Preventive Healthcare
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
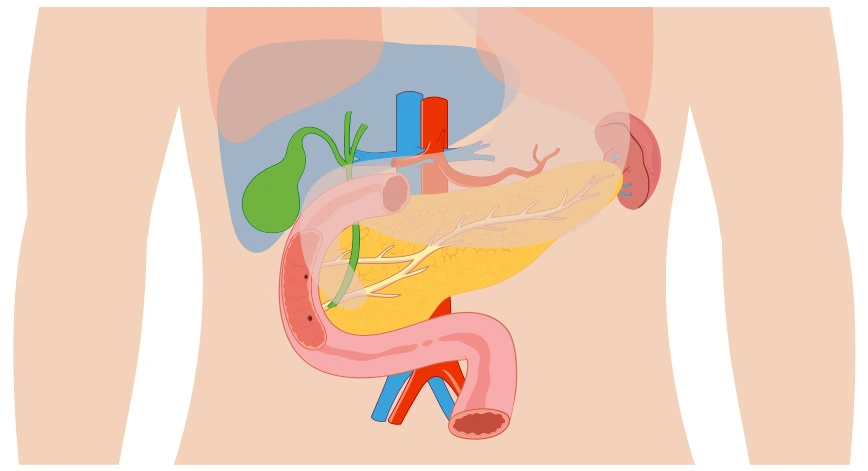
Table of Contents
What Causes Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome causes are primarily linked to the development of one or more tumours known as gastrinomas. These tumours typically form in the ‘gastrinoma triangle,’ which includes the duodenum, pancreas, and peri-pancreatic lymph nodes. When gastrinomas develop, they secrete excessive amounts of gastrin, a hormone that normally helps regulate stomach acid production. This overproduction leads to markedly elevated gastric acid secretion (hyperchlorhydria), causing severe digestive problems.
In most cases, the exact reason why gastrinomas develop remains unknown. However, studies summarised by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) show that approximately 20-25% of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome cases are associated with a genetic condition called multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1). This inherited disorder predisposes individuals to develop multiple hormone-producing tumours throughout their endocrine system.
Symptoms of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Recognising Zollinger-Ellison syndrome symptoms often mimic those of common digestive disorders, which can delay proper diagnosis. Here are the key symptoms to watch for:
- Persistent diarrhoea: This may be the only symptom in some patients
- Burning or aching upper abdominal pain: May resemble but often exceeds typical peptic ulcer pain
- Severe heartburn and acid reflux: Resistant to over-the-counter medications
- Nausea and vomiting: May occur frequently, especially after meals
- Unintentional weight loss: Due to poor nutrient absorption and appetite loss
- Loss of appetite: Often accompanied by feeling full quickly
- Gastrointestinal bleeding: May present as vomiting blood or black, tarry stools
- Recurrent or severe intestinal ulcers: Often in unusual locations
- Excessive burping: More frequent than normal
- Chest pain or difficulty swallowing (dysphagia): When acid-induced strictures develop
Imaging and Blood Tests to Diagnose Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Accurate diagnosis of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome requires a combination of blood tests and advanced imaging techniques. Your healthcare provider will typically recommend the following diagnostic procedures:
- Gastrin blood test: Measures hormone levels; elevated fasting gastrin is a key indicator
- Chromogranin A (CgA) test: A nonspecific marker elevated in many neuroendocrine tumours, including gastrinomas, but influenced by PPIs
- Biopsy with immunohistochemistry (IHC): Performed when accessible lesions are found, confirming neuroendocrine tumour origin and type through immunohistochemistry
How is Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Diagnosed?
The diagnostic process for Zollinger-Ellison syndrome follows a systematic approach to ensure accurate identification:
- Clinical assessment and history taking: Your doctor reviews symptoms, medical history, and family history of endocrine disorders or MEN They'll ask detailed questions about your digestive symptoms and their duration.
- Blood testing for gastrin levels - Fasting serum gastrin measurement is performed, Fasting serum gastrin is first measured, but levels >1,000 pg/mL are suggestive only when accompanied by low gastric pH (<2).. The Chromogranin A (CGA) test provides additional confirmation of neuroendocrine tumour activity.
- Secretin stimulation testing: This specialised test differentiates Zollinger-Ellison syndrome from other conditions causing elevated gastrin. A rise in gastrin >120 pg/mL after secretin stimulation supports the diagnosis.
- Advanced imaging studies: Multiple imaging modalities are employed to locate tumours. An abdominal CT scan provides initial assessment, while an MRI scan offers enhanced detail for small tumours. A rise in gastrin >120 pg/mL after secretin stimulation supports the diagnosis help identify tumours missed by conventional imaging.
- Tissue diagnosis through biopsy: IHC panels with reporting on lymph node biopsies provide definitive diagnosis and tumour characterisation, helping determine if tumours are benign or malignant.
- Genetic evaluation: When MEN1 is suspected, genetic testing helps identify family members at risk and guides long-term management strategies.
Treatment Options for Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome treatment focuses on two primary goals: controlling excessive stomach acid production and managing the gastrin-producing tumours.
The cornerstone of medical therapy involves proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) such as omeprazole or lansoprazole. These medications effectively reduce stomach acid production, allowing ulcers to heal and relieving symptoms. Patients typically require higher doses than those used for ordinary peptic ulcers, and many need lifelong therapy to maintain symptom control.
Surgical intervention represents another crucial aspect of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome treatment. When gastrinomas are solitary and haven't spread to other organs, surgical removal Surgical cure is possible mainly in sporadic, solitary gastrinomas but less likely in MEN1-associated cases. However, surgery becomes more complex in patients with MEN1, who often have multiple small tumours scattered throughout the pancreas and duodenum.
Can Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Be Cured?
The possibility of curing Zollinger-Ellison syndrome depends largely on early detection and the specific characteristics of the gastrinomas. In carefully selected patients where tumours are localised and haven't metastasised, complete surgical removal can achieve cure. Studies indicate that approximately 20-30% of patients with sporadic gastrinomas can be cured through surgery when tumours are detected early.
However, the reality is that many patients require ongoing management rather than cure. This is particularly true for those with MEN1-associated Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, where multiple tumours make complete surgical removal challenging.
Is Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Hereditary?
While most cases of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome occur sporadically without a hereditary component, approximately 20-25% are linked to the genetic condition MEN1. This inherited syndrome follows an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning children of affected parents have a 50% chance of inheriting the condition. Understanding the hereditary nature is crucial for family planning and screening decisions.
Living with Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome: Long-Term Outlook
Managing Zollinger-Ellison syndrome requires ongoing commitment, but with proper care, most patients maintain good quality of life. Here's what to expect:
- Lifelong monitoring and treatment: Regular check-ups, blood tests, and imaging studies ensure optimal management
- Medication adherence: Most patients require continuous PPI therapy to control acid production
- Regular follow-up appointments: Monitoring for tumour recurrence or metastasis through CT scan or MRI scan
- Symptom management: With proper treatment, most Zollinger-Ellison syndrome symptoms can be effectively controlled
- Potential complications: Watch for signs of peptic ulcers, intestinal bleeding, or tumour spread
- Dietary modifications: Some patients benefit from avoiding trigger foods that worsen symptoms
- Emotional support: Living with a chronic condition requires psychological adjustment and support
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome vs. Peptic Ulcers
While both conditions involve stomach ulcers and similar symptoms, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome causes are fundamentally different. This syndrome results from gastrin-secreting tumours that create extreme acid levels, whereas typical peptic ulcers usually stem from H. pylori infection or NSAID use.
The severity and pattern of symptoms also differ significantly. Zollinger-Ellison syndrome symptoms include more severe, recurrent ulcers that often appear in unusual locations like the jejunum. Patients frequently experience persistent diarrhoea alongside ulcer symptoms, which is uncommon in standard peptic ulcer disease.
Additionally, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome treatment requires much higher doses of acid-suppressing medications and may not respond to standard ulcer therapies.
At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand that navigating complex conditions like Zollinger-Ellison syndrome requires reliable diagnostic support. With our comprehensive portfolio of over 4,000 tests, we provide the precise diagnostics needed to guide your treatment journey. Our extensive network of 220+ laboratories and 10,000+ touchpoints across India ensures you can access these critical tests conveniently through our at-home sample collection service.
FAQs
How is Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Treated?
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome treatment involves a multi-faceted approach tailored to each patient's specific situation. The primary medical treatment consists of high-dose proton pump inhibitors to control acid production and heal ulcers. Surgical removal of gastrinomas may be recommended when tumours are localised and accessible. Regular monitoring through blood tests and imaging ensures treatment effectiveness and early detection of any complications.
What Are the Symptoms of Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome symptoms can vary but typically include persistent abdominal pain, severe diarrhoea, heartburn, nausea, and vomiting. Many patients experience recurrent peptic ulcers despite standard treatment. Other symptoms include unintentional weight loss, gastrointestinal bleeding presenting as dark stools or vomiting blood, and excessive burping.
Can Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome Lead to Cancer?
Yes, A significant proportion of gastrinomas are malignant, with the liver and lymph nodes being the most common metastatic sites to the liver and lymph nodes. This is why early diagnosis through comprehensive testing, including CT scan and MRI scan imaging, is crucial.
What Is the Long-Term Outlook for People with Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome?
The long-term outlook for Zollinger-Ellison syndrome has improved significantly with modern treatments. Most patients who receive appropriate acid suppression therapy and tumour management can expect to live normal lifespans. Those with localised, benign tumours that are surgically removed may achieve complete cure. Patients with MEN1-associated or metastatic disease require closer monitoring but can still maintain good quality of life with proper treatment.




























