vitamin d deficiency
Boost Your Bone Health Naturally: Discover 5 Vitamin D-Rich Foods to Fight Weak Bones
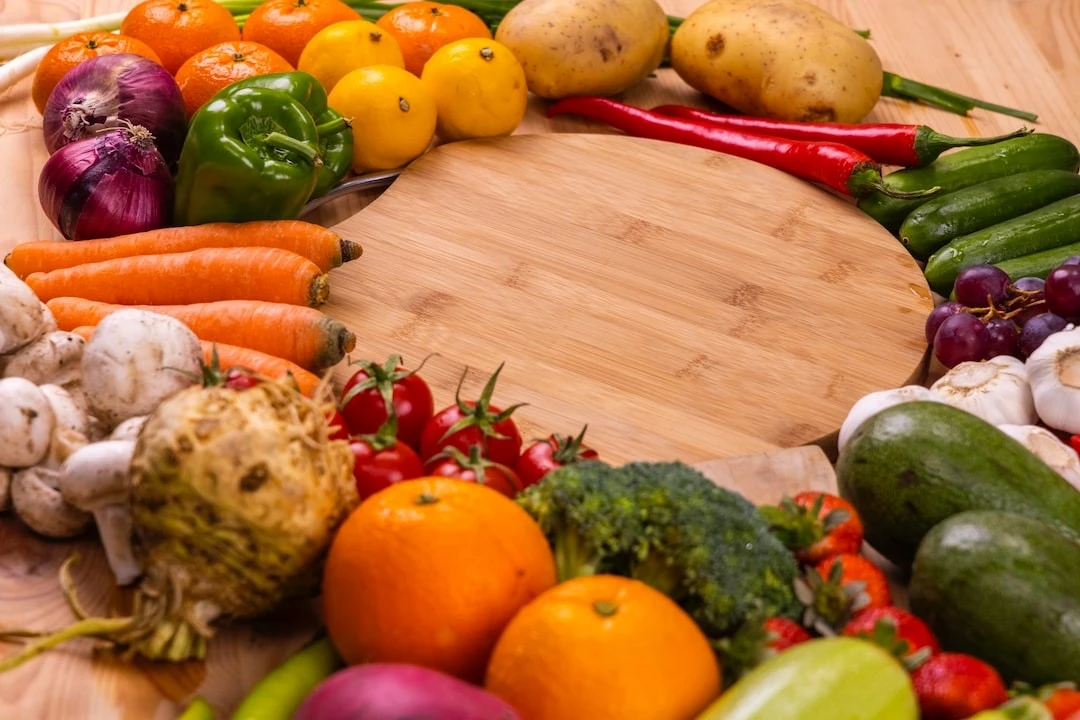
Which foods are high in vitamin D? Vitamin D is one of the most essential nutrients for health, like vitamins A, E, and K. Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin absorbed by the digestive tract with dietary fats before being sent into the bloodstream. If you want to know how to get vitamin D, then check these Vitamin D-rich foods: Salmon Cod liver oil Fortified cereals Fortified dairy (some non-dairy alternatives) Orange juice Fish that have high oil content, e.g., herring, mackerel, or tuna Whole milk Mushrooms How to increase intake of vitamin D? Vitamin D is responsible for bone health; a deficiency of this vitamin can cause osteoporosis, osteomalacia, increased risk of fractures, and brittle bones. The good news is that most people can meet their daily vitamin D requirements by simply getting enough sun exposure and consuming a balanced diet. Supplements and fortified foods can also help increase your intake of vitamin D. How to get vitamin D? Going outside is one of the easiest ways of getting an adequate amount of vitamin D. Sunlight helps the body synthesise vitamin D naturally, so just 5 to 15 minutes of sunlight 2 or 3 times a week without sunscreen or too much clothing enables you to boost your vitamin D levels. Ensure you get the sunshine in the morning or late afternoon when the sun is not too hot to avoid skin damage. If you are exposing yourself to the sun for more than 15 minutes, you must use good sunscreen. Why do we need vitamin D? Vitamin D plays a vital role in your body. It is good for the following reasons: For bone health: Vitamin D helps the body absorb calcium, an essential mineral to ensure your bones remain healthy and strong. Too little vitamin D can lead to limited calcium, weakening your bones. Immune health: Vitamin D directly interacts with cells that fight infections in the body. Hence, a lack of vitamin D is linked to respiratory illnesses. Mental health: Studies have shown links between vitamin D and depression. They also state that increasing vitamin D levels can help improve symptoms of clinical depression. Infant health: Vitamin D is essential to ensure a healthy pregnancy and a healthy child. How much vitamin D do I need per day? According to the National Institutes of Health, the recommended daily levels of vitamin D are as follows: 0-12 months: 10 micrograms (mcg)(400 IU) 1-70 years: 15 mcg (600 IU) 71 years and over 20 mcg (800 IU) However, the actual amount of vitamin D required from your diet or supplements varies depending on several factors such as: age skin tone (the amount of melanin in the skin) latitude where you live season clothing choices whether or not you are obese Doctors may assess your blood levels to check vitamin D by measuring 25(OH)D in the blood. This is the storage form of vitamin D present in the body. The lack of a single definition of optimal blood levels of vitamin D in the body makes it difficult for scientists to understand how vitamin D acts. Daily recommended dose of vitamin D According to the FDA, the daily value (DV) for vitamin D is 800 IU (20 mcg) for children who are 4 years old and above. The same amount is recommended for adults as well. Food or supplements are one of the best ways to get adequate vitamin D. You need to speak to your doctor and understand if you need to take a vitamin D supplement along with your food and sun exposure. List of foods that are high in vitamin D Here is a list of 7 foods that are natural sources of vitamin D Fatty Fish Salmon is one of the most popular vitamin D-rich foods. One 100-gram serving of farmed salmon contains 526 IU of vitamin D, 66% of your DV. Wild-caught salmon typically can contain higher amounts of vitamin D. Halibut and mackerel are other fatty fish that provide 190 and 643 IU of vitamin D. Herring and sardines Herring is another common fish eaten worldwide, often pickled or smoked. Fresh Atlantic herring can give you around 214 IU of vitamin D per 100 grams, while pickled herring has around 113 IU. Canned sardines provide 193 IU of vitamin D, which amounts to 24 % of your DV. Making them good sources of vitamin D. Cod liver oil If fish is not your thing, taking cod liver oil can help you get around 450 IU of vitamin D per teaspoon. This has been the go-to treatment for vitamin D deficiency for years, as it gives you about 54 % of your DV. Canned Tuna This easy-to-store and flavorful alternative to fresh fish can provide 269 IU of vitamin D in a 100-gram serving, making it around 34% of the DV. Egg Yolks Whole eggs are an excellent source of vitamin D for those who do not prefer fish. While most of the protein is found in the white of the egg, the fats, vitamins, and minerals are located in the yolk. The yolk of one large egg contains 37 IU of vitamin D or 5% of the DV. Mushrooms Other than fortified foods, mushrooms are the only non-animal source of vitamin D. Mushrooms can synthesise vitamin D when exposed to UV light. However, they only provide Vitamin D2 instead of D3 in animal sources, which may not be as effective as animal sources. One cup of mushrooms contains around 136 IU of vitamin D, 17% of the DV. Commercially grown mushrooms in the dark contain minimal amounts of vitamin D2, while UV-treated mushrooms contain 1,110 IU. Fortified Foods The amount of vitamin D-rich vegetarian food is minimal, and some food products that are not natural are fortified with vitamin D. These include Cow's milk: Cow's milk is a food rich in nutrients like calcium, riboflavin, and phosphorus. Many countries fortify cow's milk with vitamin D. 1 cup of fortified cow's milk contains 115 IU of vitamin D. Soy milk: Plant-based milk is a substitute for cow's milk for vegans. This is why these milks are fortified with vitamin D and other nutrients usually found in cow's milk. One cup of soy milk contains 100-119 IU. Orange juice: 65% of people worldwide are lactose intolerant, and about 2% are allergic to milk. This is why some companies fortify orange juice with vitamin D and other nutrients like calcium. One cup of fortified orange juice contains 100 IU of vitamin D. Cereals and oatmeal: Cereals like wheat bran flakes contain 145 IU of vitamin D, around 18% of the DV, while crisp rice cereal has about 85 IU. However, not all grains are fortified; you must check the nutritional labels to determine how much vitamin D is in the product. Vitamin D and calcium Vitamin D is necessary for calcium absorption in the body. Calcium is needed to maintain bone strength and skeletal integrity. Getting enough vitamin D and calcium from your diet can protect you against disorders like osteoporosis, a condition characterised by weak and brittle bones. Like vitamin D, the recommended dietary allowance for calcium varies according to age. Children between the ages of 4-8 need about 1,000 mg of calcium daily, while those between 9-18 need 1,300 mg. Adults between the ages of 19 and 50 need 1,000 mg, and those over 50 need 1,200 mg of calcium daily. How can I increase my vitamin D fast? More sun exposure and eating vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, egg yolks, and fortified foods can help increase your vitamin D levels quickly. Which vegetables are high in vitamin D? Most natural sources of vitamin D are animals. You can take some amounts of vitamin D from wild mushrooms and mushrooms exposed to UV light. Which fruits and vegetables have vitamin D? Vegetables and fruits rich in vitamin D are scarce, and those with vitamin D do not contain adequate amounts to support the recommended dietary intake. What drink has the most vitamin D? Fortified drinks include cow's milk, soy, and orange juice. Check the nutritional label as only the fortified beverages have vitamin D, veggies or fruits rich in vitamin D are few. Conclusion Vitamin D is responsible for bone density and other vital systems in the body, including our immunity. The daily recommended value of vitamin D ranges between 400 to 800 IU but can change based on several factors. Fish, eggs, mushrooms, and fortified foods are considered vitamin D-rich foods, and you can also increase your Vitamin D intake by consuming vitamin D supplements. Keeping track of your vitamin D levels can help you maintain bone health and overall immunity. Diagnostic centres like Metropolis Labs offer a range of diagnostic tests that can help you check your vitamin D levels and keep your health on track.
Low Vitamin D and COVID-19: Are they related?
Vitamin D Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin, which can be produced by exposure to sunlight. Ultraviolet B rays of the sun activate a protein in the skin called 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC), which then is metabolized to the active form of vitamin D, which is vitamin D3. Dietary sources of vitamin D include egg yolk, milk, cheese, beef or calf liver and certain fish, certain cereals, soy milk, etc. Vitamin D has a number of critical roles in your body. Among these, key functions include absorption of calcium that helps strengthen bones, efficient muscle movement, aids in nerve conduction to and from the brain. Besides, vitamin D is important for immunity as it helps regulate immune system to fight off invading pathogens like bacteria and viruses. Vitamin D and viral infection Various studies have shown that Vitamin D supplementation helps in reducing the susceptibility of developing a flu by acting as a physical barrier against the infection, or through modulation of natural and/or adaptive immunity mechanisms to reduce the risk of infection.2 Research also supports the finding that low levels of vitamin D increases the risk of community acquired-pneumonia. Get your vitamin D levels tested within the comfort of your home. Association of vitamin D and COVID-19 The novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), responsible for the COVID-19 disease, has been implicated in the deaths of over 3.5 million people globally. Currently, there is no definite treatment available for this infection, hence, measures are being taken to discover aids that can help in reducing the risk of COVID-19. Moreover, owing to its high infectivity rate, the population also requires strategies that can limit progression and severity of COVID-19 infection. A study published in the Endocrine Society's Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, revealed that over 80% of COVID-19 patients in a hospital exhibited vitamin D deficiency. Therefore, the appropriate approach includes identification and treatment of vitamin D deficiency, particularly in high-risk individuals such as the elderly, patients with comorbidities, who are the main target population for the COVID-19. Moreover, low levels of vitamin D are associated with 3.7-fold increase in the odds of dying from COVID-19 infection. Similar findings were seen in a Asian study that showed vitamin D insufficiency might compromise respiratory immune function, increasing the risk of severity and death rate in patients with COVID-19. The most commonly encountered symptom in patients with COVID-19 is fever and dry cough, whereas severe forms of the disease can lead to the development of acute respiratory disease syndrome (ARDS). Researchers have found out that vast majority of COVID-19 ARDS patients had vitamin D deficiency, and these patients required longer mechanical ventilation and were associated with a higher death rate. In addition to ARDS, heart failure is one of the fatal adverse outcomes of COVID-19. Studies have shown that Vitamin D supplementation, because of its protective effect on cardiac muscle cells, can be beneficial by reducing the risk of heart disease in these patients. Besides, comorbidities like high blood pressure, diabetes, obesity are considered as risk factors in increasing complications in people with COVID-19. Various studies have found strong correlation between deficiency of Vitamin D and increased risk of high blood pressure, diabetes and obesity. Hence, the hypothesis suggests that its supplementation can decrease the likelihood of complications in patients infected with COVID-19. Furthermore, vitamin D deficiency has been related to reduced immune function and may enhance the cytokine storm and its supplementation may reduce complications related to cytokine storm and uncontrolled inflammation in people with COVID-19. Hence as per some experts, one of the management strategies for reducing severity and death rate in patients with COVID-19 should include normalization of vitamin D levels. Beneficial effects of vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 patients Numerous research have shown that having healthy levels of vitamin D can help keep your immune system healthy and may protect against respiratory illnesses. Although there is currently no cure for COVID-19, studies have highlighted the importance of vitamin D supplements in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 complications. Some of the evidence suggesting benefits of vitamin D supplementation in COVID-19 are as follows: It has been reported that a high dose of vitamin D could reduce the need for intensive care stays in patients infected with COVID-19. Vitamin D supplementation was considered as a safe therapy, and it protected against acute respiratory tract infection. An Indian study suggested that high dose of Vitamin D3 (60000 IU) supplementation for seven days helps in coronavirus clearance. Although most older individuals, often have lower vitamin D levels and are most susceptible to COVID-19, a study showed that supplementation of vitamin D could decrease death rate in this group. Make sure to take extra care of your elderly. Book an exclusive health package for seniors. The general recommendation is to supplement people who do not belong to a risk group, are healthy with a recommended daily dose (800 IU). In view of the positive effects of vitamin D supplementation on vitamin D-deficient patients with COVID-19, few practical recommendations are as follows: Current public health guidelines for normalizing vitamin D status should always be followed Vitamin D levels should be measured in patients hospitalised with COVID-19 and should be supplemented to a level >30ng/mL (optimal 40–60ng/mL), specifically when the baseline level is <10ng/mL In Covid-19 patients with vitamin D levels under 20ng/mL, the recommended dose for correction of deficiency is 6000–7000 oral IU/ day for 6–8 weeks. For maintenance, the dose varies from 2000 to 3000 oral IU/day according to the age and clinical condition of the individual. To summarize Although India is a subtropical country with sufficient sunlight, vitamin D deficiency is extremely common. It is crucial for people to understand the importance of Vitamin D so that they can take relevant supplements to fill the gaps. Vitamin D will not prevent a patient from contracting the COVID-19 infection; however, it may reduce complications and prevent death in those who are infected. It is hard to ascertain the most appropriate beneficial dose for COVID-19, it is evident that vitamin D deficiency is harmful, and can be easily addressed with implementation of low-cost and low-risk vitamin D supplementation. It is unclear how soon the majority of the population will receive vaccines, routine vitamin D supplementation to high-risk people such as the elderly, children, those who are malnourished, and those living in overcrowded environments can be a worthwhile exercise.
Why you need more vitamin D in the Winter
The sunshine vitamin, vitamin D, requires exposure to ultraviolet-B (UVB) rays from the sun for its synthesis. During the sunny summer days, making enough vitamin D can be very efficient. However, as soon as the winter arrives, less sunlight is available and the risk of vitamin D deficiency increases. As per many researchers, your body needs vitamin D not only to maintain bone health but also to keep healthy and to fight infections. The irony is that in winter, when you need vitamin D the most, you end up getting deficient for this essential vitamin. You can fix a problem only when you know it exists. Especially during the winter months, experts recommend a blood test that assesses the amount of vitamin D in the body. It is particularly important for you to get tested for vitamin D if you are over age 70, have darker skin, have malabsorption problems or take medicines that interfere with vitamin D absorption (for example, glucocorticoids). If you have liver and kidney disease, you can be often deficient in vitamin D. These organs are required to make the active form of the vitamin, whether it comes from the sun or from food. For a good gut health during winter Enough has been known and written about vitamin D deficiency leading to bone diseases like rickets in children and osteoporosis in adults. However, research has shown that vitamin D plays an important role in maintaining a healthy digestive tract. One of the ways vitamin D functions is by keeping the gut microbes healthy. If you have sufficient vitamin D levels, you are more likely to have those healthy gut bacteria just right in number and diversity. This helps reduce inflammation throughout the body. On the other side, low vitamin D levels can be associated with inflammatory bowel disease in some people. Strong immunity needs vitamin D There has been a lot of buzz around the role of vitamin D in boosting immunity. This holds great significance in the times of COVID-19 pandemic. Some scientists have claimed that the immune system has vitamin D receptors that determine which cells can use vitamin D. Having enough of this sunshine vitamin might help improve your ability to fight infections and reduce inflammation. Less time spent outside In the winter, you are more likely to catch infections. Also, you are more likely to lie comfortably in your cozy blanket and spend less time outside. This leads to more and more of us getting vitamin deficiency in the winter. Vitamin D and Calcium, the best friends Vitamin D helps you absorb calcium from your diet. Along with vitamin D, calcium plays a significant role in keeping your bone and muscles health intact. Eat healthy to get enough vitamin D Apart from exposure to the sun, you can get enough vitamin D for your body through certain food items as well, including tuna, sardines, mushrooms and fortified dairy and orange juice. Adding vitamin D supplements can be a good way to reach the recommended vitamin D intake. Lack of sun exposure during the winter months would be less of a problem if diet provided adequate vitamin D. But there aren't many vitamin D–rich foods , and you need to eat a lot of them to cover up the recommended vitamin D intake of 10 μg/day (400 IU/day) for adults. The COVID-19 angle Some of the recent researchers have claimed that people who are deficient in vitamin D are more likely to get severe COVID-19 illness. Vitamin D deficient people might have a higher chance of getting hospitalized too. Whether vitamin D has any role in preventing coronavirus infection or not, it isn't clear yet and needs more data and robust evidence. Think you have symptoms suggestive of COVID-19? Book a COVID-19 test and get tested at home. Overdoing is prohibited, too While you aim to get enough vitamin D, keep in mind that too much vitamin D can be harmful. Want to know exactly how much vitamin D healthy adults should have? Or confused about when to get tested for vitamin D? Check out this article to stay in the know. Remember that the same UVB rays that help in vitamin D synthesis, can damage your skin as well. Under the right circumstances, 10 to 15 minutes of sun on the arms and legs a few times a week can generate nearly all the vitamin D we need. However, various factors affect this synthesis: the season, the time of day, where you live, cloud cover, and even pollution levels. In addition, your skin's production of vitamin D is influenced by age, skin color, and sunscreen use. Book a vitamin D test to be sure if your levels are enough to support a healthy you. This winter, get tested on time and don’t let your body suffer from lack of vitamin D by taking early steps. Also read "Why and when you should get tested for Vitamin D?"
Vitamin D Deficiency: 7 Symptoms and Signs of Low Vitamin D
When was the last time you saw the mild sunrays in morning? Or waited for few minutes while your skin soaked in the sunlight at dawn. Are you feeling depressed? Are you always hungry? Are you facing anxiety issues? Have you put on extra belly fat? If yes to all the above, then your body might be deficient in Vitamin-D. Vitamin-D deficiency is quite common, and yet most people are not aware when they suffer from it. That's because the symptoms are often subtle and non-specific, meaning that it's hard to know if they're caused by low Vitamin-D levels or something else. Mild sunlight in morning is the best source of Vitamin-D. Other sources of Vitamin-D are cheese, egg yolks, soymilk, fatty fish, salmon, tuna, mackerel, mushrooms. If your daily exposure to sunlight is limited because you wake up at later hour, if you stay indoors for long duration, live in northern latitudes or have an occupation that prevents sun exposure you may be at risk of Vitamin-D deficiency. If you think you may have a deficiency, it's important that you speak to your doctor and get your blood levels measured. Fortunately, a vitamin D deficiency is usually easy to fix. You can either increase your sun exposure during morning, eat more Vitamin-D-rich foods, such as fish or fortified dairy products. You can also find a variety of Vitamin-D supplements. Vitamin-D supplements should be taken by advice of a doctor. Common signs and symptoms of Vitamin-D deficiency - Common signs and symptoms of Vitamin-D deficiency - Depression and anxiety Body produces serotonin from the body chemical melatonin, melatonin is produced in response to sunlight, the more exposure to sunlight results in more melatonin thus more serotonin. Too little of serotonin leads one to feel cranky, irritable, depressed, anxious. Muscle pain, bone pain, low bone density Due to vitamin-D deficiency, there will be inadequate absorption of calcium in the body, vitamin-D helps in absorption of calcium. In case of inadequate Vitamin-D in body low bone mineral density can occur which results in chronic muscular pain, pain in joints, osteoporosis. Hair loss Stress, anxiety, depression, low immunity gradually causes hair loss. As all the above are signs of vitamin-D deficiency. Calcium, vitamins and minerals are major building components of hair and skin and nutritional deficiencies do affect their vitality. 65% of Indians have Vitamin-D deficiency! Get yourself and your family checked up for Vitamin-D. Click here to know more Unexplained infertility It is observed that the vitamin-D deficient women have less chances of getting conceived. Poor wound healing It's also been suggested that vitamin-D's role in controlling inflammation and fighting infection which is important for proper healing. Poor immune function, increased risk of illness or infections One of vitamin-D's most important roles is keeping your immune system strong so you're able to fight off viruses and bacteria that cause illness. It directly interacts with the cells that are responsible for fighting infection. Constant feeling of fatigue and tired are the signs of low vitamin-D If you find these symptoms then you lack vitamin-D, though it’s not life threatening initially but it does affect quality of life. Wishing you a very happy and healthy life. Take care. Contributed by - Dr. Anushree MV, an Ayurvedic physician specializing in weight loss, PCOS, thyroid disorders, diabetes, infertility and childcare.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload

















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp