Preventive Healthcare
Insights into Ulcerative Colitis (UC): Understanding the Condition and Its Implications
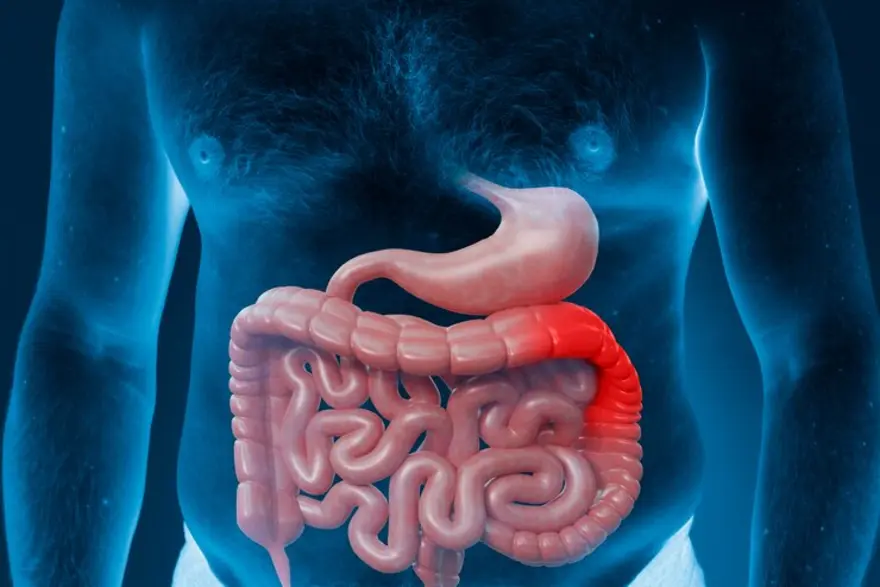
Table of Contents
- What is Ulcerative Colitis (UC)?
- What are the Types of Ulcerative Colitis?
- What are the Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis?
- What Causes Ulcerative Colitis?
- What are the Risk Factors of Ulcerative Colitis?
- What are the Complications of Ulcerative Colitis?
- How is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed?
- How is Ulcerative Colitis Treated?
- What is the Outlook for Ulcerative Colitis?
- Does Ulcerative Colitis Ever Go Away?
- What Should I Ask My Doctor Related to Ulcerative Colitis?
- Conclusion
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is more than just a gastrointestinal disorder; it profoundly impacts daily life. In this article, we'll delve deeper into UC, its symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and strategies for living well with this condition. Read on to learn more!
What is Ulcerative Colitis (UC)?
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects your large intestine (colon) and rectum. It belongs to a group of conditions known as Inflammatory Bowel Diseases (IBD). Ulcerative colitis is characterised by inflammation and ulceration of the inner lining of your colon and rectum, leading to various gastrointestinal symptoms.
What are the Types of Ulcerative Colitis?
The main types of ulcerative colitis include:
- Ulcerative Proctitis: This type of ulcerative colitis involves inflammation limited to your rectum (the lowest part of your large intestine).
- Left-sided Colitis: In left-sided colitis, the inflammation extends beyond your rectum and involves the left side of the colon (the sigmoid colon and possibly the descending colon).
- Pancolitis or Total Colitis: This type of ulcerative colitis affects your entire colon, from the rectum to the cecum (the beginning of the colon). You may be at a higher risk of developing complications such as colon cancer.
- Fulminant Colitis: Fulminant colitis is a severe form of ulcerative colitis characterised by a rapid onset of symptoms, including severe bloody diarrhoea, abdominal pain, dehydration, fever, and rapid heart rate.
How Common is Ulcerative Colitis?
Ulcerative colitis is more prevalent in developed countries, particularly in North America and Europe, compared to developing regions. Ulcerative colitis has an annual prevalence of 156 to 291 cases per 100,000.
What are the Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis?
Common ulcerative colitis symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Persistent diarrhoea with blood or mucus
- Rectal bleeding
- Urgency to have bowel movements ( even when bowels are empty: also known as tenesmus)
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Joint pain, skin rashes, or eye inflammation
It is worth noting that ulcerative colitis symptoms in females are similar to men.
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis?
The exact ulcerative colitis causes remain unknown, but it is believed to result from various factors. Potential ulcerative colitis causes include:
- Ulcerative colitis is considered an autoimmune disease, where your immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells in your digestive tract. Therefore, ulcerative colitis can be caused due to overaction of your immune system.
- Alterations in the composition and function of your gut microbiota (the community of microorganisms residing in your gastrointestinal tract) have been implicated in ulcerative colitis pathogenesis.
- Defects in your intestinal epithelial barrier, which normally protects your intestinal lining from harmful substances and pathogens, can cause ulcerative colitis.
