Preventive Healthcare
Fallopian Tube: Location, Function & Health Conditions
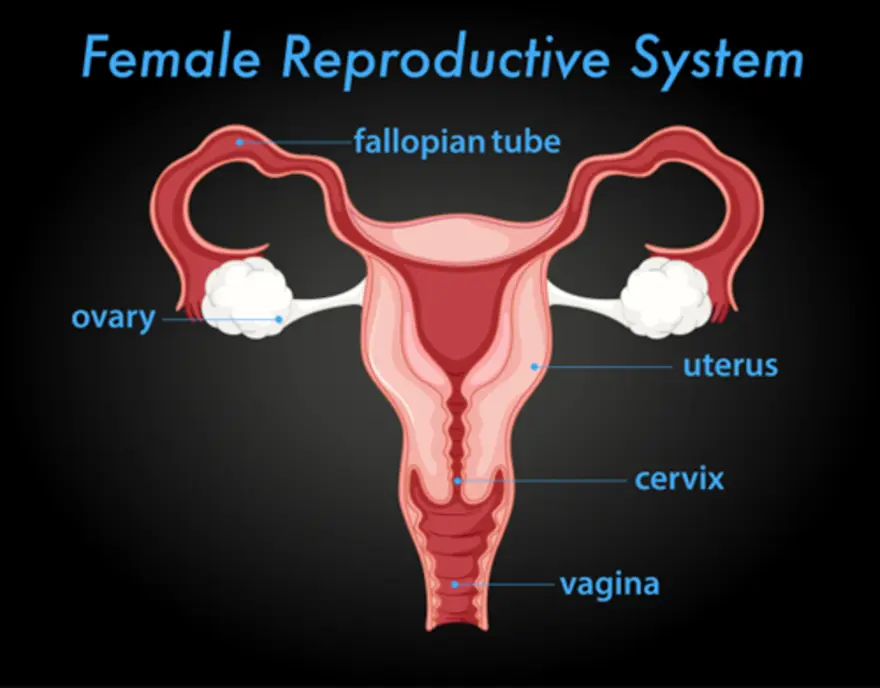
Table of Contents
- What are Fallopian Tubes?
- Location of Fallopian Tubes
- Structure of the Fallopian Tubes
- Functions of the Fallopian Tubes
- Common Fallopian Tube Health Conditions
- How to Maintain Healthy Fallopian Tubes
- Diagnosing Fallopian Tube Conditions
- Tests to Diagnose Fallopian Tube Blockage or Damage
- Treatment for Fallopian Tube Issues
- Conclusion
- FAQs
- References
What are Fallopian Tubes?
The fallopian tubes are a pair of slender, muscular ducts that form an essential component of the female reproductive system. Each fallopian tube measures approximately 10–14 centimetres in length and connects your ovaries to the uterus. These remarkable structures serve as pathways for eggs to travel from the ovaries towards the uterus, making them fundamental for natural conception.
When examining the functionality of the fallopian tubes, it becomes clear that these tubes are far more than simple conduits. They create the perfect environment for fertilisation to occur, typically within the ampulla region. The fallopian tube also provides nourishment to developing embryos during their journey to the uterus.
Location of Fallopian Tubes
Your fallopian tubes are strategically positioned within the female pelvic cavity, extending laterally from the upper corners of the uterus towards each ovary. They lie within the upper border of the broad ligament, running in a superolateral direction above and in front of the ovaries. This positioning allows the fallopian tube to efficiently capture eggs released during ovulation.
The tubes open medially into the uterine cavity and laterally into the peritoneal space near the ovaries. This anatomical arrangement ensures that eggs can travel smoothly from the ovaries through the fallopian tubes to reach the uterus. The precise location of each fallopian tube within the female reproductive system makes them vulnerable to infections ascending from the lower genital tract.
