Preventive Healthcare
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg) Test: Purpose, Procedure And Result
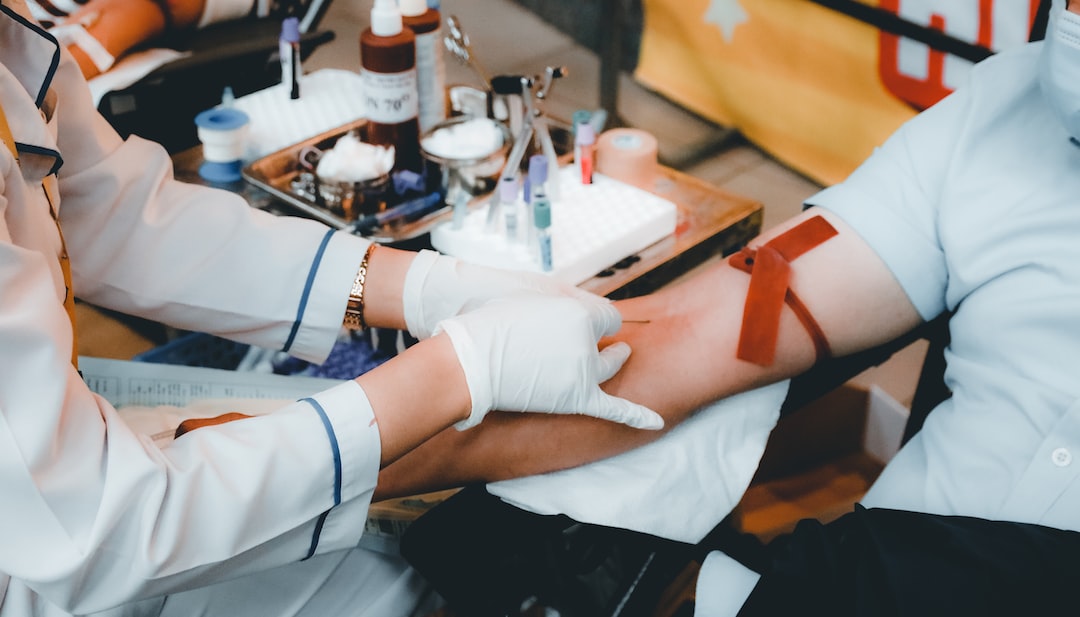
Table of Contents
What Is Hepatitis B?
Hepatitis B is a viral liver infection caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV), which can range from an acute, self-limited illness to a chronic infection that may become life-threatening. This condition affects your liver's ability to function properly and can lead to serious complications if left untreated. The infection can present as acute hepatitis B, which usually resolves within six months, or chronic hepatitis B, which persists beyond six months and requires ongoing medical follow-up.
Many people with hepatitis B infection may not experience symptoms initially, making the condition particularly dangerous. When symptoms do occur, they often include fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice. Without proper diagnosis and treatment, chronic hepatitis B can progress to severe liver damage, cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer over time.
What Is the HBsAg Test?
The HBsAg test, or the Hepatitis B Surface Antigen test, detects a specific protein found on the surface of the hepatitis B virus. This HBsAg blood test serves as the first-line screening method for identifying current hepatitis B infection in the bloodstream.
The HBsAg test is used for detecting the presence of surface antigens that indicate current infection with the hepatitis B virus. When the virus infects your liver cells, it produces these surface proteins, which then circulate in your blood. This test can identify these proteins even before symptoms develop, making it invaluable for early diagnosis.
Doctors commonly use the HBsAg test for routine screening, blood donor screening, prenatal testing, and evaluating patients with suspected liver disease.
Symptoms of Hepatitis B
• Persistent fatigue and weakness that doesn't improve with rest
• Loss of appetite and unexplained weight loss
• Nausea and vomiting, particularly in the morning
• Abdominal discomfort or pain, especially in the upper right quadrant beneath the ribs
• Dark-coloured urine and pale stools
• Joint pain and muscle aches
• Fever and general malaise
• Jaundice (yellowing of skin and eyes)
• Itchy skin or unexplained rashes
Causes and Risk Factors of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B infection occurs through exposure to infected blood or bodily fluids. Common transmission routes include unprotected sexual contact, sharing needles or personal items like razors, and mother-to-child transmission during childbirth. Healthcare workers face increased risk due to potential needlestick injuries, while individuals with multiple sexual partners or those living with infected family members also have elevated risk levels.
Certain populations face higher vulnerability, including people with compromised immune systems, those receiving dialysis treatment, and individuals travelling to regions with high hepatitis B prevalence.
How Is the HBsAg Test Performed?
- Your healthcare provider will clean the injection site, usually on the inside of your elbow, with an antiseptic solution.
- A tourniquet is placed around your upper arm to make the veins more visible and accessible for blood collection.
- A sterile needle is inserted into a vein, and blood is drawn into a collection tube or vial.
- The needle is removed, and pressure is applied to prevent bleeding while the sample is properly labelled.
- Your blood sample is sent to the laboratory, where technicians perform the HBsAg screen test using advanced testing methods.
The entire process takes just a few minutes, with minimal discomfort. You might experience slight bruising at the puncture site, but serious complications are extremely rare.
Interpreting the HBsAg Test Results
Understanding your HBsAg test results is crucial for making informed health decisions.
|
Result Category |
HBsAg Level |
Clinical Interpretation |
|
Non-Reactive |
< 0.90 IU/mL |
No hepatitis B surface antigen detected |
|
Borderline |
0.90 – 1.0 IU/mL |
Indeterminate result requiring retesting after 2–4 weeks for confirmation |
|
Reactive |
≥ 1.0 IU/mL |
Hepatitis B surface antigen present |
The HBsAg test normal range falls below 0.90 IU/mL, indicating no detectable surface antigens in your blood. A non-reactive result indicates no current hepatitis B infection, but vaccination is recommended if you are not already immune. Borderline results require repeat testing to clarify your status, while reactive results confirm hepatitis B surface antigen presence and warrant further testing to determine whether the infection is acute or chronic.
What Happens if Your HBsAg Test is Positive?
A positive HBsAg test indicates active hepatitis B infection, requiring comprehensive evaluation and monitoring. Your doctor will order additional tests to determine whether you have an acute or chronic infection and assess your liver function.
Immediate steps include informing close contacts about potential exposure, avoiding alcohol and hepatotoxic medications, and discussing treatment options. You'll need regular monitoring to prevent progression to cirrhosis, liver failure, or liver cancer through appropriate medical management.
Prevention of Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B vaccination provides the most effective prevention, offering over 95% protection when the full three-dose schedule is completed. The vaccine series consists of three injections over six months, providing long-lasting immunity against hepatitis B infection.
Additional preventive measures include practising safe sex, avoiding needle sharing, ensuring sterile medical equipment, and screening blood products. If you're pregnant, routine HBsAg testing helps prevent mother-to-child transmission through appropriate interventions.
Healthcare workers should follow standard precautions, whilst travellers to high-prevalence regions should consider vaccination before departure.
Follow-up Testing and Additional Tests
When your HBsAg screen test is positive, several additional tests help provide a complete picture of your condition:
• HBV DNA Qualitative Test (PCR Method): Detects the presence of hepatitis B virus DNA in blood and confirms active viral replication.
• HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) DNA Quantitative (Viral Load) by TaqMan, Serum or Plasma: Measures HBV viral load and assesses the severity of infection.
• Anti-HBeAg, Serum: Helps evaluate Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection status.
• HBeAg, Serum: Measures Hepatitis B e Antigen (HBeAg) in blood and helps diagnose active Hepatitis B infection.
• LFT (Liver Function Test) 1 - Maxi: Provides a comprehensive assessment of liver health and helps in diagnosing liver diseases (hepatitis, cirrhosis, liver failure).
• AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein) test: Used to monitor patients with chronic hepatitis B or cirrhosis for early signs of hepatocellular carcinoma (liver cancer).
Related Tests for Hepatitis B Diagnosis
These panels combine multiple markers to provide detailed information about your infection stage, immunity status, and treatment needs:
• HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) Acute Profile: Helps differentiate between acute and chronic HBV infection.
• HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) Chronic Profile: Diagnoses chronic HBV infection and assesses liver disease progression.
• HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) Combo Profile - 1: Detects multiple HBV markers for comprehensive hepatitis B evaluation.
• HBV (Hepatitis B Virus) Monitoring Profile: Monitors viral load and disease progression in HBV patients.
Conclusion
The HBsAg test serves as a critical screening tool that enables early detection and intervention before significant liver damage develops.. Understanding what the HBsAg test is and its normal range empowers you to make informed decisions about your health screening needs.
Regular HBsAg screening proves especially important if you have risk factors, while vaccination remains your best protection against future infection. Early detection through the HBsAg blood test can prevent progression to cirrhosis, liver failure, and liver cancer through timely medical management.
At Metropolis Healthcare, we make hepatitis B screening accessible and reliable through our comprehensive diagnostic services. With over 4,000 advanced tests available through our network of 220+ laboratories, we provide accurate HBsAg testing alongside complete hepatitis B monitoring profiles. Our convenient home sample collection service, spanning 10,000+ touchpoints across India, ensures you can access essential liver health screening from the comfort of your home.
FAQs
How long does it take to get HBsAg test results?
HBsAg test results are typically available within 8 hours after the sample reaches the lab. This quick turnaround helps ensure you can consult your doctor and receive appropriate guidance without delay.
What happens if my HBsAg test is negative?
A negative HBsAg test indicates no current hepatitis B infection, but your doctor may recommend vaccination if you're not immune. Additional testing might be needed to confirm your immunity status and determine if you require protective vaccination.
References
- https://www.cdc.gov/hepatitis-b/hcp/diagnosis-testing/index.html
- https://www.hepb.org/prevention-and-diagnosis/diagnosis/hbv-blood-tests/
- https://www.who.int/southeastasia/activities/hepatitis-b-is-preventable-with-safe-and-effective-vaccines




























