related Symptoms Consider consulting a healthcare provider if you experience persistent low mood, chronic pain sensitivity, or difficulty managing stress. Your doctor can evaluate whether underlying conditions such as depression, chronic pain syndromes, or hormonal and neurochemical imbalances may be influencing your endorphin system. Conclusion Understanding endorphins empowers you to harness your body's natural healing mechanisms through exercise, stress management, and healthy lifestyle choices. These remarkable chemicals demonstrate your body's incredible capacity for self-care and healing. At Metropolis Healthcare, we support your wellness journey with comprehensive diagnostic services that help monitor your overall health. Our network of over 4,000 tests and profiles can assess various health markers that influence your body's natural processes, including hormone levels and stress indicators. With convenient home sample collection across 10,000+ touchpoints nationwide, you can easily access the insights needed to optimise your wellbeing. FAQs What causes endorphin release? Endorphin release occurs naturally in response to pain, stress, intense exercise, laughter, spicy foods, music, and pleasurable activities. Your body uses these chemicals to manage discomfort and promote wellbeing. How do endorphins make you feel happier? Endorphins bind to opioid receptors in your brain, blocking pain signals whilst activating pleasure centres. This dual action creates feelings of euphoria, contentment, and improved mood. Do endorphins really reduce pain? Yes, endorphins are genuine natural painkillers. They work on the same receptor pathways as morphine, providing significant pain relief during injury, illness, or stress. How long do endorphins last in the body? Endorphin effects typically last from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the trigger and individual factors. Exercise-induced endorphins often provide mood benefits for 2-4 hours post-activity. Can certain foods boost endorphins? Spicy foods, dark chocolate, and foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids can stimulate endorphin production. What's the difference between endorphins and dopamine? Endorphins primarily provide pain relief and immediate pleasure, whilst dopamine drives motivation and reward-seeking behaviour. References • https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470306/ • https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/endorphins-the-brains-natural-pain-reliever • https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23040-endorphins • https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320839
Broccoli Benefits: A Superfood for Immunity, Heart Health & Detox
When you think about powerful vegetables that can transform your health, broccoli stands out as nature's green powerhouse. This cruciferous broccoli vegetable delivers remarkable health benefits that support your immune system, protect your heart, and help your body detox naturally. The broccoli plant has earned its reputation as a superfood through extensive research showing its ability to fight disease and promote wellness. Understanding broccoli's benefits can help you make informed choices about incorporating this nutritious vegetable into your daily diet for optimal health. Nutritional Value of Broccoli Broccoli nutrition is truly impressive, packing essential vitamins, minerals, and protective compounds into every serving. This remarkable broccoli vegetable provides substantial nutrition while remaining low in calories, making it perfect for health-conscious individuals. Nutrient Amount per Cup (91g) Calories 31 Protein 2.6 g Dietary Fibre 2.4 g Vitamin C 91 mg Vitamin K 93 mcg Folate 57 mcg Potassium 288 mg Calcium 43 mg Iron 0.7 mg Broccoli provides powerful phytochemicals, including sulforaphane (an isothiocyanate formed from glucoraphanin) and other glucosinolates. Why Broccoli Is a Global Immunity Superfood What makes broccoli's benefits so remarkable for immune support? The answer lies in its exceptional vitamin C content and unique bioactive compounds. Broccoli is an excellent source of vitamin C—one cup provides about 90 mg, comparable to or higher than some citrus fruits—making it an outstanding immune-supportive food. Sulforaphane, a key isothiocyanate compound derived from glucoraphanin, activates cellular detoxification enzymes (via the Nrf2 pathway) and supports immune and antioxidant defense. Research shows that regular consumption of this cruciferous vegetable can enhance your body's ability to fight infections and reduce inflammation. The combination of vitamin C, antioxidants, and glucosinolates in broccoli creates a powerful shield against illness, making it an essential food for maintaining strong immunity throughout the year. 12 Benefits of Broccoli The extensive broccoli benefits extend far beyond basic nutrition, offering comprehensive health support: Boosts immune system through exceptional vitamin C levels and antioxidant compounds Supports heart health by reducing cholesterol and blood pressure naturally Promotes detoxification via sulforaphane activation of liver enzymes May help reduce cancer risk by providing glucosinolates and sulforaphane, which support detoxification and protect against cellular oxidative damage Supports digestive health through dietary fibre that promotes beneficial gut bacteria and regular bowel movements Regulates blood sugar due to fibre and bioactive compounds supporting glucose control Supports bone health with calcium, vitamin K, and essential minerals Aids weight management through low calories and high satiety from fibre Enhances skin health via antioxidants and vitamin C supporting collagen production Improves eye health with carotenoids like lutein and zeaxanthin Protects brain health through anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties Associated with lower mortality risk in observational studies of diets rich in cruciferous vegetables How to Prepare Broccoli to Maximise Nutrient Absorption Preparing broccoli properly ensures you receive maximum benefits from this nutritious vegetable: Chop and let rest for about 30–40 minutes before cooking to allow the enzyme myrosinase to convert glucoraphanin into sulforaphane Steam lightly for 3-5 minutes to preserve vitamin C while enhancing sulforaphane availability Avoid prolonged boiling which destroys water-soluble vitamins and beneficial compounds Microwave briefly (1–2 minutes) with minimal water to preserve heat-sensitive vitamins and bioactive compounds. Include healthy fats like olive oil to improve absorption of fat-soluble vitamins Add a small amount of mustard seed or powder when cooking frozen broccoli to reintroduce myrosinase, which enhances sulforaphane formation These preparation methods help you maximise broccoli's nutrition while maintaining the vegetable's natural flavour and texture. Steamed vs. Raw Broccoli: Which Has More Benefits? Both raw and steamed broccoli offer substantial health advantages, but their nutrient profiles differ slightly. Raw broccoli retains the highest vitamin C and enzyme (myrosinase) activity, while light steaming enhances sulforaphane bioavailability, making it excellent for immediate antioxidant benefits. However, Light steaming (3–5 minutes) increases sulforaphane availability by preserving myrosinase activity, which is destroyed by prolonged heat. A key study published in the International Journal of Scientific & Technology Research indicates that steaming broccoli for 3-5 minutes optimises the balance between nutrient retention and compound activation. This gentle cooking method preserves most vitamins while making beneficial compounds more bioavailable. For optimal broccoli benefits, consider including both raw and lightly steamed preparations in your diet. Raw broccoli works excellently in salads and as crudités, while steamed broccoli complements main dishes perfectly. Best Times to Eat Broccoli for Health