- While not fully understood, medications (e.g., antibiotics, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) and microbial infections may trigger or exacerbate ulcerative colitis symptoms in some cases.
What are the Risk Factors of Ulcerative Colitis?
Here are some of the risk factors:
- Having a first-degree relative (parent, sibling, or child) with UC colitis increases the risk of developing the disease given the autoimmune nature of the disease.
- Multiple genetic variants such as ABCB1, IL10RA, IL10RB and PTPN2 increase the risk ulcerative colitis susceptibility.
- Ulcerative colitis most commonly develops during late adolescence or early adulthood, with a second peak in incidence occurring between ages 50 and 80. Therefore, increasing age is a risk factor.
- Factors such as your diet, smoking, stress etc may influence the development and progression of ulcerative colitis.
What are the Complications of Ulcerative Colitis?
Complications of ulcerative colitis include:
- Colon cancer
- Severe inflammation can lead to a dangerous dilation of the colon.
- Perforated colon
- Chronic bleeding and inflammation can lead to iron deficiency, causing anaemia
- Bone thinning
- Ulcerative colitis may cause primary sclerosing cholangitis or autoimmune hepatitis
How is Ulcerative Colitis Diagnosed?
Ulcerative colitis diagnosis involves the following:
- Evaluation of your medical history
- Physical examination and abdominal palpation
- Blood tests may be performed to check for signs of inflammation (e.g., elevated C-reactive protein or Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate - ESR) and to evaluate for anaemia or nutritional deficiencies
- Stool samples may be analysed for the presence of blood, mucus, or infectious agents
- Colonoscopy is the gold standard for diagnosing ulcerative colitis. A thin, flexible tube with a camera (colonoscope) is inserted into your rectum and advanced through your colon to examine the lining for signs of inflammation and ulceration
- In cases where a full colonoscopy is not feasible, flexible sigmoidoscopy may be performed to visualize the lower part of the colon and rectum
- Upper endoscopy or capsule endoscopy may be performed in cases where ulcerative colitis involvement is suspected beyond the colon and rectum
How is Ulcerative Colitis Treated?
Common ulcerative colitis treatment approaches include:
- Medications: Aminosalicylates, Corticosteroids and Immunosuppressants
- Biologic Therapies: Anti-tumour necrosis factor (TNF) agents (e.g., infliximab, adalimumab), anti-integrin agents (e.g., vedolizumab), or anti-interleukin 12/23 agents (e.g., ustekinumab) are reserved for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis that doesn't respond to other treatments
- JAK Inhibitors: Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors (e.g., tofacitinib) may be prescribed for moderate to severe ulcerative colitis therapy in adults
- Rectal Therapies
- Rectal 5-aminosalicylate: This can be used to treat inflammation localised in the rectum or lower part of the colon.
- Corticosteroid Enemas: If you have left-sided ulcerative colitis or proctitis, rectal corticosteroid formulations (e.g., hydrocortisone or budesonide enemas) may be prescribed.
- Colectomy: Surgical removal of the colon (total colectomy) may be necessary in cases of severe ulcerative colitis.
What is the Outlook for Ulcerative Colitis?
The outlook for ulcerative colitis varies widely among patients and depends on factors such as disease severity, extent of inflammation, response to ulcerative colitis treatment, and presence of complications. With proper management, many patients with ulcerative colitis can achieve remission and lead fulfilling lives, although the condition may require lifelong monitoring and treatment.
Does Ulcerative Colitis Ever Go Away?
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic condition with no known cure. While symptoms can be managed with treatment, ulcerative colitis typically follows a relapsing-remitting course, with periods of remission and flare-ups.
What Should I Ask My Doctor Related to Ulcerative Colitis?
When discussing ulcerative colitis with your doctor, consider asking questions such as:
- What is the extent and severity of my ulcerative colitis?
- What are the potential risks and benefits of each treatment?
- How can I manage ulcerative colitis symptoms?
- Are there any lifestyle modifications or dietary changes that may help?
- How often should I follow up with you for monitoring and adjustments to my treatment plan?
- What are the signs of complications I should watch for?
Conclusion
Understanding the biology of ulcerative colitis is essential for effectively managing this chronic condition. With proper treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and regular monitoring, one can achieve remission and lead a healthy life despite its challenges. If one is experiencing symptoms suggestive of ulcerative colitis, do not delay and get in touch with Metropolis Healthcare for a comprehensive blood test to evaluate the C- reactive protein levels and ESR. Metropolis Healthcare offers at-home testing by expert phlebotomists with prompt and reliable digital reports at zero extra charges! Book your test today!




























