liver function test
Liver Cirrhosis: Symptoms, Tests and Treatment
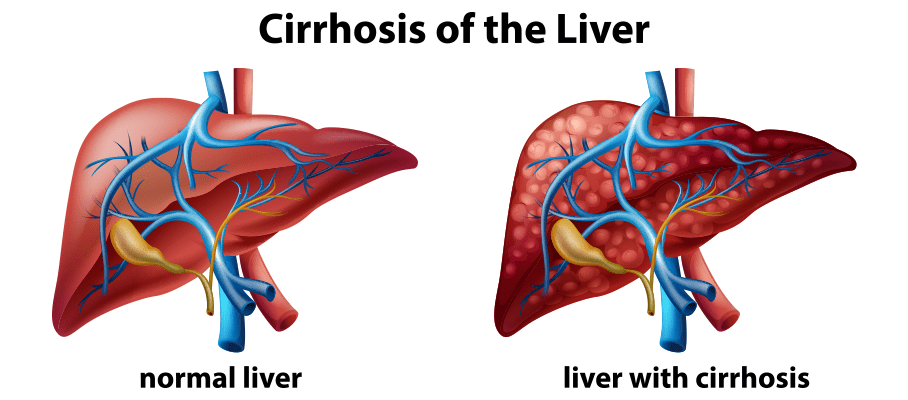
Liver is one of the major abdominal organs in humans performing the important function of metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats along with detoxification of harmful substances and toxins from the body by production of bile. It also functions as a major site for production of proteins and clotting factors. It also serves to store glycogen reserves for the body as well as storage of important vitamins and minerals. Keep an eye on your liver health with a liver function test. Here, we have discussed late-stage liver disease called liver cirrhosis, a condition in which the normal architecture of the liver is replaced by fibrotic tissue. Usually after cirrhosis sets in, it is irreversible. As the normal functions of liver are hampered due to fibrosis in liver over time, multiple complications arise, and the most important and troublesome of it is portal hypertension, where blood coming from portal vein (draining blood from entire GIT) toward liver faces excessive resistance due to fibrosis in the liver. Clinically patients with portal hypertension are identified by presence of low blood platelet count and enlarged spleen. Symptoms of Liver Cirrhosis The clinical signs and symptoms in cirrhosis mimic the level of fibrosis in the liver. The early signs usually include feeling tired or weak, loss of appetite, unintentionally losing weight, nausea, vomiting, mild pain or discomfort in the abdomen. Other features associated with loss of normal liver functions are development of jaundice coagulation disorder, encephalopathy, etc. While any liver insult can ultimately lead on to cirrhosis unless intervened in time, the most common causes are chronic alcohol use, chronic viral infections affecting liver like hepatitis B and C viruses, biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune liver inflammation and rarely some inherited liver disorders. Overall chronic alcohol consumption remains to be a major cause for cirrhosis in India and worldwide. The accurate diagnosis of alcohol causing liver cirrhosis requires accurate history regarding the amount and duration of intake along with corroborative symptoms like vague upper abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and even malaise. Meanwhile a few patients may present straight away with complications of cirrhosis like abdominal distension, edema and even gastrointestinal variceal haemorrhage. Test for Liver Cirrhosis Laboratory investigations may reveal signs of acute blood loss as in anemia along with nutritional deficiency with low platelet counts commonly. Liver function tests may show signs of mild increase in serum bilirubin as fibrosis in liver hampers its elimination along with elevation in levels of liver enzymes in blood, both ALT and AST are elevated but AST levels higher than ALT approximately in a ratio of 2:1 are typical of alcoholic liver disease and cirrhosis. Coagulation profile may show increased PT time. Pathological confirmation of cirrhosis can be obtained with the help of liver biopsy. For patients with suspected viral cause for cirrhosis blood tests may be done for detecting HCV RNA, HBsAg, HBeAg and Anti HBe levels along with quantitative HBV DNA levels. For autoimmune causes of cirrhosis, blood levels of antinuclear antibody (ANA) or anti-smooth-muscle antibody (ASMA) may be done. Anti-Mitochondrial auto-antibodies (AMA) are present in patients developing cirrhosis due to biliary cause along with other signs of cholestasis. Fibroscan may help detect the level of fibrosis in the liver and the need for liver transplant in future. For patients who have risk factors associated with development of cirrhosis it is prudent to rule out development of portal hypertension at the earliest. One should be vigilant for development of ascites and features of hypersplenism like low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia) and low WBC counts (leukopenia). It is important to rule out variceal bleeding in suspected patients at onset of cirrhosis with the help of endoscopy. Ascitic fluid study may be done to rule out other causes for it. Apart from these radiological investigations like CT scan or MRI abdomen should be done to evaluate the level of cirrhosis and portal hypertension. Treatment for Liver Cirrhosis Management of people with cirrhosis primarily revolves around 2 main components- first managing the etiology causing it and other managing the complications arising due to cirrhosis. All the complications arising due to cirrhosis require specific management. In general, the main treatments include reducing salt from your diet and taking a type of medicine called a diuretic. For people developing liver cirrhosis due to excessive consumption of alcohol abstinence is the cornerstone of therapy. Patients who are unable to abstain from alcohol are shown to have significantly low 5 year survival. Occasionally patients with alcoholic cirrhosis have been shown to benefit from the use of