itching
Managing Itching & Itchy Skin (Pruritus): Causes, Treatment, and Home Remedies
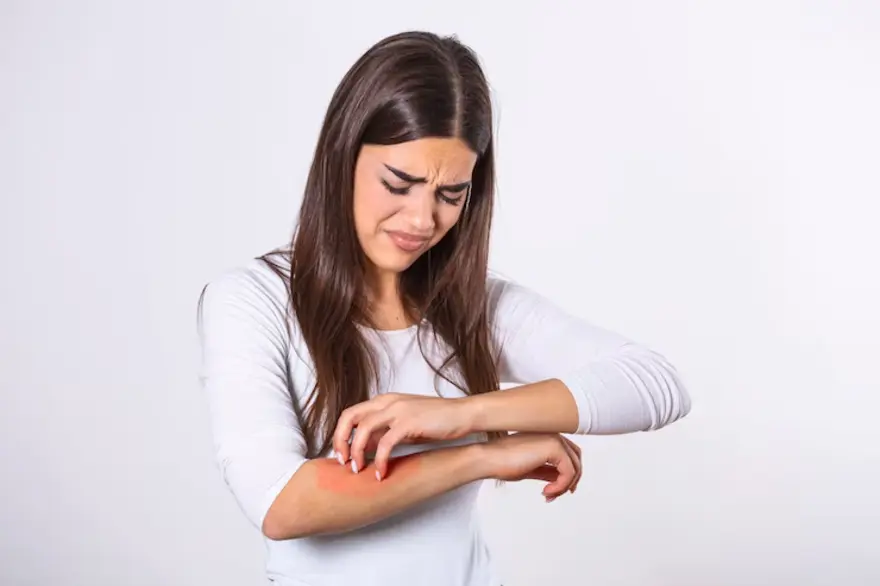
What is itching? Itching, also known as pruritus, is an unpleasant sensation that prompts the desire to scratch. It can affect the skin or mucous membranes and is often a symptom of an underlying issue rather than a condition itself. Itching can vary in intensity and duration, ranging from mild and temporary to chronic and debilitating. What are the most common causes of itching? Itching can stem from a multitude of factors, with some of the most common causes of itchy skin including skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis. Allergic reactions to substances such as chemicals, plants, or certain foods can also cause itching. Insect bites, dry skin, and excessive sweating are frequent triggers. Additionally, systemic conditions like liver or kidney diseases, thyroid disorders, and diabetes may manifest with itching as a symptom. Psychological factors like stress and anxiety can exacerbate itching sensations. Can stress worsen itching symptoms? Yes, stress can exacerbate itching symptoms. Psychological factors like stress and anxiety can trigger or intensify itching sensations through complex physiological pathways. Stress prompts the release of neurotransmitters and hormones that can stimulate nerve endings in the skin, leading to heightened itch perception. Moreover, stress weakens the body's immune system, making individuals more susceptible to inflammatory skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis, which are often accompanied by itching. What are the types of itching? There are various itching types characterised by their location, duration, and underlying causes. Itching, or pruritus, manifests in various forms depending on its underlying causes and characteristics: Localised Itching: This type affects specific areas of the body and is often attributed to external factors such as insect bites, contact with irritants, or localised skin conditions like eczema or dermatitis. Generalised Itching: Generalised itching involves the entire body and can be a symptom of systemic conditions such as liver disease, kidney failure, or certain infections like scabies or chickenpox. Neuropathic Itching: Neuropathic itching arises from dysfunction or damage to the nervous system, leading to abnormal signaling of itch sensations. It can occur with conditions like neuropathy, multiple sclerosis, or spinal cord injuries. Psychogenic Itching: Psychogenic itching is driven by psychological factors such as stress, anxiety, or obsessive-compulsive disorders, without any identifiable physical cause. Home remedies for itchy skin Several home remedies for itchy skin can give you relief without the need for medication. Aloe vera gel or calamine lotion can be applied topically to soothe itching and reduce inflammation. Taking a lukewarm bath with colloidal oatmeal or baking soda can alleviate itching and provide relief. Incorporating foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as salmon or flaxseeds, into your diet can help reduce inflammation from within. Regularly moisturise your skin to prevent dryness, which can exacerbate itching. Avoid scratching, as it can further irritate the skin and worsen itching. Wear loose-fitting clothing made of breathable fabrics can help prevent further irritation and promote healing of itchy skin. However, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional if itching persists or worsens despite home remedies. What are the treatments for itching? The itchy skin treatment depends on the severity and causes of itchy skin: Prescription medications such as oral corticosteroids, immunosuppressants, or antifungal agents may be necessary for more severe cases or underlying medical conditions. Phototherapy, involving exposure to specific wavelengths of light, can be effective for certain skin conditions causing itching. Addressing systemic issues contributing to itching, such as liver or kidney diseases, through appropriate medical management is essential for long-term relief. What tests diagnose itching? Various tests diagnose the underlying cause of itching including: Skin biopsy: Involves removing a small sample of skin for examination under a microscope to identify any abnormalities or underlying skin conditions. Blood tests: Measure levels of certain substances in the blood, such as liver enzymes, thyroid hormones, or specific antibodies, to detect systemic conditions contributing to itching. Allergy testing: Helps identify allergens triggering allergic reactions and itching. Imaging tests: Such as ultrasound or MRI, may be used to evaluate internal organs for abnormalities associated with itching, such as liver or kidney disease. How do I get rid of itching? To get rid of itching, follow the below tips: Apply cold compresses or ice packs to numb the skin and reduce inflammation. Keep your living environment clean and free of allergens, such as dust mites or pet dander, which can trigger itching in sensitive individuals. Consider over-the-counter antihistamines to counter allergic reactions causing itching. Topical corticosteroids can target inflammation and provide relief from itching. How can I prevent itching in the future? To prevent itching in the future: Moisturise regularly to keep the skin hydrated. Use gentle, fragrance-free skincare products. Avoid hot showers and harsh soaps. Wear loose-fitting, breathable clothing. Maintain a healthy lifestyle with balanced nutrition and stress management techniques. What can I expect if I have itchy skin? If you have itchy skin, you can expect sensations of discomfort, irritation, and an urge to scratch. Itching may vary in intensity and duration, depending on the underlying cause, and can sometimes be accompanied by visible skin changes or lesions. When should I see a doctor for itching? You should see a doctor for itching if it persists for more than a few weeks, is severe and interferes with daily activities, is accompanied by other symptoms like rash, fever, or fatigue, or if over-the-counter treatments fail to provide relief. Persistent itching may indicate an underlying medical condition needing attention. Conclusion In conclusion, itching, though common, can significantly impact one's quality of life, ranging from mild discomfort to severe distress. While home remedies for itchy skin can offer relief for mild cases, persistent or severe itching warrants medical attention to address underlying conditions. Prevention through proper skincare, lifestyle adjustments, and avoidance of triggers is key. For comprehensive diagnostic tests schedule an appointment with Metropolis Labs today. We provide at-home testing facility, if you are unable to visit our diagnostic labs. Book your test now.
Understanding Conjunctivitis Symptoms and Signs : A Comprehensive Guide
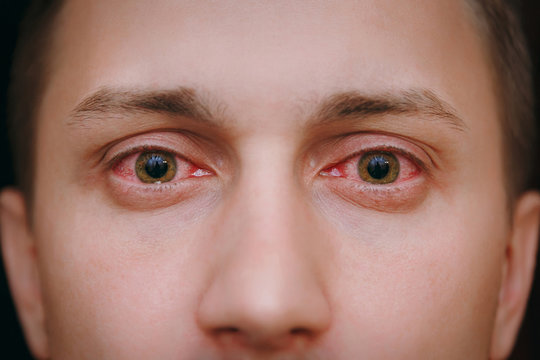
Conjunctivitis, also referred to as pink eye or eye flu, is an eye condition that can make people feel uncomfortable, irritated, and have red eyes. The thin membrane that covers the white area of the eye and the inner surface of the eyelids, the conjunctiva, becomes inflamed, which is how it is identified. To assist you in recognising and comprehending this widespread eye condition, we will break down the conjunctivitis symptoms and indicators in this post. Redness of the Eye The redness of the eyes is one of the main and most obvious signs of conjunctivitis. Because of the pink or red colour of the eye caused by the inflamed blood vessels in the conjunctiva, the condition is frequently referred to as "pink eye." Depending on the underlying cause of conjunctivitis, the degree of redness can range from mild to severe. Itching and Irritation Conjunctivitis frequently causes itching and irritation in the affected eye or eyes. People may feel the urge to touch their eyes to ease the itching, which can range from mild to severe. However, in the event of infectious conjunctivitis, scratching the eyes can exacerbate the illness and possibly transmit the infection. Watery or Discharge from the Eye Conjunctivitis can cause the eyes to tear excessively or discharge. While bacterial conjunctivitis may provide a thicker, yellow or greenish discharge, viral conjunctivitis typically results in a clear and watery discharge. Due to the body's immunological reaction to allergens, allergic conjunctivitis can also result in watery discharge. Swollen Eyelids Conjunctivitis occasionally results in swollen eyelids, making it difficult to fully open or close the eyes. The inflammation that affects the tissues of the eyelids usually causes swelling. Sensitivity to Light (Photophobia) Conjunctivitis can cause photophobia, a condition in which the eyes become sensitive to light. People who have conjunctivitis may experience discomfort and suffering when exposed to bright lights or sunshine. Crust Formation on the Eyelids Particularly after waking up in the morning, bacterial conjunctivitis can cause the development of crusts or "eye boogers" on the eyelids. These crusts develop as a result of dry discharge gathering on the eyelids while you sleep. Foreign Body Sensation Some people with conjunctivitis could feel as though they have grit or a foreign body in their eyes. This sensation may be uncomfortable and increase the desire to massage one's eyes. For early detection and suitable care, it is essential to recognise the symptoms and signs of conjunctivitis. A qualified eye care practitioner must be consulted if you suffer redness, irritation, excessive tearing, or discharge from your eyes in order to make an accurate diagnosis and receive the appropriate treatments. While the majority of conjunctivitis instances are not dangerous and can be treated with self-care or medical procedures, prompt treatment can help reduce discomfort and stop the conjunctivitis from spreading to other people. Keep in mind that having healthy eyes is crucial for sustaining vision and general wellbeing.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload












 WhatsApp
WhatsApp