Benefits Timing your broccoli consumption can enhance its health benefits. Including it with meals containing healthy fats, such as lunch or dinner, improves absorption of fat-soluble vitamins A and K. The nutrients work synergistically with other foods, making it ideal for balanced meals. Consistency matters more than specific timing when maximising broccoli's benefits. Regular weekly consumption supports immune, cardiovascular, and detoxification functions through nutrient and antioxidant synergy. Many nutritionists recommend consuming broccoli 2-3 times weekly as part of a varied diet. For sensitive stomachs, eating broccoli with other foods may reduce potential digestive discomfort while ensuring optimal nutrient absorption. Common Mistakes to Avoid When Eating Broccoli Avoiding these common errors helps you maximise broccoli's nutrition value: Overcooking through prolonged boiling destroys heat-sensitive vitamins and reduces beneficial compounds Not allowing chopped broccoli to rest before cooking prevents enzyme activation Discarding nutrient-rich stems and leaves wastes valuable nutrition from the broccoli Excessive raw intake may interfere with iodine uptake due to goitrogenic compounds, but moderate, cooked portions are safe for most individuals with adequate iodine intake Adding heavy, high-sodium sauces that mask the natural benefits of this healthy vegetable Poor storage practices leading to nutrient loss and spoilage Global Variations: How Different Cultures Use Broccoli for Wellness Cultures worldwide incorporate broccoli's benefits into traditional wellness practices. Western cuisines often feature steamed or roasted broccoli as a nutritious side dish, emphasising its health-promoting qualities. Asian cooking traditions frequently stir-fry the vegetable with garlic and ginger, both offering additional anti-inflammatory benefits. Mediterranean approaches often combine broccoli with olive oil and herbs, creating nutrient-dense preparations that maximise absorption. Many cultures value both florets and stems of the broccoli, ensuring complete utilisation of its nutritional profile. These diverse preparation methods demonstrate how different societies recognise and harness broccoli nutrition for optimal health outcomes. Serving Sizes & Daily Recommendations for Broccoli Optimal broccoli consumption guidelines help you achieve maximum health benefits: Aim for ½ to 1 cup per serving of cooked or raw broccoli as part of balanced meals Consume 2-3 servings weekly to experience measurable health improvements and reduced disease risk Include variety with other cruciferous vegetables like cauliflower and Brussels sprouts for broader benefits Adjust portions for children starting with ¼ to ½ cup servings based on age and tolerance Epidemiological studies suggest that consuming three or more servings of cruciferous vegetables weekly, including broccoli, is linked to approximately 10% lower all-cause mortality risk. This makes regular broccoli consumption a simple yet powerful investment in long-term health. Possible Side Effects & Precautions Broccoli is generally safe for most people when consumed in normal food amounts. However, excessive consumption, particularly raw broccoli, may cause digestive discomfort including gas and bloating due to high fibre and complex carbohydrate content. These effects typically diminish as your digestive system adapts. Individuals with thyroid conditions should moderate raw broccoli intake, as compounds called goitrogens may interfere with thyroid hormone production when iodine levels are insufficient. Cooking largely inactivates these compounds, making cooked broccoli safer for those with thyroid concerns. People on blood-thinning medications (e.g., warfarin) should maintain consistent broccoli intake because its vitamin K can influence anticoagulant effectiveness. Conclusion From boosting immunity and supporting heart health to facilitating natural detoxification, broccoli provides comprehensive wellness support that's both accessible and affordable. Whether you prefer it steamed, raw, or incorporated into favourite recipes, this versatile vegetable offers powerful protection against chronic diseases while supporting optimal daily health. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand that optimal nutrition works hand-in-hand with regular health monitoring. Backed by a CAP proficiency score exceeding 98%, placing it among the top 1% of labs globally, Metropolis ensures precise and reliable results for nutritional assessments and health profiles. With NABL & CAP accredited labs, home sample collection, and online report access, Metropolis empowers you to make informed dietary decisions with confidence. FAQs What happens to your body when you eat broccoli every day? Daily broccoli consumption can significantly enhance immune function, support cardiovascular health, improve digestion, and provide powerful antioxidant protection. Regular intake helps maintain stable blood sugar levels while supporting your body's natural detoxification processes. The high fibre content promotes healthy gut bacteria, while vitamin C supports collagen production for healthier skin and stronger immunity. Is broccoli healthier cooked or raw? Both forms offer distinct advantages. Raw broccoli provides maximum vitamin C and enzyme activity, while lightly steamed broccoli increases sulforaphane availability—the key compound responsible for many protective benefits. Light steaming for 3-5 minutes represents the optimal balance, preserving most nutrients while enhancing bioactive compound absorption. How much broccoli should you eat per day for health benefits? Nutritionists recommend ½ to 1 cup of broccoli per serving, consumed 2-3 times weekly rather than daily. This approach provides substantial health benefits while allowing dietary variety. Consuming approximately 2-3 cups weekly aligns with research showing reduced disease risk and improved health outcomes. Can broccoli really help boost the immune system? Yes, broccoli's exceptional vitamin C content—providing over 90% of daily requirements per cup—significantly supports immune function. The sulforaphane and other antioxidants help activate immune cells and reduce inflammation, creating a robust defence against infections and disease. What is the best way to cook broccoli for maximum nutrients? Light steaming for 3-5 minutes after allowing chopped broccoli to rest for 40 minutes maximises both nutrient retention and beneficial compound activation. This method preserves vitamin C while optimising sulforaphane availability, providing the best of both nutritional worlds. Are there any side effects of eating too much broccoli? Excessive broccoli consumption may cause digestive discomfort, including gas and bloating, particularly when eaten raw. People with thyroid conditions should limit raw broccoli intake, while those on blood-thinning medications should maintain consistent consumption levels. Moderate intake typically prevents these issues. References • https://www.ijstr.org/final-print/sep2021/Effect-Of-Various-Cooking-Methods-On-Vitamin-C-Levels-In-Broccoli-Smoothies.pdf • https://www.nutritionvalue.org/Broccoli%2C_raw_nutritional_value.html • https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/foods/broccoli • https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10376324/
5 Incredible Health Benefits of Brazil Nuts You Didn’t Know About
What are Brazil Nuts? Brazil nuts are large, triangular seeds harvested from the Brazil nut tree (Bertholletia excelsa), a native Amazonian species that can grow up to 50 metres tall and live for centuries, which can grow up to 50 metres tall and live for over 500 years. These impressive trees thrive exclusively in the pristine Amazon rainforest across Brazil, Bolivia, and Peru. Brazil nut trees rely on specific rainforest conditions and large bee species (Euglossa spp.) for pollination, making large-scale cultivation extremely difficult. Each Brazil nut pod contains 12-24 individual nuts arranged like orange segments. The nuts have a rich, buttery flavour with a slightly sweet, earthy taste that makes them incredibly satisfying. What sets Brazil nuts apart from other nuts is their exceptional selenium content; Just one Brazil nut can often meet or exceed your daily selenium requirement. Nutrition Profile of Brazil Nuts Understanding the nutritional powerhouse that Brazil nuts represent helps explain their remarkable health benefits: Selenium superstar: Selenium content varies between 50–100 µg per nut (90–180% of the daily value), depending on the soil where it grows. Healthy fats: Rich in monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats supporting cardiovascular health Quality protein: About 4 grams per 28-gram serving Essential minerals: High in magnesium (26% daily value), copper, manganese, phosphorus, and zinc Vitamins: Good source of thiamine (vitamin B1) and vitamin E Fibre content: Provides dietary fibre for digestive health Low carbohydrates: Naturally low in carbs and sodium-free How Brazil Nut Benefits Begin With Selenium The extraordinary Brazil nut benefits stem primarily from their unmatched selenium content. Selenium functions as a crucial trace mineral that your body needs for optimal health but cannot produce independently. This powerful antioxidant mineral supports the production of selenoproteins, which play vital roles in DNA synthesis, thyroid hormone metabolism, and cellular protection. In selenium-deficient regions, consuming one Brazil nut daily for several weeks can normalize selenium levels, according to clinical studies. As per The Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, this makes them one of the richest food sources of selenium globally. However, selenium content varies significantly depending on the soil conditions where the Brazil nut tree grows, with some nuts containing up to 91 mcg per nut whilst others may have considerably less. 5 Incredible Health Benefits of Brazil Nuts 1. Potent Antioxidant Defence Brazil nuts provide exceptional antioxidant protection through their selenium content, which boosts your body's natural antioxidant enzyme activity. These enzymes protect your cells from oxidative damage caused by free radicals, potentially reducing your risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease and certain cancers. Regular consumption, in moderation, may support the body’s defence against oxidative stress and inflammation. 2. Supports Thyroid Function Your thyroid gland requires selenium to convert inactive thyroid hormones into their active forms. Brazil nut benefits for thyroid health are particularly significant—adequate selenium intake supports healthy thyroid function and may help prevent thyroid disorders. This is especially important for maintaining proper metabolism, energy levels, and temperature regulation. 3. Improves Heart Health The healthy unsaturated fats in Brazil nuts help improve your cholesterol profile by lowering harmful LDL cholesterol while increasing beneficial HDL cholesterol. Studies suggest that moderate consumption may improve cholesterol profiles and support cardiovascular health, though long-term outcome data are limited through improved blood lipid levels. 4. Enhances Brain Function and Mood Selenium plays a crucial role in cognitive health and mood regulation. Adequate selenium intake has been associated with improved mood and cognitive function, while deficiency may be linked to anxiety or cognitive decline. Brazil nut benefits extend to supporting neurotransmitter balance and protecting brain cells from oxidative stress. 5. Boosts Immune System Your immune system relies on selenium to function optimally. Brazil nuts strengthen your immune response by enhancing white blood cell activity and supporting your body's natural defence mechanisms against infections and inflammatory conditions. Other Emerging Advantages of Brazil Nuts Cancer protection potential: Selenium's antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties may help reduce cancer risk Male fertility support: Selenium contributes to sperm motility and overall reproductive health in men Hair and nail health: Essential for maintaining strong, healthy hair and nail structure Blood sugar regulation: Preliminary research suggests potential benefits for glucose control Skin health enhancement: Antioxidants support collagen production and skin repair Brazil Nut Benefits Females: What Women Should Know When it comes to nutrition, few foods offer as many targeted advantages for women as Brazil nuts. Rich in selenium, antioxidants, and essential minerals, Brazil nuts benefit females in many ways: Thyroid health support: Women are five times more likely to develop thyroid disorders than men Reproductive health: Selenium supports fertility and healthy pregnancy outcomes Hormonal balance: May help alleviate mood swings and anxiety related to hormonal changes Skin, hair, and nail health: Supports beauty from within through antioxidant protection Bone health: Contains minerals essential for maintaining bone density How to Include Brazil Nuts in Your Diet Daily snacking: Enjoy 1-3 whole nuts as a nutritious snack Smoothie boost: Blend into morning smoothies for creamy texture Salad topping: Chop and sprinkle over salads for added crunch Trail mix: Combine with other nuts and dried fruits Baking ingredient: Incorporate into homemade granola or energy bars Brazil nut butter: Blend into a creamy spread for toast Breakfast enhancer: Add chopped nuts to porridge or yoghurt How Many Brazil Nuts a Day? Safe Intake Guidelines Due to their exceptionally high selenium content, moderation is crucial when consuming Brazil nuts. Most nutrition experts recommend limiting intake to 1-3 Brazil nuts daily for adults to avoid selenium toxicity. Each nut can provide between 68-91 mcg of selenium, easily meeting or exceeding the recommended daily intake of 55 mcg for adults. The Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) for selenium is 400 µg per day for adults, according to NIH guidelines; exceeding this may cause toxicity, making portion control essential. The variable selenium content means some nuts may contain significantly more than others, so consistent moderation helps ensure safe consumption whilst maximising Brazil nut benefits. Potential risks or when to avoid Brazil nuts While Brazil nuts offer impressive health benefits, excessive consumption can lead to Excessive selenium intake (selenosis) can cause symptoms such as hair loss, brittle nails, nausea, garlic-like breath odour, fatigue, and in severe cases, neurological damage. People with tree nut allergies should avoid Brazil nuts completely. Individuals on thyroid or anticoagulant medications should consult their healthcare provider before increasing selenium intake. Additionally, individuals managing their weight should consume Brazil nuts mindfully due to their high calorie content—Approximately 186 kcal per 28 g (1 oz) serving, primarily from healthy unsaturated fats. Conclusion: Maximise Brazil Nut Benefits Smartly Brazil nuts offer remarkable health benefits when consumed as part of a balanced diet. Their unique selenium profile makes them a powerful ally for thyroid health, antioxidant protection, and immune support. Brazil nut benefits for females are particularly noteworthy, supporting hormonal balance and reproductive health. At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of monitoring your nutritional status and overall health. With our comprehensive portfolio of over 4,000 tests and profiles, including specialised nutritional assessments and thyroid function panels, we help you understand how dietary choices like adding Brazil nuts impact your wellbeing. Our convenient home sample collection service, spanning 10,000+ touchpoints across India, makes health monitoring accessible and stress-free. FAQs How many Brazil nuts should I eat daily? Limit yourself to 1-3 Brazil nuts daily