typhoid fever blood test
Metropolis Experts Explain How to Stay Away from Typhoid with Handwash and Vaccines
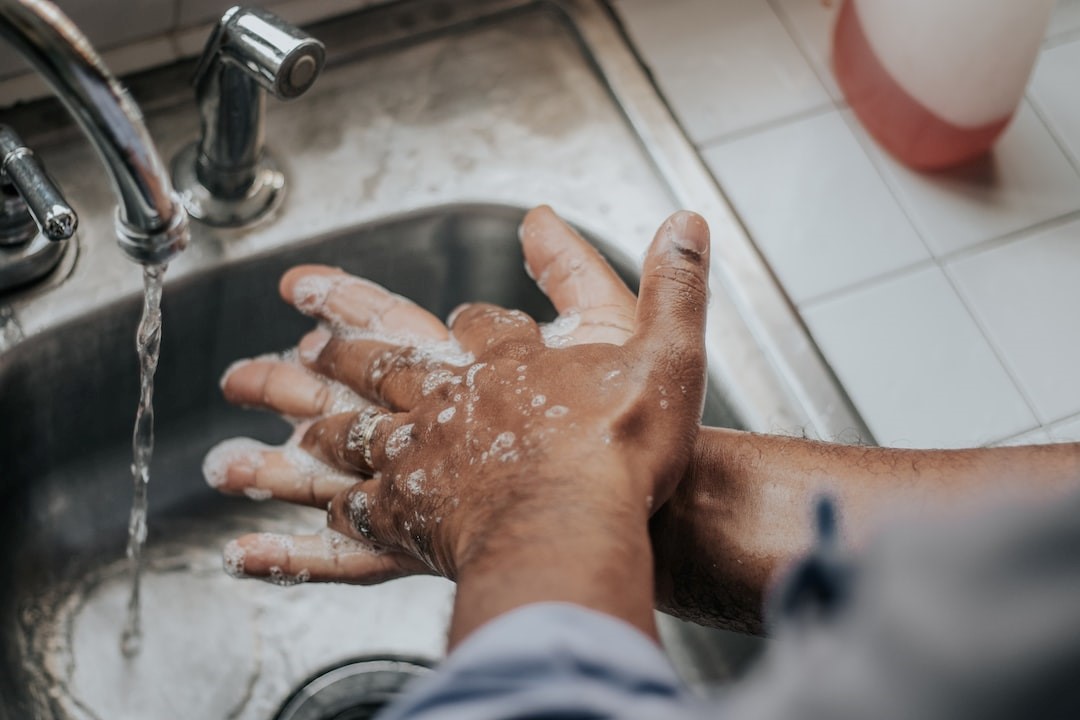
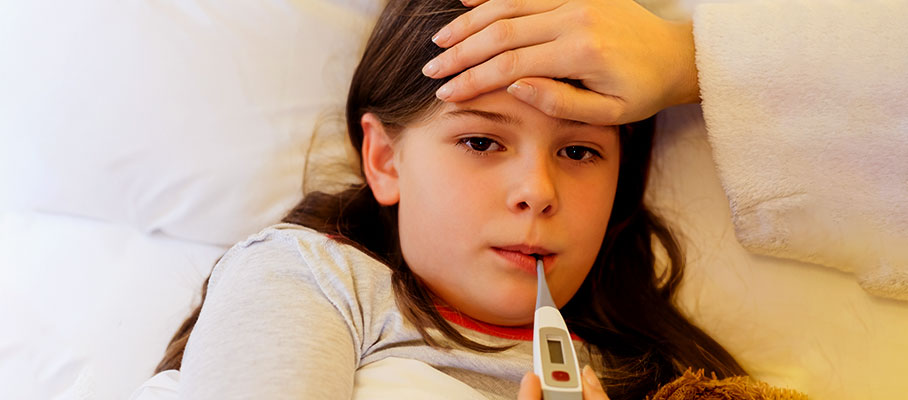
Typhoid is one of the epidemical health issues that has affected humans through the centuries. The first outbreak was witnessed in 430 BC. Later in 1850, English physician William Budd described it as a water-borne disease caused by bacteria. During early recognition, people were unaware of its consequences and safety measures. But now, many counter-solutions are present to fight back against the disease or prevent it. For instance, several medicines and antibiotics have been invented, and multiple items like water filters, soaps, and handwash are readily available to save people from life-taking illnesses. According to Dr R Lakshmi Priya, Senior Consultant Microbiologist & Molecular Biologist, at Metropolis Healthcare, Chennai, parents are reluctant to give street food to their children because typhoid spreads through contaminated food and water. She says that typhoid spreads through Salmonella enterica bacteria which can lead to two types of fever: typhoid caused because of Salmonella typhi and paratyphoid caused because of Salmonella paratyphi. What is Typhoid? Typhoid is a bacterial infection caused by Salmonella typhi. It spreads through infected food and water and multiplies after entering the blood. Under proper medical supervision and guidance, typhoid patients recover within 7 to 10 days, but in some cases, they may also take up to two weeks. However, if left unnoticed for a long time, it may prove to be fatal. Complications associated with typhoid include developmental issues in the bone, meningitis, and intestinal ulcers or perforation. Causes of typhoid Even though multiple health programs, promotions, and guidelines have been declared by the World Health Organisation (WHO), there are countless typhoid attacks today. It mainly hovers on the Asian and African belts. Nearly millions of people die every year from typhoid fever. An eye-opening fact is that the people here often lack the basic amenities of life. Hence, they cannot manage to protect themselves from the bacterial strike. The most probable causes of typhoid are: ● Poor hygiene and sanitation ● Insufficient water supply ● Unfiltered water and contaminated food intake ● Rising slums and crowds ● Inadequate medical supplies ● Lack of information and awareness Recently, people have been diagnosed with a resistant strain of typhoid bacteria. According to Dr Laxmi Priya, the bacteria has modified itself in such a way that it has become resistant to new medications but remains sensitive to old ones. Therefore, it is necessary to stop the overuse and misuse of antibiotics. Nevertheless, she adds that most antibiotics are still effective against bacteria. Symptoms of typhoid It is beneficial to seek medical advice at an early stage of the disease to prevent complications. Generally, a person shows the following symptoms if typhoid bacteria enters the body. ● High fever throughout the day ● Chills ● Muscle aches and rashes ● Headache and stomach pain ● Weakness and tiredness ● Alternating constipation or diarrhoea ● Vomiting ● Cough It is advisable to consult a physician to know about the curative measures to eliminate the illness. Several advanced technologies are available to help analyze one's condition and get the necessary treatment. When should one visit a doctor? The bacteria, Salmonella typhi, has an incubation period of two weeks. However, patients can start showing symptoms as early as 2 