type 2 diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes: Symptoms, Causes and Risk Factors
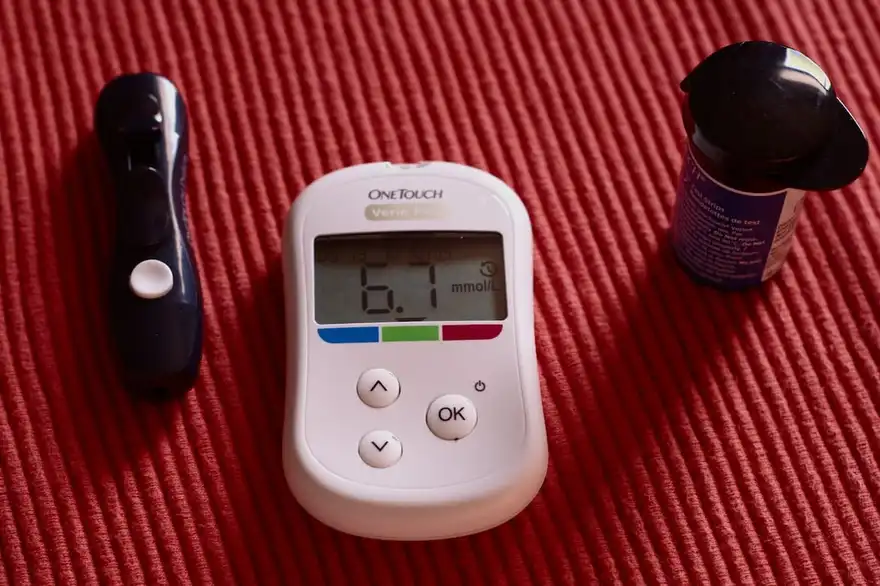
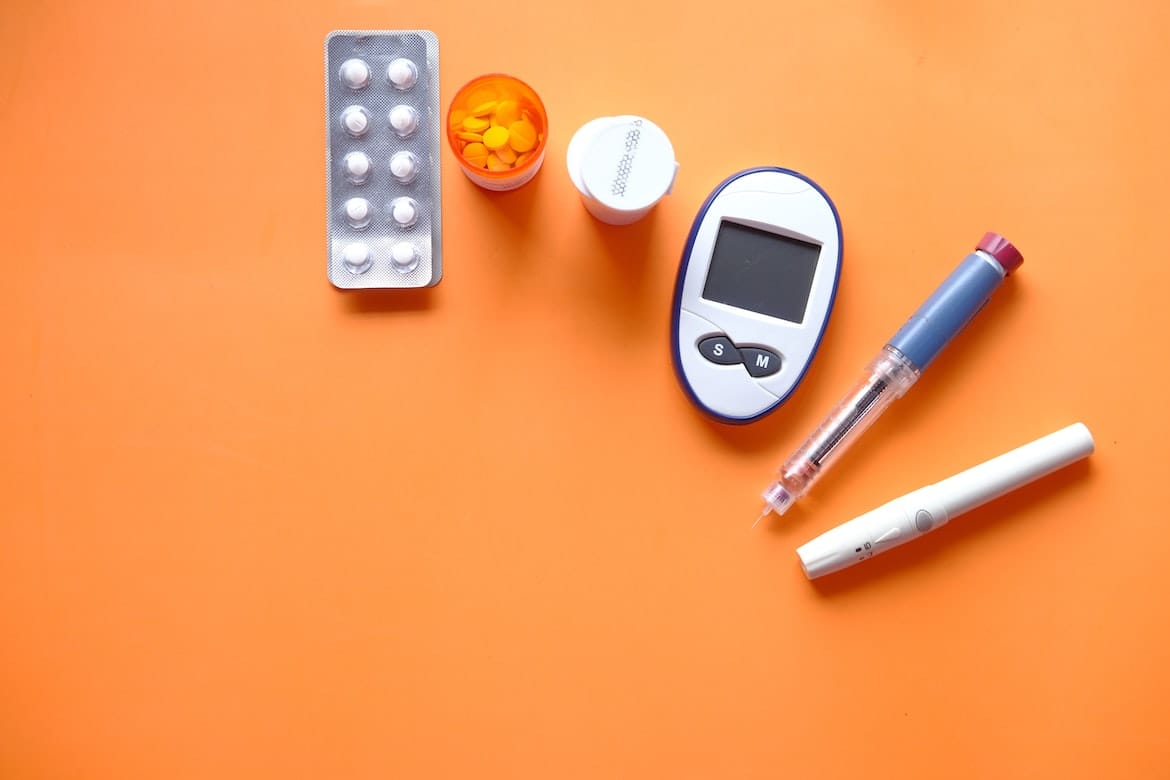
India is known as the diabetes capital of the world. With a large number of people, including youngsters developing this condition, it has become imperative to understand more about this condition. Diabetes is characterised by high blood sugar levels. There are three types of diabetes: Type 1: Also called juvenile diabetes, it develops in childhood. Type 2: Also called diabetes mellitus, it usually develops later in life. Gestational: It develops in some women during pregnancy. Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic health condition in which the blood sugar levels are higher than normal. This happens because your body is unable to use the glucose (sugar) from the food properly. Let’s understand more about what causes diabetes, its many symptoms, risk factors, treatment and prevention in this blog! Type 2 diabetes and its causes When you eat food, it is broken down and processed into glucose and other nutrients. Your pancreas makes a hormone called insulin that ensures this glucose reaches all the cells in the body for energy. However, when your cells do not respond normally to insulin, it results in insulin resistance. To overcome this resistance, your pancreas produces more insulin to stimulate the cells to take up the glucose. Eventually, your pancreas gives up and stops producing adequate insulin. As a result, your blood sugar levels rise, resulting in type 2 diabetes. High blood sugar levels are harmful to your body and a major risk factor for heart disease, vision loss and kidney problems. You may be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes if your blood sugar levels show the following values: Fasting glucose test 126 or higher Random (anytime) glucose test 200 or higher A1c test 6.5% or higher Oral glucose tolerance test 200 or higher Risk factors of type 2 diabetes While you can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, it used to be more common among those over 45. However, in recent times, due to unhealthy dietary habits and sedentary lifestyles, this condition is increasingly becoming common in people under 35. Besides age, a few factors that may increase your risk for type 2 diabetes include: Family history Being overweight or obese Lack of physical activity Gestational diabetes during pregnancy Symptoms of type 2 diabetes In the early stages of type 2 diabetes (insulin resistance and prediabetes), you may not observe any signs or experience any symptoms. As the condition progresses, common type 2 diabetes symptoms appear and may include: Increased thirst and urination Increased hunger Fatigue Tingling sensation in hands and feet Blurring of vision Non-healing ulcers or wounds Unexplained weight loss Since the symptoms of type 2 diabetes develop slowly, earlier symptoms are usually mild and difficult to identify. For this reason, doctors recommend getting your blood sugar levels checked at regular intervals during the year. Early detection can help reverse prediabetes or send type 2 diabetes into remission, thereby preventing further health complications. What are the complications of type 2 diabetes? Untreated type 2 diabetes can result in a host of complications, such as: Digestive issues (like gastroparesis) Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic neuropathy Gum diseases Foot conditions like ulcers Heart disease Kidney and liver disease Liver conditions like non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Urinary tract infections (UTI) Stroke In severe cases of uncontrolled diabetes, it may result in a life-threatening condition called diabetic ketoacidosis. Treatment and management of type 2 diabetes Unfortunately, there is no cure for type 2 diabetes. However, with the right support from your doctor and healthcare team, you can maintain your blood sugar levels within the normal range. Management of type 2 diabetes typically involves: Medications to bring down your blood glucose levels Controlling blood pressure and cholesterol levels Eating a healthy diet rich in fibre, lean proteins and minimal carbohydrates and zero added sugar Regularly monitoring blood sugar levels Managing stress levels with deep breathing, meditation, yoga and mindfulness Exercising regularly Can type 2 diabetes be prevented? The good news is that type 2 diabetes can be prevented. Whether you have a high risk of developing the condition or have prediabetes, here are some ways to prevent type 2 diabetes: Eat a healthy, clean diet. You can seek help from a nutritionist who can guide you in choosing the right foods. Exercise regularly Lose weight and maintain it within the normal range In a Nutshell Armed with this knowledge about type 2 diabetes, you are better equipped to recognise the early warning signs, make informed lifestyle choices, and work closely with healthcare professionals to manage this condition effectively. If you have been diagnosed with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes, you must understand that this condition does not define you and can be effectively managed to ensure you lead a normal, healthy, productive life. It is important to get your blood sugar levels checked periodically to detect changes and manage them in time. Need help with your diagnostic requirements? Book your diabetes profile test with Metropolis Labs today!
