Preventive Healthcare
Mood Changes in Menopause: Why They Happen & Solutions
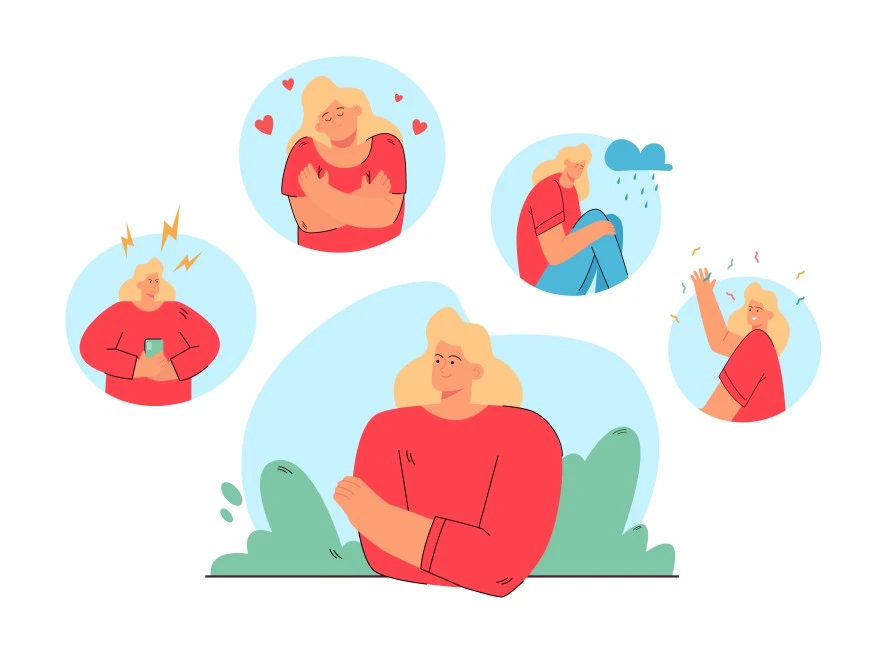
Table of Contents
Understanding Mood Changes During Menopause
Mood changes during menopause arise from complex interactions between hormonal shifts, physical symptoms, and life stressors. During perimenopause and menopause, oestrogen and progesterone levels fluctuate dramatically before eventually declining, affecting neurotransmitters like serotonin and norepinephrine that regulate mood.
Sleep disruption caused by night sweats and hot flashes further reduces emotional resilience and stress tolerance. Many women also face midlife pressures, including caregiving responsibilities, career demands, and relationship changes, which can add to stress during this vulnerable period.
The Science Behind Hormonal Fluctuations
Oestrogen plays a crucial role in maintaining a stable mood by regulating serotonin, the neurotransmitter responsible for feelings of well-being. As oestrogen levels rise and fall unpredictably during perimenopause, these brain systems become destabilised, contributing to mood swings and tearfulness.
Progesterone — often called "calming hormone" — also decreases during menopause, further affects emotional stability. Research indicates that rapid, dynamic hormonal changes, rather than consistently low levels, are most strongly linked to mood symptoms during this transition. Your genetic makeup, mental health history, and current life circumstances all influence how severely these hormonal changes affect your mood.
How Perimenopause Affects Your Mood
Perimenopause, the transitional years before periods stop completely, often presents the most intense mood symptoms. During this phase, hormones fluctuate wildly rather than declining steadily, making emotional regulation especially challenging.
According to a study published by the NIH, women are two to four times more likely to experience major depression during perimenopause and the early postmenopausal period. Physical symptoms such as severe hot flashes and disrupted sleep further worsen mood stability. Women with a history of premenstrual mood issues, postpartum depression, or mental health disorders (such as Parkinson's disease) face a higher risk during this transition.
Common Emotional Symptoms of Menopause
- Sudden mood swings shifting from calm to sad, angry, or tearful.
- Increased irritability and feeling easily frustrated by minor issues.
- Persistent low mood or sadness that may progress to clinical depression.
- Heightened anxiety or nervousness.
- Loss of confidence, self-esteem, and increased negative self-talk.
- Feeling overwhelmed by usually manageable daily demands.
- Chronic fatigue and low energy affect emotional resilience.
- Frequent crying spells or unusual emotional sensitivity.
- Difficulty concentrating, forgetfulness, or "brain fog".
- Sleep disturbances from night sweats leading to daytime irritability.
Mood Swings and Irritability
- Fluctuations in oestrogen and progesterone alter brain chemistry, making emotional responses unpredictable.
- Sleep disruption from hot flashes increases fatigue, lowering stress tolerance.
- These emotional shifts can resemble severe PMS but occur unpredictably.
- External stressors intensify irritability when coping resources are already stretched.
- Most women find that mood swings improve as hormone levels stabilise post-menopause.