to 3 days after contracting the bacteria. The best way to confirm the bacterial attack is a blood test. If a person gets a positive result, he or she must instantly consult a medical practitioner. Wasting a single moment can bring out severe aftereffects. As per Dr Laxmi Priya, if a patient is not vaccinated or if the infection remains undiagnosed or untreated, then it may lead to complications like perforation and haemorrhage. The doctor will recommend medicines, antibiotics, and rest to ensure complete recovery. Treatment and diagnosis of typhoid For diagnosing typhoid, several kinds of blood tests may be performed. These include: Blood culture test: This is done to confirm the presence of bacteria. It is usually done twice, once for confirmation and the second time after taking medications. Typhidot rapid antibody test: This test detects antibodies against the bacteria and is done in the second week of diagnosis. Widal antibody test: This test also detects antibodies against the bacteria and is done within six to seven days of fever. Stool and urine culture test: This is done in the fourth week of infection. This test is also done to diagnose asymptomatic typhoid carriers who do not show symptoms but show the presence of bacteria in their stool or urine. There are several antibiotics which are effective in typhoid. These medications work by killing or disintegrating bacterial cell membranes. Patients need to take proper doses of antibiotics as typhoid can come back if treated inappropriately. If the duration of the antibiotic is not appropriate or in case the right antibiotics are not taken, then it will allow bacteria to survive in the body. Such bacteria may remain in the bone marrow, intestine or bloodstream and can recur in 2-3 weeks after initial recovery. What are the steps to tackle typhoid? Medical specialists are concerned about the advent and spread of antibiotic-resistant strains of the bacteria. Research is ongoing, and doctors are struggling to find cures for the uncommon strains of typhoid bacteria. Moreover, the government and NGOs are working together to guide people about the new strain and educate them to take the required preventive measures. Preventive measures include: ● Washing hands before and after eating ● Washing hands after using the toilet ● Avoiding eating open and stale food, especially from street vendors ● Using filters and chlorinated water for regular drinking ● Washing fruits and vegetables before eating ● Using hand wash and hand sanitisers Apart from the above-mentioned points, people should also take proper vaccinations. There are two types of vaccines available, one is an inactive vaccine (injection) and the other is a live vaccine(oral). But it must be noted that these vaccines are not 100% effective and cannot work as a replacement for eating and drinking hygienic food. According to Dr Lakshmi Priya, there is a new typhoid vaccine available called typhoid conjugate vaccine, which provides longer immunity against the disease. Conclusion Typhoid has been a concerning health problem for years. However, it is a treatable condition if diagnosed on time and treated appropriately. In addition, since it is a food and water-borne disease, people may protect themselves from falling prey to typhoid bacteria through preventive measures. Therefore, people must eat hygienic food and drinks, avoid food kept in the open, clean their surroundings, use handwash before eating food, and take vaccines on time to avoid being infected. If symptoms occur, one should immediately visit a doctor and take medications as prescribed.
