Types of Kidney Biopsy
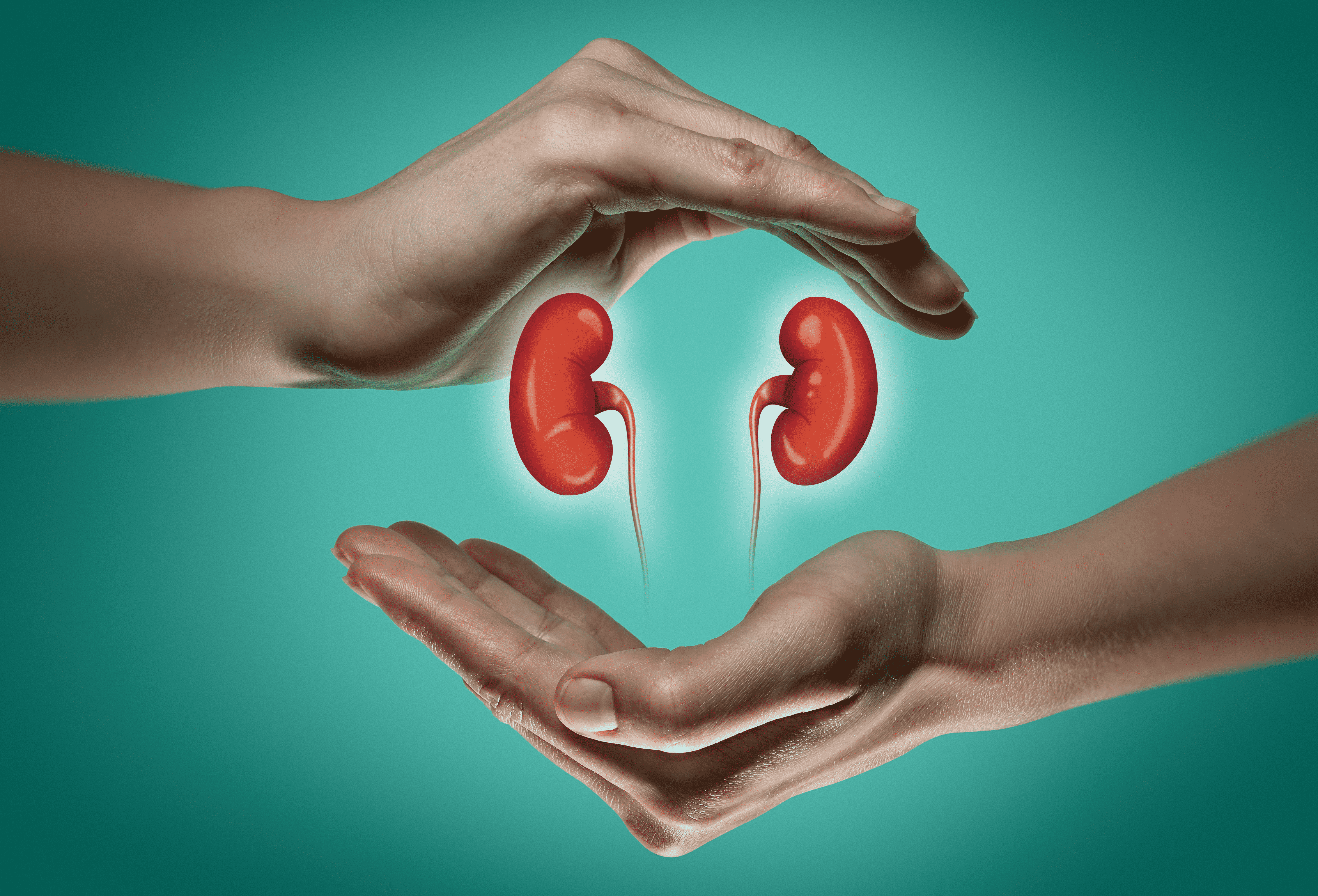
What is Kidney Disease? All You Need To Know
Introduction Chronic kidney diseases affect around 10% of the Indian population. Statistics show that close to 1 lakh cases of renal failure are reported every year. Kidney disease results from kidney damage, making them unable to carry out their functions. This damage can be caused due to high blood pressure, diabetes or other long-term health conditions. Kidney disease can also lead to other health problems, such as nerve damage, weak bones and malnutrition. What is kidney disease? Kidneys are the organs responsible for regulating your body’s pH levels, salt, potassium, and various functions. They are two bean-shaped organs that are usually the size of your fists. Your kidneys carry out three main functions: filtering excess water and waste out of the blood and creating urine. Kidney disease results from kidney damage, making it difficult for them to filter the blood as they should. Here you will understand more about the function of the kidneys and the causes, symptoms, types and treatment of kidney disease. The longer you wait before treating this condition, the more chances it may result in total renal failure. In this case, you would need to undergo dialysis, a form of treatment that helps filter and purify your blood with the help of a machine. As there is no known cure for kidney failure, the individual will have to undergo dialysis for the rest of their life. Types and causes of kidney disease Here is a comprehensive kidney disease list that describes the different types and causes of kidney diseases so that you know the risk and the mode of action required for such conditions. Chronic kidney disease This is one of the most common types of kidney disease. It is a long-term condition that does not improve over time and can result from high blood pressure. This happens because of the pressure applied on the glomeruli (a network of tiny blood vessels in the kidneys that helps purify the blood). Over a period, the increased pressure on these can cause damage to these vessels, which in turn limits kidney function. Ultimately the kidney function declines to the point where the kidneys cannot carry out their function correctly, causing the individual to need dialysis and, in more severe cases, a kidney transplant. Diabetes is another major cause of chronic kidney disease. In this case, the increased sugar level in the blood causes the blood vessels in the kidneys to get damaged over time. The kidneys cannot clean the blood properly, so the body can get overloaded with various toxins. Kidney stones Another common problem is the presence of kidney stones. This disease occurs because substances like minerals crystallise in the kidneys and form solid masses, also known as stones. When urinating, these stones are often dispelled from the body, but the process can be significantly painful. Polycystic kidney disease This genetic disorder often results in the growth of multiple tiny sacs of fluid known as cysts in the kidneys. These cysts can interfere with the kidneys' optimum functioning, resulting in kidney failure. Note that individual kidney cysts are relatively common among individuals and can be harmless. It is only polycystic kidney disease that can be life-threatening. Glomerulonephritis Glomerulonephritis is a kidney disease in which the glomeruli get