Diabetes in Children: Types, Symptoms & Management
Diabetes is a common chronic condition affecting people of all ages including children. As per the estimated results, around 463 million people worldwide were diagnosed with diabetes in 2019. But now, more than 500 million adults are estimated to be living with diabetes. Millions of children worldwide also have this medical condition. According to Dr Moumita Misra, Head-Lab Operations, Metropolis Healthcare Mumbai,diabetes is a serious problem for children and adults as it can cause serious health complications. It can result in several risks to life, especially if left unchecked for a long time. India is the diabetic capital of the world and the number of children affected by it are increasing every day. What is Diabetes? Diabetes is a medical condition characterized by higher blood sugar levels than normal. It occurs when the pancreas either does not produce enough insulin or when the body does not respond to the insulin produced. When either of these happens, the body cannot absorb sugar from the blood, resulting in excess blood sugar levels. Incidence of Diabetes in Children Previously, type 1 diabetes was found to be the most widespread form of diabetes affecting children and adolescents. So it was referred to as juvenile diabetes. This type of diabetes results from malfunctioning of the pancreas, which does not produce a hormone called insulin. This hormone is responsible for facilitating the absorption of sugar or glucose by the cells in the body, thus providing them with the necessary energy. But now, younger people are also getting diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, referred to as adult-onset diabetes. The increasing prevalence of obesity has also caused it to become more common in children and teenagers. This condition results in the (child's) body's inability to effectively produce and use insulin. Children pose a higher risk of type 2 diabetes if they are overweight, have very little physical activity, have a history of diabetes in the family, etc. Causes of Diabetes in Children The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is still unknown but genetics and environmental factors are believed to cause this condition. If left untreated, high blood sugar levels can lead to life-threatening complications. Modern lifestyles with increased consumption of processed or junk food, reduced physical activity and prolonged screen time are all leading to the growing incidence of childhood obesity. It is often linked to metabolic syndrome and polycystic ovary syndrome. These two syndromes are proven risk factors for the development of type 2 diabetes. Children with a family history of diabetes might get diagnosed with this medical condition. Additionally, pregnant women who develop diabetes are at a higher risk of giving birth to infants with a risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Symptoms of Diabetes in Children Parents can ensure early detection of diabetes in their children by looking out for the following symptoms: Increased thirst Extreme hunger Frequent urination Fatigue Blurred vision Dehydration Fruity smelling breath Behaviour change or irritability Tired and thinner Diagnosis of Diabetes in Children Taking your child to the hospital immediately is important if they experience any symptoms of diabetes. These are some of the methods that help diagnose diabetes in children: Type 1 Diabetes Random blood sugar test Glycated haemoglobin test: Testing the child’s average blood sugar for 3 months (the past 3 months). Fasting blood sugar test: A blood sample is taken from a child who hasn't eaten anything for hours. Type 2 Diabetes Random blood sugar test Fasting blood sugar test Glycated haemoglobin test Oral glucose tolerance test: The test is conducted after the child fasts for a night and then is given a sugary liquid. Treatment for diabetes includes medication and monitoring of blood glucose levels. Treatment of Diabetes in Children Taking insulin injections Children with type 1 diabetes must take insulin injections daily. Rapid-acting insulin, intermediate-acting insulin, long and ultra-long-acting insulin and short-acting insulin are the different types of insulin. Blood sugar monitoring At least 4 times a day, blood sugar monitoring may be advised. Continuous glucose monitoring Continuous glucose monitoring using temporary monitoring of the skin installed underneath the skin may be essential for some children. Medication Medicines like Metformin (Glumetza) and Liraglutide (Victoza) are prescribed for type 2 diabetes in children. How Can Diabetes in Children Be Prevented? Maintain healthy eating habits and body weight. Cut down on too much consumption of junk food Ensure your children engage in regular physical activities (make them stay active). Limit their screen time on tv, computer and other appliances. Ensure that they are getting enough sleep. Check their blood sugar levels on a routine to make small changes in their food, physical activities, etc. Conclusion Diabetes in children may be overwhelming at times but your child is not alone. There are support groups where you can connect with other parents of children living with diabetes. Diabetes can be controlled by making the necessary lifestyle changes and your child can live a normal life with medications. In case of any queries, you must reach out to your child’s diabetes care team, they can address all your queries and can help your family to move ahead in this journey of living with childhood diabetes.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload











1715579024.webp)

 WhatsApp
WhatsApp