Anxiety and Depression During Menopause
Depression becomes significantly more common during the menopause transition, with studies showing increased risk during perimenopause and early menopause. Symptoms include persistent sadness, loss of interest in activities, sleep changes, fatigue, and difficulty concentrating.
Anxiety may appear for the first time or worsen during menopause, manifesting as persistent worry, restlessness, or physical symptoms like sweating and nausea. Risk factors include previous depression or anxiety, severe premenstrual symptoms, intense hot flashes, high stress levels, or limited social support.
How to Manage Mood Changes During Menopause
- Consult healthcare professionals to discuss symptoms, rule out other medical causes, and develop personalised treatment plans.
- Prioritise sleep hygiene with regular bedtime routines, cool bedrooms, and hot flash management strategies.
- Engage in regular physical activity, including aerobic exercise and strength training, to boost mood naturally.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques like mindfulness, deep breathing, yoga, or meditation.
- Strengthen social connections through trusted friends, family, or menopause support groups.
- Limit alcohol, nicotine, and excessive caffeine, which can worsen sleep and mood instability.
- Consider professional counselling, such as cognitive behavioural therapy, for depression and anxiety management.
- Explore medical treatments, including antidepressants or hormone therapy, when symptoms are severe.
Natural Remedies for Mood Swings
- Regular exercise several times weekly to boost mood-regulating endorphins.
- Consistent sleep schedule with a cool, dark bedroom environment.
- Mind-body practices like meditation, yoga, or tai chi for emotional regulation.
- Balanced nutrition emphasising whole foods, omega-3 fats, and limiting processed sugars.
- Reduced alcohol and caffeine intake to prevent mood and sleep disruption.
- Active social engagement and support groups for validation and coping strategies.
Medical Treatments for Emotional Symptoms
- Antidepressant medications have been proven effective for menopause-related mood symptoms.
- Hormone replacement therapy for women with severe symptoms and a suitable medical history.
- Anti-anxiety medications for short-term relief of severe anxiety symptoms.
- Sleep medications may be used when sleep disruption significantly impacts mood.
- Complementary therapies like acupuncture or herbal supplements under medical guidance.
The Role of Support Systems During Menopause
Strong support networks significantly improve outcomes for women experiencing mood changes during menopause. Family members, friends, and doctors who understand this transition provide essential emotional validation and practical assistance during challenging times.
How Therapy Can Help with Menopause Mood Swings
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) has proven particularly effective for managing mood changes during menopause. This approach helps women identify negative thought patterns, develop coping strategies, and adapt to the life changes accompanying this transition. Therapy provides tools for managing stress and improving emotional regulation.
Can Hormone Replacement Therapy Help During Menopause?
Hormone replacement therapy (HRT) can effectively treat mood symptoms in women experiencing perimenopause or early menopause. By stabilising hormone levels, HRT often reduces mood swings, anxiety, and depression. However, treatment decisions require careful consideration of individual health factors and discussion with doctors.
Conclusion
Mood changes during menopause are real, common, and treatable experiences affecting millions of women worldwide. Understanding that hormonal fluctuations, sleep disruption, and life stressors contribute to these emotional symptoms helps normalize your experience and guide effective treatment approaches.
Whether through lifestyle modifications, natural remedies, professional counselling, or medical interventions, numerous solutions can help you regain emotional stability and well-being.
At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of comprehensive health monitoring during menopause. Our extensive portfolio of over 4,000 tests includes hormone panels and health check-ups specifically designed to support women through this transition. With our convenient home sample collection service spanning 10,000+ collection points across India, you can access precise diagnostics from the comfort of your home.
FAQs
What causes mood swings during menopause?
Fluctuating oestrogen and progesterone levels disrupt brain chemicals like serotonin, whilst physical symptoms like hot flashes and sleep disruption compound emotional instability and stress responses.
Can menopause cause depression?
Yes, women are two to four times more likely to experience major depression during perimenopause and early menopause compared to premenopausal years due to hormonal changes.
How long do mood swings last during menopause?
Mood swings typically peak during perimenopause and early menopause, often improving as hormone levels stabilise in later postmenopausal years, usually within several years.
What are some natural remedies for menopause mood swings?
- Regular aerobic exercise and strength training
- Stress-reduction techniques like meditation and yoga
- Consistent sleep hygiene and a cool bedroom environment
- Balanced nutrition with omega-3 fats and limited processed foods
- Strong social support networks and connections
Can I take medication for menopause mood changes?
Yes, antidepressants, hormone replacement therapy, and anti-anxiety medications can effectively treat mood symptoms when prescribed and monitored by qualified healthcare professionals.
References
1. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK507826/
2. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3584692/
3. https://mentalhealth-uk.org/menopause-and-mental-health/
4. https://womenshealth.gov/menopause/menopause-symptoms-and-relief
5. https://www.health.harvard.edu/womens-health/menopause-and-mental-health




