Typhoid Fever: Signs, Symptoms, Causes, Stages & How Long Does it Last?
Typhoid is one of the most common intestinal (enteric) infections known to mankind. An estimated 11–21 million cases of typhoid fever and 200,000 deaths occur worldwide annually. An estimated 5 million cases of paratyphoid fever occur worldwide each year, with the highest number of cases in Southeast Asia. Typhoid fever is a disease that spreads through contact with affected persons or by ingesting or drinking contaminated substances. It is caused by Salmonella typhi. Common symptoms of typhoid fever include stomach cramps, nausea, vomiting, and high body temperature. If typhoid fever is caught early, medications can be highly effective. Typhoid has a high mortality rate in cases of delayed treatment. Beware.. the monsoon season may exacerbate typhoid. Experiencing symptoms suggestive of typhoid? Book your Typhoid Serum Test. Typhoid Fever Causes Typhoid fever is a serious and sometimes life-threatening infection that mostly affects people in developing countries, where sanitation is poor and getting clean water is a problem. Typhoid is caused by a bacterium called Salmonella typhi which is also related to the Salmonella bacteria that results in food poisoning. It is transmitted when a person eats or drinks something contaminated with the bacteria. When the bacteria get into the body, it quickly multiplies and spreads into the bloodstream. There are certain factors which can elevate the risk of typhoid fever. These include: Traveling to areas where typhoid fever is common (endemic areas). Being in a profession where exposure to the bacteria is likely, for example, those working in hospitals and laboratories. Coming in close contact with a person suffering from typhoid. Typhoid Fever Symptoms As typhoid is an enteric infection, it affects the intestine and hence, the typhoid symptoms one experiences are related to digestion. Generally, the signs and symptoms of typhoid fever start showing up gradually over a period of 10-14 days after exposure to the bacteria. The duration of the typhoid illness is about 3-4 weeks. Some signs and symptoms of typhoid fever which indicate you might be infected with the condition include: Irregular fever that can go as high as 104.9 ˚F (40.5 ˚C) Headache Pain in the abdomen Feeling of tiredness and weakness Muscle pain Loss of appetite/anorexia Nausea and vomiting Constipation or diarrhea Without treatment, typhoid fever may last a month or more and become very serious, even life-threatening. Fever can occur due to various other infections as well. Do not rely on guesswork and get yourself tested. Book a fever panel package and check for 5 diseases at one go. How Do People Get Typhoid Fever? Typhoid fever is spread by the consumption of unhygienic food or water. Acutely unwell patients pose a threat to the water supply because their faeces contain a high quantity of germs. Because water is used to grow, process and transport food, any contamination of that water might poison the food itself. After recovering from a severe infection, between 3 and 5% of people continue to have the bacterium. Some people have undetected, minor illnesses. These people are at risk of becoming chronic carriers of the disease. Bacteria populate the intestine after multiplying in the liver, bile ducts, or gallbladder. This bacteria may live in water or dry sewage for weeks. These asymptomatic chronic carriers may be the cause of future typhoid epidemics. What are The Stages of Typhoid Fever? If you have typhoid, you might be wondering when you’re going to feel better. But there’s not just one answer because there are different stages of typhoid fever. There are 4 Stages of Typhoid Fever or enteric fever and each lasts up to a week. The First Stage In this typhoid stage, the patient experiences some of the preliminary typhoid symptoms such as dry cough, indolence or headache. This may or may not be accompanied with fever. Even if fever occurs, your body temperature will not be much higher than normal. The Second Stage During this typhoid stage, fever runs high and the stomach becomes bloated. Weight loss is another significant sign of this stage. Hallucinations or fever dreams are common. The person might feel lethargic and agitated in alternation. The Third Stage This is the stage when things get really