to avoid selenium toxicity. Just one Brazil nut often provides your entire daily selenium requirement, making moderation essential for safe consumption. Are Brazil nuts safe for anyone with thyroid issues? Brazil nuts can benefit people with thyroid conditions, particularly those with selenium deficiency. However, individuals with autoimmune thyroid diseases should consult their healthcare provider before increasing selenium intake, as excessive amounts may worsen some conditions. Can Brazil nuts help lower cholesterol? Yes, research shows that Brazil nuts can significantly improve cholesterol profiles. Clinical studies have shown that consuming 1–4 Brazil nuts can improve blood lipid profiles within days, with effects lasting up to one month. What’s the benefit of Brazil nuts for brain health? Brazil nuts support brain health through their high selenium and vitamin E content, which protect brain cells from oxidative damage. This may help preserve memory, improve cognitive function, and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Are there side effects of eating too many Brazil nuts? Consuming too many Brazil nuts can lead to selenium toxicity, causing symptoms like hair loss, nail brittleness, digestive upset, and neurological problems. Stick to the recommended 1-3 nuts daily to avoid these issues. Can Brazil nuts be part of a weight-loss diet? Brazil nuts can support weight management when eaten in moderation. Their protein and healthy fats promote satiety, helping control appetite. However, they're calorie-dense, so portion control is crucial for weight-loss goals. References • https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3693158/
10 Reasons Why Brown Rice Is a Must-Have in Your Healthy Diet
What is Brown Rice? Brown rice is a whole grain that retains its bran and germ layers, which are removed during the polishing process that produces white rice. These layers provide fibre, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. This minimal processing preserves the natural brown rice nutrition, including essential vitamins, minerals, and dietary fibre that make it a superior choice for health-conscious individuals. The distinctive nutty flavour and slightly chewy texture of brown rice result from these intact outer layers. When you compare brown rice vs. white rice, the difference becomes immediately apparent, brown rice maintains its natural colour and nutrient density, while white rice loses significant fibre, magnesium, and B-vitamins during polishing. Brown Rice Nutrient Values: What's Inside Each Grain? Nutrient Brown Rice (1 cup, cooked) Calories 215–225 Carbohydrates 45-52 g Protein 4.5-5.5 g Fat 1.6-2 g Fibre 3.2-3.5 g Magnesium 84 mg (about 20% of the daily value) Manganese 1.8 mg Selenium 19 mcg 10 Brown Rice Benefits You Can't Ignore Superior Fibre Content: Brown rice is rich in dietary fibre, which supports smooth digestion, prevents constipation, and promotes a healthy gut environment. High Magnesium Levels: Its impressive magnesium content helps strengthen bones, support nerve activity, and improve muscle function. Excellent Manganese Source: Manganese in brown rice boosts metabolism, enhances antioxidant protection, and aids collagen formation. Heart-Healthy Properties: Regular consumption may help lower cholesterol levels and support healthier blood pressure, contributing to long-term heart wellness. Blood Sugar Regulation: The moderate glycaemic index (GI 50–55) of brown rice helps stabilise blood glucose levels and supports diabetes prevention. Weight Management Support: Fibre-rich whole grains like brown rice increase satiety, control appetite, and help prevent overeating. Selenium for Immunity: Brown rice contains selenium, a powerful mineral that supports immune strength and helps maintain thyroid balance. Naturally Gluten-Free: As a naturally gluten-free grain, it is ideal for individuals with celiac disease or gluten sensitivities. Chronic Disease Prevention: Its antioxidants and whole-grain nutrients may lower the risk of stroke, certain cancers, and other chronic illnesses. Wide Culinary Versatility: Brown rice adapts to countless recipes, from bowls and stir-fries to salads and soups, making healthy eating simple and enjoyable. Key Nutrients in Brown Rice That Drive Health Benefits The remarkable brown rice benefits stem from its concentrated nutrient profile: Dietary fibre: Promotes digestive health and blood sugar control Magnesium: Essential for bone health and energy production Manganese: Supports metabolism and antioxidant defence Selenium: Crucial for immune function and DNA repair B-vitamins: Including thiamine, niacin, and vitamin B6 Phosphorus: Vital for bone formation and cellular energy Antioxidant compounds: Protect against cellular damage Brown Rice Benefits for Heart Health Brown rice nutrition provides substantial cardiovascular advantages through multiple mechanisms: Lowers LDL cholesterol: Soluble fibre binds cholesterol particles for elimination Reduces blood pressure: Magnesium and potassium support healthy circulation Prevents arterial plaque: Antioxidants protect blood vessel integrity Supports heart rhythm: Essential minerals maintain proper cardiac function Brown Rice Benefits for Blood Sugar and Diabetes Prevention The benefits of brown rice for diabetes are particularly noteworthy for those managing blood glucose levels. Studies show that Studies indicate replacing white rice with brown rice may reduce type 2 diabetes risk by up to 23%. Lower glycaemic index: Prevents rapid blood sugar spikes after meals Sustained energy release: Complex carbohydrates provide steady glucose Improved insulin sensitivity: Fibre enhances the body's glucose processing Reduced diabetes risk: Whole grain consumption correlates with lower type 2 diabetes incidence Brown Rice Benefits for Weight Management The ICMR recommends choosing brown rice and other whole grains over refined options like white rice to enhance overall diet quality and reduce the risk of diabetes as well as obesity. Brown rice supports weight control due to its fibre and nutrient density, helping regulate appetite and improve energy balance: Enhanced satiety: High fibre content promotes feeling full longer Reduced cravings: Steady blood sugar prevents hunger spikes Metabolic support: B-vitamins aid efficient energy conversion Portion control: Nutrient density satisfies nutritional needs with smaller servings Brown Rice Benefits for Digestion and Gut Health The exceptional fibre content in brown rice transforms digestive wellness. This dietary fibre acts as a prebiotic, feeding beneficial gut bacteria and promoting a healthy microbiome. Regular consumption supports bowel regularity, reduces constipation risk, and is associated with lower colorectal cancer risk. Additionally, brown rice benefits include: Improved nutrient absorption Reduced inflammatory markers in the digestive tract Enhanced gut barrier function Better overall digestive comfort Brown Rice vs. White Rice: Which is Better for Nutrition? Feature Brown Rice White Rice Processing Minimal (whole grain) Extensive (refined) Fibre content 3.5g per cup 0.6g per cup Magnesium 84 mg 19 mg Glycaemic index Lower (50-55) Higher (70-75) Satiety factor Higher Lower Chronic disease protection Significant Minimal This comparison clearly demonstrates why brown rice nutrition surpasses white rice in virtually every health metric. Brown Rice Benefits for Gluten-Free and Allergy-Sensitive Diets Brown rice is naturally gluten-free and safe for people with coeliac disease or non-coeliac gluten sensitivity. Unlike wheat-based grains, brown rice is naturally gluten-free while maintaining superior nutritional value. This makes it particularly valuable for those following restricted diets who still need adequate brown rice protein and essential nutrients. Complementing brown rice with the benefits of black rice or the benefits of red rice adds an extra layer of antioxidant-rich nutrition, offering even more wholesome options for individuals with specific dietary needs. Brown Rice Benefits for Chronic Disease Prevention Regular consumption of brown rice may significantly reduce various health risks: Type 2 diabetes prevention: Meta-analyses show whole grain intake is associated with about 16% lower diabetes risk Cardiovascular disease reduction: Improved cholesterol profiles and blood pressure Cancer protection: Antioxidants and fibre may reduce colorectal cancer risk Stroke prevention: Enhanced circulation and reduced inflammation markers Brown Rice Benefits from Magnesium, Manganese & Selenium These three minerals make brown rice nutrition exceptionally valuable for overall health. Magnesium supports over 300 enzymatic reactions, including energy metabolism and bone formation. Manganese acts as a powerful antioxidant while supporting carbohydrate and amino acid metabolism. Selenium enhances immune function and may reduce cancer risk through its role in DNA repair mechanisms. Brown Rice as a Versatile Staple for Global Cuisines Brown rice adapts beautifully to Indian cooking styles, from fragrant biryanis to comforting dal-chawal combinations, and sweet treats like kheer and payasam. Its robust texture pairs effortlessly with spicy curries, and its nutty flavour elevates classic desert preparations. Beyond Indian cuisine, brown rice also shines in global dishes — from Asian stir-fries and Thai rice bowls to Mexican burrito fillings, Mediterranean rice salads, and even hearty Buddha bowls. Its ability to blend seamlessly into traditional and international recipes makes it a wholesome, flavourful choice without compromising taste or cultural authenticity. Brown Rice as a Sustainable Choice in Whole-Grain Diets Choosing brown rice supports both personal health and environmental sustainability by reducing processing energy and promoting whole-grain diets. The minimal processing required preserves nutrients while reducing energy consumption. This whole grain approach aligns with sustainable eating patterns that benefit both individual wellness and planetary health. How to Prepare Brown Rice for Best Taste and Nutrients Rinse thoroughly under cold water until water runs clear Soak for 30-60 minutes to improve digestibility and reduce cooking time Use proper water ratio - typically 2:1 water to rice Bring to boil, then simmer covered for 40-50 minutes Rest for 10 minutes before fluffing with a fork Add aromatics like bay leaves or whole spices during cooking Store cooked brown rice in the refrigerator for up to 4–5 days in an airtight container Possible Downsides of Brown Rice Higher arsenic content: Brown rice may contain slightly higher levels of inorganic arsenic, especially when grown in certain regions. Consuming a variety of grains and cooking rice in excess water can help minimise exposure. Longer cooking time: It typically requires more soaking and a longer cooking duration than white rice, which may demand extra planning and preparation. Digestive adjustment: The higher fibre content may initially cause bloating or gas in individuals who are not used to fibre-rich foods, though this often improves over time. Phytic acid presence: Brown rice contains phytic acid, a natural antioxidant that can reduce mineral absorption slightly; soaking or fermenting rice before cooking helps minimise this effect. Storage considerations: Due to its natural oils, brown rice has a shorter shelf life and can turn rancid more quickly if not stored properly in a cool, airtight environment. Conclusion Brown rice stands as a nutritional powerhouse that transforms ordinary meals into health-promoting experiences. From managing blood sugar and supporting heart health to enhancing digestion and preventing chronic diseases, the benefits of incorporating brown rice into your daily diet are both immediate and long-lasting. At Metropolis Healthcare, we support your health journey with comprehensive diagnostic services that help you monitor the positive impacts of dietary changes like adding brown rice to your meals. Our extensive network of over 4,000 tests—including diabetes panels, lipid profiles, and nutritional assessments—provides the insights you need to optimise your health. Backed by a CAP proficiency score exceeding 98%, placing it among the top 1% of labs globally, Metropolis ensures precise and reliable results. FAQs Is brown rice really healthier than white rice? Absolutely. Brown rice benefits include significantly higher fibre, magnesium, and antioxidants compared to white rice. The whole grain structure provides sustained energy and better blood sugar control, making it nutritionally superior for most individuals. What are the top brown rice benefits for weight loss? Brown rice's calories work effectively for weight management through enhanced satiety, stable blood sugar levels, and improved metabolism. The high fibre content helps you feel full longer, naturally reducing overall calorie intake while providing essential nutrients. Is brown rice suitable for people with diabetes? Yes, brown rice for diabetes offers excellent benefits. The benefits of brown rice for diabetes include lower glycaemic index, better blood sugar control, and improved insulin sensitivity compared to refined grains. However, portion control remains important for optimal glucose management. How much brown rice should I eat daily? A half-cup serving of cooked brown rice provides optimal brown rice nutrition without excessive brown rice calories. This portion delivers approximately 108 calories and substantial nutrients whilst supporting healthy weight management and blood sugar control. Is brown rice safe to eat daily? Daily consumption of brown rice is generally safe and beneficial. However, vary your grain choices to minimise arsenic exposure and ensure dietary diversity. Include other whole grains like quinoa, millet, and oats alongside brown rice for optimal nutrition. Does brown rice contain arsenic? How to reduce risk? Brown rice does contain naturally occurring arsenic, though levels vary by growing region. Reduce exposure by rinsing rice thoroughly, cooking with excess water, and varying your grain choices. The health benefits typically outweigh risks with moderate consumption. References • https://www.inorder.in/public-education/a-look-at-the-new-icmr-dietary-guidelines-for-indians/ • https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35681238/ • https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/nutrition-basics/whole-grains-refined-grains-and-dietary-fiber
Health Benefits of Cranberry: 11 Things You Need to Know for Better Wellness
What is Cranberry? A Nutrition Primer on Cranberry Fruit Cranberry (Vaccinium macrocarpon) is a small, ruby-red berry that grows on evergreen shrubs in acidic bogs, primarily in North America. European cranberries (Vaccinium oxycoccos) are closely related but smaller in size. The cranberry fruit belongs to the same family as blueberries and contains an impressive array of nutrients that contribute to its powerful health-promoting properties. Fresh cranberries contain about 46–51 calories per 100 g serving, making it an excellent choice for weight management. The fruit contains 4g of dietary fibre, which supports digestive health and helps regulate blood sugar levels. What makes cranberry particularly special is its exceptionally high vitamin C content, providing essential immune support, along with vitamin E, vitamin K, and important minerals like potassium and manganese. The distinctive tart taste of cranberry comes from its natural organic acids, including citric and malic acid, which also contribute to its preservation qualities. Whether consumed fresh, as cranberry juice, or in cranberry dry fruit form, this remarkable berry delivers consistent nutritional benefits that have made it a staple in health-conscious diets worldwide. Understanding "Cranberry Benefits": Key Nutrients & Phytochemicals The exceptional cranberry benefits stem from its unique concentration of bioactive compounds that work synergistically to promote health: Proanthocyanidins (PACs): Type-A proanthocyanidins (PACs) in cranberry uniquely prevent E. coli adhesion to urinary tract walls, reducing infection recurrence Anthocyanins: The pigments responsible for cranberry's vibrant red colour, offering potent anti-inflammatory and cardiovascular protective effects Flavonoids: Including quercetin and myricetin, which support immune function and help reduce oxidative stress throughout the body Vitamin C: A single serving provides significant immune-boosting antioxidant protection, with fresh cranberry containing 29 mg per 100 g Dietary Fibre: Supporting digestive health and helping maintain stable blood sugar levels Organic Acids: Contributing to cranberry's natural antimicrobial properties and supporting urinary tract health Potassium: Essential for heart health and blood pressure regulation, with cranberries provide approximately 80–90 mg potassium per 100 g serving Vitamin E and K: Supporting cellular health and proper blood clotting function respectively 11 Health Benefits of Cranberry Cranberries are one of the most researched functional fruits, packed with antioxidants, fibre, vitamins, and unique plant compounds that support multiple aspects of health. Here’s a detailed look at 11 key cranberry benefits: Prevents Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) Cranberries help prevent recurrent UTIs, especially in women, by preventing bacterial adhesion. They are effective as a preventive aid—not a treatment—for active infections. Supports Cardiovascular Health Regular cranberry intake can improve cholesterol balance by raising HDL (good cholesterol) and lowering LDL (bad cholesterol). Their anti-inflammatory properties also help maintain healthy blood vessels and overall heart function. Boosts Immune System Function Cranberries are rich in vitamin C and other antioxidants that strengthen your immune defences. These nutrients help the body fight infections more effectively and support daily immune resilience. Provides Powerful Antioxidant Protection Cranberries rank among the top antioxidant-rich fruits. Their wide range of antioxidant compounds helps neutralise free radicals, protecting cells from damage and reducing the risk of chronic diseases. Promotes Digestive Health The fibre in cranberries supports the growth of healthy gut bacteria and promotes regular bowel movements. This contributes to better digestion and overall gut balance. May Reduce Cancer Risk Laboratory studies suggest cranberry polyphenols may inhibit cancer cell growth in vitro, though human evidence remains preliminary, particularly in colon and prostate cancers. These findings highlight their potential role in long-term cellular protection. Supports Oral Health Cranberry extracts have shown potential to reduce bacterial adhesion in the mouth, possibly lowering plaque formation risk. They inhibit bacterial adhesion in the mouth, similar to their effect in the urinary tract. Helps Regulate Blood Sugar Cranberrie's fibre and polyphenols may modestly improve post-meal glucose control and insulin sensitivity, though data are limited. This makes them a supportive food for maintaining balanced blood sugar levels. Protects Brain Function Emerging research, including studies published in Frontiers in Nutrition, suggests Early studies suggest cranberry flavonoids may improve memory and brain perfusion in older adults, though more research is needed. Maintains Healthy Blood Pressure Cranberries contain potassium and other heart-friendly nutrients that help support normal blood pressure and overall cardiovascular stability. Supports Liver Health Both traditional uses and modern studies indicate that cranberries may help protect the liver from oxidative stress, promoting healthier liver function over time. When Cranberry Benefits May Not Apply: Who Should Be Cautious? While cranberry is generally safe for most people, certain individuals should exercise caution when consuming cranberry products. Individuals taking warfarin should consult their healthcare provider before using cranberry supplements or juice regularly, as high intake may potentiate anticoagulant effects before regularly consuming cranberry juice or supplements, as cranberry may enhance the effects of these medications. Individuals with calcium oxalate kidney stones should limit cranberry supplement use, as cranberries are moderately high in oxalates that could potentially contribute to stone formation. Those with diabetes need to be mindful of sugar content in commercial cranberry juice products, which often contain added sweeteners that can affect blood glucose levels. If you experience stomach upset, diarrhoea, or other digestive issues after consuming cranberry products, you may be sensitive to the fruit's natural acids. Starting with smaller amounts and gradually increasing your intake can help determine your tolerance level. Pregnant and breastfeeding women can safely consume food amounts of cranberry but should avoid high-dose supplements unless prescribed of cranberry rather than concentrated supplements unless specifically recommended by their healthcare provider. Summary: Quick Recap of 11 Key Things You Need to Know About the Health Benefits of Cranberry UTI Prevention: Cranberry's proanthocyanidins prevent harmful bacteria from adhering to urinary tract walls Heart Health Support: Regular consumption helps improve cholesterol levels and supports cardiovascular function Immune System Boost: High vitamin C content strengthens your body's natural defence mechanisms Antioxidant Powerhouse: Cranberry provides exceptional protection against cellular damage from free radicals Digestive Health: Fibre content promotes beneficial gut bacteria growth and regular bowel movements Cancer Prevention Potential: Laboratory studies suggest possible protective effects against certain cancer types Oral Health Benefits: Natural antibacterial properties may help prevent plaque and gum disease Blood Sugar Regulation: Compounds in cranberry help slow sugar absorption and improve insulin sensitivity Brain Protection: Antioxidants may support cognitive health and protect against mental decline Blood Pressure Support: Potassium and other compounds contribute to healthy cardiovascular function Liver Health: Traditional and modern research supports cranberry's potential protective effects on liver function At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of comprehensive health monitoring to support your wellness journey. Whether you're incorporating cranberry into your diet for UTI prevention or overall health enhancement, our extensive portfolio of more than 4,000 tests can help track your progress and identify areas for improvement. Our convenient home sample collection service—available across 10,000+ touchpoints throughout India—makes it easy to monitor key health markers like immune function, cardiovascular health, and nutritional status that cranberry consumption can positively influence. FAQs Can cranberry benefits really prevent urinary tract infections? Yes, cranberry benefits for UTI prevention are well-established through numerous clinical studies. The proanthocyanidins in cranberry prevent E. coli bacteria from adhering to the walls of the urinary tract, significantly reducing infection risk. Research shows that regular consumption of cranberry juice or supplements can Meta-analyses show cranberry products can reduce UTI recurrence by approximately 26–35% in women at risk. However, cranberry works best as a preventive measure rather than a treatment for active infections, which require proper medical attention and antibiotics. How many cranberries or how much cranberry juice should you drink daily? For general UTI prevention, 240 ml of unsweetened cranberry juice or 500 mg of standardized cranberry extract (36 mg PACs) daily has shown benefit in studies. When choosing cranberry dry fruit, limit portions to 1-2 tablespoons due to concentrated sugars. Always choose unsweetened varieties when possible, as added sugars can counteract many of the health benefits of cranberries. Are there side effects or risks of taking cranberry every day? Daily cranberry consumption is generally safe for most people, but some individuals may experience mild digestive upset. People taking blood thinners should monitor their medication effects closely, as cranberry may enhance anticoagulant properties. Additionally, those prone to kidney stones should limit intake due to oxalate content. Is cranberry juice as good as fresh cranberries for benefits? Unsweetened cranberry juice provides many of the same antioxidants and proanthocyanidins found in fresh cranberries, but it doesn’t offer the fibre you get from whole fruit. Many commercial juices contain added sugar, which reduces their overall health value, so it’s important to read labels. For UTI prevention, both fresh cranberries and pure juice can help, but whole fruit offers extra digestive and blood-sugar support that processed juice can’t provide. Can people with diabetes enjoy cranberries? People with diabetes can enjoy cranberries by choosing low-sugar options. Fresh cranberries are low in sugar and high in fibre, making them helpful for blood-sugar control. Unsweetened cranberry juice is fine in moderation, but sweetened juices and dried cranberries should be limited due to higher sugar content. What is the best form of cranberry for health benefits – juice, dried, or capsule? The best form depends on your specific health goals and preferences. Fresh cranberry fruit provides the most complete nutritional profile with maximum fibre and antioxidants. Unsweetened cranberry juice offers convenience while retaining most beneficial compounds. Dried cranberries retain beneficial antioxidants but often contain added sugars; choose unsweetened varieties or limit to 1–2 tbsp. References • https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9160193/ • https://www.nutritionvalue.org/Cranberry_juice%2C_unsweetened_nutritional_value.html • https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8911768/
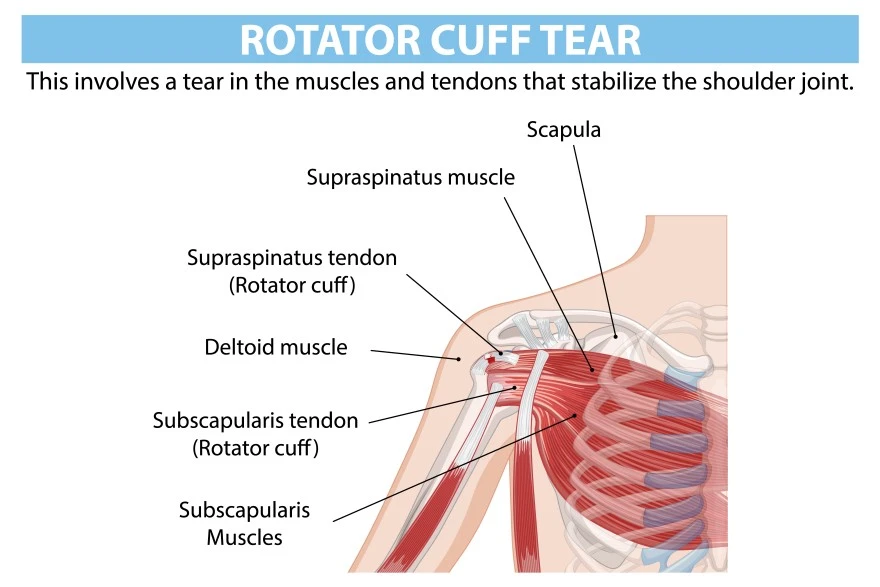
Rotator Cuff Muscles: Anatomy, Function & Common Injuries
What Is the Rotator Cuff and Why Does it Matter? The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their tendons that encircle the glenohumeral (shoulder) joint, forming a dynamic cuff that stabilises and moves the shoulder. These muscles play a vital role in stabilising the ball-and-socket structure of your shoulder while allowing an extensive range of arm movements. Without a properly functioning rotator cuff, your shoulder would lack the stability needed for lifting, rotating, and reaching overhead activities. Recent imaging studies indicate that asymptomatic rotator cuff tears are common in middle-aged and older adults, including in the Indian population, particularly those over 40 years of age. The rotator cuff matters because it's essential for maintaining shoulder strength and preventing the humeral head from dislocating during movement. Anatomy of the Rotator Cuff Muscles (SITS) The four rotator cuff muscles are easily remembered using the acronym "SITS": Supraspinatus: Originates from the supraspinous fossa of the scapula and initiates arm abduction (first 15 degrees) before the deltoid takes over (lifting your arm away from your body). It's the most commonly injured rotator cuff muscle due to its position under the bony arch. Infraspinatus: Positioned at the back of your shoulder blade, this muscle is responsible for external rotation of your arm, such as when you reach out to shake hands or wash your hair. Teres Minor: This smaller muscle also assists with external rotation and provides additional stability to the back of your shoulder joint during movement. Subscapularis: The largest and strongest of the rotator cuff muscles, located at the front of your shoulder blade. It handles internal rotation movements, like tucking in your shirt or reaching across your body. How the Rotator Cuff Tendons Attach and Stabilise the Shoulder Joint The rotator cuff tendons insert onto the greater and lesser tubercles of the humerus and fuse with the joint capsule, forming a continuous cuff that stabilises the humeral head, forming a musculotendinous collar around your shoulder. This arrangement creates a "cuff" that envelops the humeral head and compresses it into the shallow socket, preventing dislocation during dynamic movements. The tendons cover the front, top, and back aspects of your shoulder joint, working together to maintain stability whilst allowing remarkable mobility. Blood Supply, Innervation and Biomechanics of the Rotator Cuff Each rotator cuff muscle receives its nerve supply from specific branches of the brachial plexus. The suprascapular nerve controls the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles, whilst the axillary nerve innervates the teres minor, and the subscapular nerves control the subscapularis. Blood supply is derived mainly from the suprascapular, subscapular, and circumflex humeral arteries. Biomechanically, the rotator cuff functions synergistically with the deltoid and scapular stabilisers to maintain centralisation of the humeral head during motion while preventing abnormal joint translation. Primary Functions of the Rotator Cuff Your rotator cuff muscles serve three primary functions that are essential for normal shoulder operation. First, they enable rotation of your arm both internally and externally, allowing you to perform activities like throwing a ball or combing your hair. Second, they assist with elevation by initiating abduction and working with the deltoid muscle to lift your arm. Third, and perhaps most importantly, they provide dynamic stability to your shoulder joint by maintaining proper positioning of the humeral head within the socket throughout all movements. Common Movements Involving the Rotator Cuff Abduction: Lifting your arm out to the side, such as reaching for items on high shelves Internal rotation: Moving your arm toward your body, like fastening a seatbelt or reaching behind your back External rotation: Rotating your arm outward, as when preparing to throw or reaching to wash the opposite shoulder Overhead activities: Painting ceilings, serving in tennis, or placing items in overhead compartments Carrying and lifting: Supporting loads whilst maintaining shoulder stability What Happens When the Rotator Cuff Fails When your rotator cuff becomes weak, torn, or dysfunctional, several problems can develop. The humeral head may move abnormally within the socket, leading to instability and increasing your risk of subluxation or dislocation. This altered movement pattern can lead to subacromial impingement, where the supraspinatus tendon or subacromial bursa become compressed beneath the acromion of your shoulder, resulting in pain and inflammation. Over time, these altered mechanics can lead to joint degeneration, reduced shoulder function, and compensatory problems in your neck and opposite shoulder. Chronic dysfunction may lead to subacromial bursitis or secondary adhesive capsulitis (frozen shoulder). Who Is at Risk for Rotator Cuff Problems? Several factors increase your risk of developing rotator cuff injuries: Age-related factors: Adults over 40 years experience natural tendon degeneration and reduced blood supply to rotator cuff tissues Occupational risks: Manual labourers, painters, carpenters, and others who perform repetitive overhead work Athletic activities: Overhead sports like tennis, swimming, baseball, and volleyball place significant stress on rotator cuff muscles Anatomical predispositions: Individuals with narrow shoulder arches or specific bone shapes may be more prone to impingement Types of Rotator Cuff Injuries Rotator cuff tendinitis (acute tendinopathy): Inflammation and microtrauma of tendon fibres, typically due to overuse or repetitive overhead activity Tendinosis: Chronic degeneration of tendon fibres without significant inflammation, typically developing over time Partial rotator cuff tears: Incomplete splits in the tendon tissue that may progress if left untreated Full-thickness rotator cuff tear: Complete tear from the articular to the bursal surface, leading to marked weakness and limited range of motion Symptoms and Signs of a Rotator Cuff Injury Recognising rotator cuff injury symptoms early can prevent progression to more severe problems: Shoulder pain that worsens with overhead activities or at night, often disturbing sleep Weakness when lifting or rotating your arm, particularly noticeable during daily activities Limited range of motion in your shoulder joint, making it difficult to reach behind your back Crackling or popping sensations during shoulder movement Swelling or tenderness around the front and side of your shoulder Pain radiating down your arm, sometimes extending to your elbow How Rotator Cuff Tears are Diagnosed Diagnosing rotator cuff injuries typically begins with a thorough clinical examination, including your medical history and physical tests that assess range of motion, strength, and specific rotator cuff function. Your healthcare provider may perform special tests like the rotator cuff injury test to evaluate individual muscle function. Imaging studies help confirm the diagnosis and assess injury severity. A musculoskeletal ultrasound for the shoulder can visualise tendon tears and assess dynamic movement patterns. Shoulder X-rays can help identify acromial spurs, calcific deposits, or degenerative joint changes contributing to impingement that might contribute to your symptoms. Conservative Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Injuries Rest and activity modification to allow healing while avoiding aggravating movements Physical therapy focusing on strengthening weak rotator cuff muscles and improving flexibility Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to manage pain and inflammation during the acute phase Corticosteroid injections into the subacromial space may be used short-term for pain control when conservative therapy fails Ice and heat application to manage pain and promote healing Supportive devices like slings during acute pain episodes to protect the healing tissue When is Surgery Needed for a Rotator Cuff Tear? Surgical repair is indicated for full-thickness or large partial-thickness tears causing functional loss or persistent pain unresponsive to ≥3–6 months of conservative care. Options include arthroscopic or open repair, while tendon transfers are reserved for chronic, irreparable tears. The choice depends on tear severity, age and functional demands. Rehabilitation and Recovery: Post-Treatment Exercises and Return to Activity Passive range-of-motion (ROM) exercises are initiated early post-surgery or injury to prevent stiffness while protecting the repair Active-assisted movements as pain decreases and healing progresses Progressive strengthening of rotator cuff muscles and surrounding stabilisers Gradual return to overhead activities and sports-specific movements Functional training tailored to your work or recreational demands Regular monitoring to ensure proper healing and prevent re-injury Prevention Strategies for Maintaining a Healthy Rotator Cuff Regular rotator cuff exercises to maintain strength and flexibility in all four muscles Proper warm-up before sports or demanding physical activities Ergonomic modifications at work to reduce repetitive overhead stress Gradual progression when increasing activity levels or starting new exercises Early intervention for shoulder pain or dysfunction before problems worsen Rotator Cuff Injuries in Specific Populations Different populations face unique challenges with rotator cuff health. Athletes performing overhead motions place high demand on the cuff and often need sport-specific rehabilitation. Older adults may recover more slowly due to degenerative changes. Manual workers benefit from ergonomic support and conditioning programmes. Localised Advice: Adapting Rotator Cuff Care to Your Region Effective rotator cuff care should consider regional factors that influence shoulder health. Workplace ergonomics programmes can help reduce injury rates in industries with high shoulder demands. Sports medicine approaches should account for popular local activities and training methods. Cultural factors, including traditional activities involving heavy lifting or overhead work, may require specific educational strategies for injury prevention and early intervention. Common Myths and Misconceptions about the Rotator Cuff "Only athletes get rotator cuff injuries" Fact: Anyone can develop these problems, especially with age "Rest alone will heal all problems" Fact: Many conditions require active treatment and rehabilitation "Surgery is always necessary for tears" Fact: Many tears respond well to conservative treatment "Pain always indicates serious damage" Fact: Early symptoms may respond well to simple interventions When to Seek Professional Help For Your Shoulder/Cuff Pain Persistent shoulder pain lasting more than a few weeks despite rest Sudden loss of shoulder strength or inability to lift your arm Night pain that regularly disrupts your sleep Progressive worsening of symptoms over time Inability to perform normal daily activities due to shoulder problems Signs of serious injury following trauma or sudden onset of severe pain Prognosis: What to Expect with Rotator Cuff Injuries The outlook for rotator cuff injuries varies depending on several factors, including your age, the extent of injury, and how quickly treatment begins. Most people with rotator cuff tendinitis, rotator cuff tendinopathy or impingement syndrome, or partial tears respond well to conservative treatment, with significant improvement within 3-6 months. Full-thickness tears may require longer recovery periods, particularly if surgery is needed. Summary: Key Takeaways About the Rotator Cuff Muscles The rotator cuff is vital for stability, strength and coordinated movement. Understanding its anatomy and recognising symptoms early helps prevent long-term problems. Whether dealing with rotator cuff tendinitis, degeneration or a tear, timely care and rehabilitation support lasting shoulder health. At Metropolis Healthcare, we support your journey toward optimal shoulder health with comprehensive diagnostic services. Our network of over 220 laboratories and 4,600+ service centres ensures you have access to precise shoulder imaging and blood tests that help identify inflammatory markers. FAQs What is the rotator cuff, and what does it do? The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and tendons that stabilise the shoulder joint and allow lifting, rotation, and overhead movements. How long does it take to recover from a rotator cuff tear? Minor tears may heal in 6–12 weeks, partial tears in 3–6 months, and full-thickness tears in 6–12 months, especially if surgery and rehab are required. What exercises strengthen the rotator cuff? Key exercises include band-based external and internal rotations, scapular strengthening, wall slides, pendulum exercises, and light resistance training. How can I prevent rotator cuff injuries in manual labour or overhead sports? Strengthen the cuff regularly, warm up properly, use correct technique, avoid repetitive overhead strain, and address shoulder pain early. When should I see a doctor for shoulder pain related to the rotator cuff? Consult a doctor if pain lasts weeks, disturbs sleep, limits movement, or if you experience sudden weakness or difficulty lifting your arm. References • https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40511354/ • https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rotator-cuff-injury/symptoms-causes/syc-20350225 • https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/rotator-cuff-tears/ • https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/shoulder-pain/