inflamed. This is usually caused due to drugs, infections or congenital abnormalities. It usually gets better on its own. Urinary tract infections Urinary tract infections are caused because of bacterial infections in the urinary system. This kind of infection is usually seen in the urethra or bladder. They are easy to treat but, if left untreated, can also cause kidney disease. symptoms of Kidney disease Kidney diseases may go unnoticed as their symptoms are less noticeable than other diseases. However, if left without treatment, it can have severe consequences. Here are a few early kidney disease symptoms. Fatigue Trouble sleeping Muscle cramps Dry and scaly skin Swelling in ankles and feet Poor appetite Morning puffiness around the eyes Frequent urination Difficulty concentrating Severe kidney disease symptoms may include: Nausea Vomiting Changes in the output of urine A sudden rise in your potassium levels Pericardium inflammation Decrease in sex drive Fluid retention Anaemia Treatment for kidney disease Treatment for any kidney disease involves trying to control the underlying cause of the disease. The treatment options include: Medications Your doctor might prescribe several medications in the case of kidney disease based on the cause, these include: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers help lower blood pressure A phosphate if your kidneys are having trouble eliminating phosphate A diuretic to eliminate the excess fluid build-up Medicines that help reduce cholesterol levels Vitamin D and calcitriol for bone preservation Erythropoietin helps build red blood cells in patients with anaemia Changes in diet and lifestyle Those with reduced kidney function need to preserve the remaining function so that it can last for longer. Here are a few diet and lifestyle changes you will have to make in your diet and lifestyle Make regular doctor visits Manage your blood sugar levels in case of diabetes Avoid the consumption of painkillers as other non-essential medicines Choose a kidney-friendly diet with limited proteins, sodium and potassium Be more active Don't smoke Try and remain at a weight that is healthy for you Dialysis As there is no known cure for kidney disease your healthcare provider will suggest dialysis when you are in the end stages of kidney disease. There are two main types of dialysis: Hemodialysis: In this case, the blood is circulated through a device that helps get rid of excess waste products before the blood is sent back to the body. Peritoneal dialysis: Here a dialysis solution is placed directly into the abdomen with the help of a catheter. This solution absorbs the waste and can be removed using the same catheter before adding a fresh solution. Book Kidney Function Test Conclusion The kidneys carry out the essential job of waste and excess fluid from the body. When your kidneys stop functioning optimally, they can cause several health issues. Regular health checkups and blood tests help to keep track of your health. You should go the extra mile to get blood and urine tests done if you suspect you may have kidney disease. Metropolis Labs helps their customers with at-home sample collection so that you can keep up with your health from the comfort of your home. Metropolis Healthcare assures accurate results within 48 hours of sample collection. Check out the entire list of diagnostic tests provided to find the ones you need.
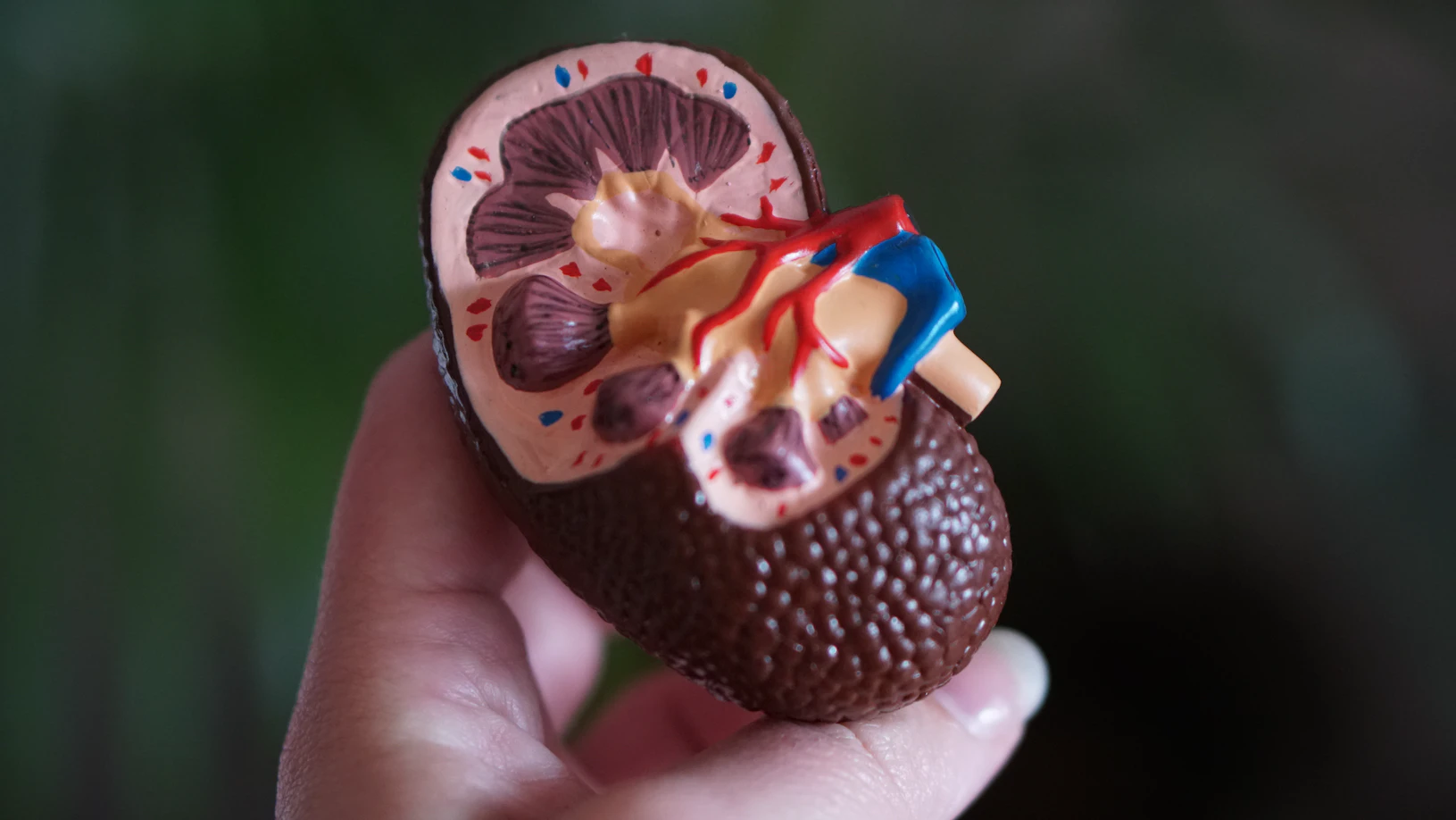
Kidney Biopsy Test: Objectives, Types, Procedure, and Results
What is a Kidney Biopsy Test? A kidney (or renal) biopsy is the procedure to remove kidney tissue for laboratory analysis. The test helps your doctor determine the kind of kidney disease, its severity, and the best course of treatment. A renal biopsy aims to ascertain whether kidney therapy is sufficient and whether problems following a kidney transplant exist. Objectives of a Kidney Biopsy Test In a healthy individual, two working kidneys carry out several tasks. The kidney's function is to eliminate urea, a liquid-solid waste, from the blood. If routine urine and blood tests reveal that your kidneys aren't operating correctly, your doctor could recommend that you have an invasive renal biopsy. Your physician may also mandate the test. These are the objectives of a kidney biopsy: Identify the malignant or benign nature of a kidney tumour. Test the effectiveness of a freshly given kidney. Examine the underlying cause of (blood in urine). Discover the root of the problem (high protein levels in urine). Recognize the level of escalating renal failure and the progression pace. Make a strategy to repair the damaged kidney. Types of Kidney Biopsy Test 1. Percutaneous biopsy Fine needle biopsy Needle core biopsy 2. Open Biopsy Procedure for Kidney Biopsy Test Needle-probe biopsy: This type of kidney biopsy is the most common. A doctor extracts kidney tissue using a small biopsy needle during this procedure. The hand can be directed towards a specific kidney region using an ultrasound or a CT scan. Complete biopsy (surgical biopsy): A thorough biopsy (surgical biopsy). To do this procedure, the surgeon creates skin incisions around the kidneys. The physician can examine the kidneys to decide where tissue samples should be taken. A kidney biopsy is frequently carried out as an outpatient procedure at a hospital. A radiology facility may be used for the process if a CT scan or ultrasound technology is required. Percutaneous biopsy is by far the most popular kind of renal biopsy. A doctor must puncture the skin with a biopsy needle to retrieve kidney tissue. In an open biopsy, the surgeon identifies the location from which tissue samples will be taken by making a tiny incision in the skin around the kidneys. Risks Involved in a Kidney Biopsy Test A renal biopsy may help your doctor identify your kidney problems and choose the best course of action. Infections that develop after surgery are a serious concern. But that is not typical. After your kidney biopsy, watch out for any symptoms that could point to a disease: Vivid blue blood or blood clots in your urine persisting for more than 24 hours Feel sick, develop a fever, or experience swelling, redness, bleeding, or other discharges as a result of an increasing discomfort at the biopsy site Feel weak or flimsy Infection, which may cause internal damage to the target organ or other nearby sites Preparation for Kidney Biopsy Test Usually, preparing for a kidney biopsy doesn't involve much work. Any prescription/over-the-counter/herbal supplements you are taking must be disclosed to your doctor. Ask your doctor if you should stop taking them before the test, take a different dosage, or both. Your doctor may give you additional instructions if you are presently taking any drugs that might potentially alter the outcomes of the kidney biopsy. Results of Kidney Biopsy Test The tissue sample from the kidney biopsy is taken to a laboratory for examination. A pathologist - a medical professional with specialised expertise in sickness diagnosis - examines the tissue. Both an analysis and a microscopic inspection of your specimen employ reactive dyes. The pathologist will examine and assess any fresh scars or deposits. Additionally, infections and other anomalies may be discovered. After examining the results, the pathologist will send the report to your doctor. The results will be available in a week. A kidney biopsy is considered abnormal if changes are seen inside the renal tissue. Numerous factors contribute to this, and your kidneys may occasionally get affected from conditions involving the other areas of your body. If results don't meet expectations, it could mean: Connective tissue disorders - kidney infections affecting the connective tissues Impeded or restricted blood flow to the kidneys Transplanted kidneys being rejected Kidney cancer Complicated urinary tract infections having a detrimental impact on kidney function To determine the best course of treatment, the doctor may prescribe further testing. After the kidney biopsy, they will walk you through the next steps and thoroughly go over your results and health. Recovery After Kidney Biopsy Before you may leave the hospital, the kidney biopsy will need to recover and be monitored. Your exact release time may fluctuate depending on your physical state, your doctor's method, and how you respond to the therapy. If you've undergone an organ transplant, you'll rest on your stomach and back for the following six to eight hours. A doctor or nurse will monitor your vital indicators, including your temperature, blood pressure, pulse, and breathing rate. Tests on the blood and urine are done to look for internal haemorrhages or other issues. The doctor will prescribe medications to ease the pain at the biopsy site. You will be allowed to leave the hospital and return home after your vital signs have returned to normal. It often happens 12 to 24 hours following the procedure. Brilliant red blood cells in your urine are typically seen for up to 24 hours following the biopsy. If the issue persists for more than a day, you must inform your doctor. If you're hungry, you may typically resume your regular eating routine. Your doctor might suggest you rest for 12 to 24 hours after your biopsy. Avoid any strenuous physical activity and heavy lifting for two weeks. It is advised to refrain from jogging, aerobics, and any other exercise that includes bouncing for two weeks following the biopsy. If the biopsy site is painful, you may take medications. How Often Should You Have a Kidney Biopsy Test? A kidney biopsy test is a procedure used to determine a kidney's size, shape, and composition. If you have any suspicion whatsoever that you could have a kidney problem, it’s important to get tested. If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms, you should have a kidney biopsy test: - Pain in your back or side - Blood in your urine - Urine that smells fruity or metallic - Urinary stones A kidney biopsy test is typically done as an outpatient procedure in a hospital or doctor’s office. The test is often done as part of a doctor's evaluation of a person's overall health. Conclusion A kidney biopsy test is a procedure doctors use to look for the cause of renal disease or other kidney problems. Most renal specialists will order a kidney biopsy if suspected of having a renal disease or if they have symptoms such as high blood pressure or proteinuria (a urine sample showing increased protein levels). Kidney Biopsy Test reports typically take six to eight weeks to come back. If there is any suspicion that the patient has cancerous cells in their kidneys, then additional tests may be required before making a final diagnosis. After a kidney biopsy, most patients can return to their normal routine within days or weeks if there is no disease indication. However, additional tests may be required for an accurate diagnosis if renal cancer is suspected. If you are planning on having a kidney biopsy test, talk to your doctor about what test would be best for you and when to schedule it. FAQs How Often Does a Kidney Biopsy Need to be Done? the decision about when to have a Kidney Biopsy Test depends on the underlying condition and may vary from patient to patient. In general, however, most doctors recommend having one every few years as long as no signs of disease are present. What are the Risks Associated With Having a Kidney Biopsy? The main risks of having a Kidney Biopsy Test include pain, bleeding, and infection. However, these risks generally occur only in rare cases. Moreover, most people experience minor side effects following surgery, such as swelling and fatigue. What are the Benefits of Having a Kidney Biopsy Test? The benefits of having a kidney biopsy test include the possibility of detecting cancer or other abnormalities, which may lead to improved health and/or prolonged life.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload











 WhatsApp
WhatsApp