glucocorticoids or oral pentoxifylline (drug causing decrease in pro inflammatory cytokines). For patients developing cirrhosis due to viral etiologies antiviral drugs have shown to benefit. For Hepatitis B virus Entecavir or tenofovir are useful, and for patients with cirrhosis due to Hepatitis C Virus direct antivirals have replaced the use of pegylated interferon and ribavirin. For patients developing cirrhosis due to autoimmune inflammation of the liver, immunosuppressive therapies are useful. UDCA is shown to help cirrhotic patients with etiology of biliary stasis. Managing complications arising due to cirrhosis revolves around managing complications of portal hypertension. The measures revolve around managing portal hypertension and ascites. In people with advanced cases of liver cirrhosis, a liver transplant may be the only treatment option as the liver may not be functional. Make sure to follow your doctor's advice and get all tests done as advised.
4 Signs Your Liver is in Trouble and How You Can Help
Your liver is one of the vital organs that help perform several life-sustaining processes. From breaking down food to detoxifying the body, your liver goes a long way in keeping your body function at its best. But, not many people are aware of the importance of liver health. In fact, health experts say liver symptoms are often unnoticed and very few people seek help on time. Thinking that you might also have ignored your liver until now? Well, there is some relieving news! Your liver allows you to arrest, and even reverse the damage in most conditions. The first step towards keeping your liver health intact is to get a liver function test and see how well your liver works. Book a test here. Let us get you aware of some of the signs that can tell if your liver is in trouble: 1. Pale-colored or clay-colored stool: The normal color ofstools range from brownish to yellowish brown in most people. It is given the dark colour by the bile salts that the liver normally releases. If your stool color has changed to pale or clay color, the liver might be facing some troubles. Clay-colored stools can indicate that you could have a liver infection that has decreased bile production, or flow of bile out of the liver is obstructed. 2. Fluid retention: This is the most common sign of liver disease. About 50 percent of people who have liver cirrhosis, a condition in which scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, experience fluid retention. This fluid can cause distension in your abdomen or even swelling in the legs. 3. Jaundice Bilirubin is a pigment that forms when red blood cells break down, passes through the liver, gets converted into bile, and is excreted through the body via stool. However, when bilirubin builds up in your bloodstream, it can cause yellowing of skin, eyes, and urine, called jaundice. One of the main causes of jaundice is a damaged liver due to viral hepatitis or excessive alcohol consumption. 4. Confusion: Your liver helps remove toxins from the body. If the liver is under trouble and not functioning well, it may be unable to filter the toxins, which can travel to your brain. This results in a condition called hepatic encephalopathy and leads to memory problems and confusion. Apart from these, nausea, vomiting, pain in the abdomen, chronic fatigue are some of the other common symptoms that can give hints about an unhealthy liver. Simple things you can do to avoid liver disease: Eat a healthy diet that is low in sugar and processed foods. Choose fruits, vegetables and high-fiber foods instead. Avoid junk food that is overly oily and spicy. Drink alcohol in moderation. Each time your liver filters alcohol, some of your liver cells die. Drinking too much alcohol over many years can reduce your liver’s ability to regenerate. This can lead to permanent liver damage. In fact, if you can quit altogether- even better! The best part about quitting alcohol is that alcohol-caused fatty liver is a reversible health condition. Maintain a healthy weight. Studies show that losing 10 percent of your weight causes liver enzymes to improve. This correlates with a decrease in the liver inflammation caused by the extra fat. Opt for a low-sodium diet. It may help alleviate mild fluid retention. Keep yourself physically active. Exercise at least five times a week for at least 30 minutes each time. It helps decrease adverse cellular processes and keeps your liver going. Do not ignore health symptoms. If you feel any discomfort, reach out to your doctor proactively. Keep taking liver function tests regularly, at least once in a year even if you are absolutely healthy. This helps identify any liver related condition early on and start the treatment. Always opt for protected sexual activity. Unprotected sex can increase chances of getting hepatitis B, a sexually transmitted infection. One can also get it from contaminated needles and syringes. It can also be commonly passed on from a mother to her baby during birth.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload











 WhatsApp
WhatsApp