Structure of the Fallopian Tubes
Understanding the anatomy of the fallopian tube reveals four distinct fallopian tube parts, each with specific functions:
- Intramural (Interstitial) Part: Located within the uterine wall, this narrowest section connects the fallopian tube to the uterine cavity
- Isthmus: A narrow, muscular segment next to the uterus, measuring about 2-3 centimetres in length
- Ampulla: The widest and longest section where fertilisation typically occurs, comprising about two-thirds of the the fallopian tube’s length
- Infundibulum: The funnel-shaped end featuring finger-like projections called fimbriae that capture eggs from the ovary
The fallopian tube's anatomy includes specialised ciliated epithelial cells lining the interior. These microscopic hairs create gentle currents that help transport eggs and early embryos towards the uterus. The muscular walls of the fallopian tube contract rhythmically, further assisting in egg transport.
Functions of the Fallopian Tubes
The fallopian tube's function encompasses several critical roles in reproduction:
- Egg Capture: Fimbriae at the end of each fallopian tube sweep over the ovarian surface to capture released eggs
- Egg Transport: Coordinated muscular contractions and ciliary action move eggs towards the uterus
- Fertilisation Site: The ampulla region provides the optimal environment for sperm and egg to meet
- Early Embryo Nourishment: Secretions from the fallopian tube provide nutrients for developing embryos
- Sperm Pathway: The fallopian tube serves as a conduit for sperm to reach the egg
Common Fallopian Tube Health Conditions
Several conditions can affect fallopian tube health and function:
- Fallopian tube blockages preventing egg transport
- Ectopic pregnancy occurring within the tube
- Pelvic inflammatory disease causing scarring and damage
- Hydrosalpinx involving fluid accumulation in blocked tubes
- Paratubal cysts developing near the fallopian tube
- Fallopian tube cancer (rare but serious)
- Endometriosis affecting tube function
Fallopian Tube Blockage
According to a study published in PubMed Central. that fallopian tube blockages represent one of the most common causes of female infertility, affecting approximately 30-40% of women with fertility challenges. These blockages prevent eggs from travelling through the fallopian tube to reach the uterus, making natural conception impossible. The blockage may be partial or complete, occurring at any point along the length of fallopian tube.
Most women with blocked fallopian tubes experience no symptoms unless the underlying cause produces additional effects. The silent nature of many blockages means they're often discovered only during fertility investigations when couples struggle to conceive.
Ectopic Pregnancy and Fallopian Tubes
An ectopic pregnancy occurs when a fertilised embryo implants outside the uterine cavity, with approximately 95% occurring within the fallopian tube. This represents a medical emergency because the fallopian tube cannot accommodate a growing pregnancy. As the embryo develops, it can cause the fallopian tube to rupture, leading to life-threatening internal bleeding.
Early signs of ectopic pregnancy include sharp abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and dizziness. Prompt treatment can often preserve the affected fallopian tube and your future fertility prospects.
Infections and Fallopian Tube Health
Pelvic inflammatory disease represents a serious threat to fallopian tube health, often resulting from untreated sexually transmitted infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea. These infections can ascend from the lower genital tract through the female reproductive system to reach the fallopian tubes, causing inflammation and scarring.
The resulting damage can lead to chronic pelvic pain, increased ectopic pregnancy risk, and infertility due to fallopian tube blockages. Statistics show that women with pelvic inflammatory disease have a 10-20% chance of developing tubal infertility after a single episode, with risks increasing significantly after multiple infections.
How to Maintain Healthy Fallopian Tubes
Protecting your fallopian tube health requires proactive measures:
- Practise safe sex to prevent sexually transmitted infections
- Seek prompt treatment for any pelvic infections or unusual symptoms
- Attend regular gynaecological check-ups for early detection of problems
- Manage chronic conditions like endometriosis under medical supervision
- Avoid unnecessary pelvic procedures that might cause scarring
Impact of Lifestyle Choices on Fallopian Tubes
Your lifestyle choices significantly influence fallopian tube health:
- Smoking cessation: Tobacco use impairs fallopian tube function and increases ectopic pregnancy risk
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces inflammation that can affect reproductive organs
- Stress reduction: Chronic stress may impact hormonal balance, affecting the female reproductive system
- Regular exercise: Moderate physical activity promotes healthy circulation to reproductive organs
- Nutritious diet: Adequate nutrition supports tissue health and immune function
Diagnosing Fallopian Tube Conditions
Healthcare providers use various approaches to assess fallopian tube health:
- Detailed medical history focusing on previous infections, surgeries, or fertility concerns
- Physical examination including pelvic assessment to detect abnormalities
- Laboratory tests to identify current infections or inflammatory markers
- Imaging studies to visualise the fallopian tube's structure and function
Tests to Diagnose Fallopian Tube Blockage or Damage
Several fallopian tube test options help evaluate tube patency and function:
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG): X-ray examination using contrast dye to visualise fallopian tube patency
- Sonohysterography: Ultrasound procedure with saline infusion to assess tube openness
- Laparoscopy: Minimally invasive surgery allowing direct visualisation of fallopian tubes and surrounding structures
- Blood tests: Screening for infections like chlamydia and gonorrhea that commonly cause tube damage
Treatment for Fallopian Tube Issues
Treatment approaches vary depending on the specific condition affecting your fallopian tube:
- Antibiotic therapy for active infections causing pelvic inflammatory disease
- Surgical repair procedures like salpingostomy or fimbrioplasty to restore function
- Tubal removal (salpingectomy) in cases of severe damage or recurrent ectopic pregnancy
- Assisted reproductive technologies like IVF when natural conception isn't possible
- Pain management for chronic symptoms associated with fallopian tube disorders
Conclusion
Understanding your fallopian tube anatomy, function, and potential health challenges empowers you to make informed decisions about your reproductive health. Regular check-ups, prompt treatment of infections, and awareness of symptoms can help maintain optimal fallopian tube function throughout your reproductive years.
At Metropolis Healthcare, we support your journey toward better reproductive health with comprehensive diagnostic services. Our extensive portfolio of over 4,000 tests includes specialised assessments for infections, hormonal imbalances, and other factors affecting your female reproductive system. Through our network of 10,000+ touchpoints across India, you can access convenient at-home sample collection services, ensuring comfort while receiving accurate, timely results.
FAQs
What are fallopian tubes?
Fallopian tubes are paired structures in the female reproductive system that transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus. Each fallopian tube consists of four distinct parts and plays crucial roles in fertilisation and early embryo development.
What causes blocked fallopian tubes?
Blocked fallopian tubes commonly result from pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis, previous pelvic surgeries, or sexually transmitted infections. These conditions can cause scarring and adhesions that obstruct the normal passage through the fallopian tube, preventing eggs from reaching the uterus.
Can you get pregnant with one fallopian tube?
Yes, pregnancy is possible with one healthy fallopian tube. Many women successfully conceive naturally using their remaining tube, provided it functions normally and ovulation occurs regularly. The key is ensuring the remaining fallopian tube can effectively capture eggs and transport them to the uterus.
How do I know if my fallopian tubes are blocked?
Blocked fallopian tubes rarely cause noticeable symptoms, making diagnosis challenging without specific testing. Most women discover blockages during fertility evaluations when they experience difficulty conceiving. A fallopian tube test like hysterosalpingography can definitively assess tube patency.
What happens if an ectopic pregnancy occurs in a fallopian tube?
An ectopic pregnancy in the fallopian tube creates a medical emergency requiring immediate treatment. As the pregnancy grows, it can rupture the tube, causing severe internal bleeding. Prompt medical intervention is essential to prevent life-threatening complications and preserve future fertility.
References
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9717713/
- https://teachmeanatomy.info/pelvis/female-reproductive-tract/fallopian-tubes/
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/body/23184-fallopian-tubes
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/female-infertility/symptoms-causes/syc-20354308
- https://www.webmd.com/infertility-and-reproduction/blocked-fallopian-tubes-test




