serious. Severe intestinal perforation may cause abdominal haemorrhage. Encephalitis or inflammation of the brain may set in. The person may become dehydrated which increases the intensity of the delirium. The person faces difficulty in sitting up, let alone standing or walking. The Fourth Stage This typhoid stage is characterized by extremely high fever. It brings along several other health complications including severe infections, kidney failure, pneumonia, inflammation of the pancreas or Meningitis. In some people, the bacteria that causes typhoid can remain in the body for a prolonged period of time. According to Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), it is estimated that between 1% and 4% of treated patients still excrete Salmonella typhi bacteria in their feces 12 months or more after they are ill with typhoid. A long course of antibiotics is necessary to get rid of the typhoid bacteria in these people. Some people who are treated for typhoid fever also experience a relapse, which is when symptoms return. In these cases, the symptoms usually return around a week after antibiotic treatment has ended. The second time around, symptoms of typhoid are usually milder and last for a shorter time than the original illness, but further treatment with antibiotics is usually recommended. It is best to consult your doctor as soon as possible if your symptoms return post the treatment. How is Typhoid Fever Diagnosed If you experience any signs and symptoms of typhoid fever, it is wise to consult a doctor, who will do a physical examination and order a few tests to diagnose the condition. Physical findings in early stages point to abdominal tenderness, enlarged spleen and liver, enlarged lymph nodes, and development of a rash (also known as rose spots because of their appearance). Your medical provider may ask for a few laboratory investigations as follows: Blood tests to detect IgM and IgG antibodies and blood culture test to detect the bacteria Salmonella typhi. Stool and urine analysis to check for the presence of the bacteria. Widal antigen test is a simple, inexpensive test and takes only a few minutes, but there is a longer waiting phase of about 10 days till results can be seen. The conventional Widal test detects antibodies to the bacteria from week-2 of onset of symptoms. Typhi dot tests can serve as a marker for recent infections and can detect early rising antibodies that are predominantly IgM. Bone marrow culture is also recommended but it is rarely required except in patients who have already received antibiotics and whose condition doesn’t seem to improve. It is one of the most sensitive tests for typhoid fever. Monsoon may increase chances of gut infections As typhoid is quite common during monsoon due to high chance of water and food contamination, is it advised to keep note of any symptoms and get tested early on time. Also, if anyone in your family suffers from the condition, it is important to follow all the necessary hygiene and sanitation protocols. How is Typhoid Fever Treated? For the signs of recovery from typhoid fever to show, antibiotics are recommended by doctors. If caught early, the infection is typically relatively manageable, and a 7- to 14-day course of antibiotic pills will do the trick. To administer antibiotic injections for more severe instances of typhoid fever, hospitalisation is typically required. Most patients will feel better after taking antibiotics for only a few days, and severe problems almost seldom occur. Nowadays, typhoid-related deaths in India are extremely rare. Despite this, it is believed that up to one out of five persons infected with typhoid fever may perish if they do not receive treatment, and some of those who do survive may be left with severe physical or mental problems. What are The Signs of Recovery? Signs of recovery from typhoid fever are here: Restored appetite Nobody pains, including headaches and stomach aches Normal body temperature (i.e., no fever) Diminished fatigue Reduced diarrhoea No chest congestion Takeaway Early diagnosis is key to effective treatment for typhoid fever. Antibiotics are the only way to cure typhoid. It can be deadly if caught too late. Get yourself tested for typhoid fever if you notice its symptoms growing in your body.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp