pregnancy symptoms
Accurate and Safer Diagnosis with Metropolis PregascreenTM Reflex Testing with NIPT: A Metropolis Study
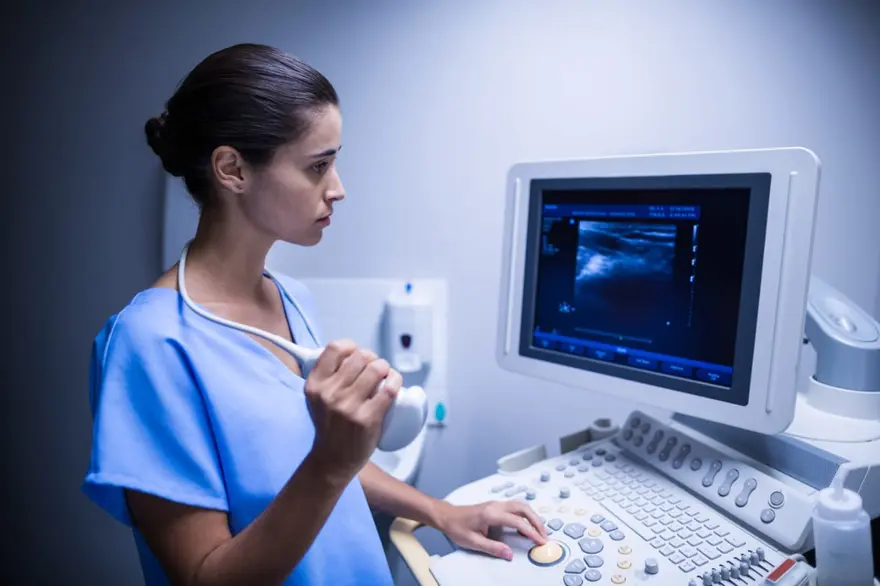
In the realm of prenatal care, ensuring the health and well-being of both mother and child is paramount. The early detection of chromosomal anomalies in fetuses plays a crucial role in providing families with accurate information and facilitating informed decision-making. The advancement of medical technology has led to the development of innovative screening approaches, offering more accurate results and reducing the need for invasive procedures. One such groundbreaking method is the Metropolis PregascreenTM reflex testing with Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT), which promises accurate and safer diagnosis. Understanding Prenatal Screening Prenatal screening has undergone significant evolution over the years, moving from basic ultrasound assessments to sophisticated genetic testing methods. Traditional approaches, such as maternal biochemical dual and quadruple markers, have been widely used to assess the risk of fetal chromosomal abnormalities. However, these methods have limitations in terms of their detection rates and potential for false positives. Enter Metropolis PregascreenTM Reflex Testing The Metropolis PregascreenTM reflex testing approach introduces a paradigm shift in prenatal screening. This innovative strategy combines traditional maternal biochemical markers with cutting-edge technology to provide more accurate and comprehensive results. The crux of this approach lies in the incorporation of NIPT, a method that evaluates cell-free fetal DNA (cfDNA) from maternal blood to detect common chromosomal abnormalities. The Metropolis Study To assess the clinical validity of the Metropolis PregascreenTM reflex testing approach, a comprehensive study was conducted. The study involved analyzing retrospective data from 51,574 Indian women who underwent maternal marker screening between January 2021 and March 2022. The goal was to determine the effectiveness of this approach in accurately identifying high-risk cases and providing a safer diagnostic path. The study yielded promising results, showcasing the potential of the Metropolis PregascreenTM reflex testing approach. Out of the total high-risk cases identified through traditional screening methods, a significant portion—34.65%—opted for NIPT. This choice reflects the growing trust in the accuracy and reliability of NIPT in identifying chromosomal anomalies. Furthermore, the study demonstrated that NIPT had the ability to reclassify a substantial percentage of high-risk cases as low risk, leading to a more accurate assessment and potentially reducing unnecessary stress for expectant parents. Advantages of Metropolis PregascreenTM Reflex Testing The Metropolis PregascreenTM reflex testing approach offers several advantages that contribute to accurate and safer diagnosis: Reduced Need for Invasive Procedures: One of the most significant benefits is the reduced reliance on invasive procedures like chorionic villus sampling and amniocentesis. NIPT provides a non-invasive option that yields accurate results without the associated risks of miscarriage. High Accuracy: The study showcased that the accuracy of NIPT, when integrated with the Metropolis PregascreenTM reflex testing approach, is comparable to karyotyping, the gold standard for chromosomal anomaly detection. Informed Decision-Making: Accurate and early diagnosis empowers expectant parents with the information they need to make informed decisions regarding their pregnancy. Safer Diagnostic Journey: By minimizing the need for invasive procedures, the approach reduces potential risks to both the mother and the fetus, leading to a safer diagnostic journey. Conclusion The Metropolis PregascreenTM reflex testing approach with NIPT heralds a new era in prenatal care. Its ability to accurately identify high-risk cases and provide a safer diagnostic path signifies a positive transformation in the way we approach prenatal screening. The study's findings underscore the significance of integrating advanced technology with traditional screening methods to achieve more accurate results, greater patient satisfaction, and ultimately, healthier outcomes for both mothers and their unborn children. As we continue to embrace the potential of innovative approaches, we move closer to a future where accurate and safer diagnoses become the norm in prenatal care. Read the Original Article here - Clinical utility of PregascreenTM reflex genetic testing for pre-natal screening in Indian population: A new diagnostic approach - IJOGR
Early Symptoms of Pregnancy And When To Get Tested
Significant hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy trigger a variety of symptoms. These symptoms of an early pregnancy may vary dramatically from woman to woman. Some women may experience many of the symptoms of pregnancy, while others may notice only a few or no symptoms at all. Some women feel certain they're pregnant within the first few days of pregnancy, or others don’t notice anything until they miss a period. The earliest symptoms of pregnancy are more than the hallmark symptom of a missed period. They may also include morning sickness, fatigue, spotting, breast changes, and frequent urination. Early symptoms of pregnancy can sometimes be confusing because these symptoms can be caused by other factors and do not necessarily mean that you are pregnant. It’s really important not to compare your pregnancy to someone else’s because pregnancy is a unique experience for each woman. Your doctor will usually order an hCG blood test to confirm pregnancy. Book a test here with Metropolis and get results online. Common early symptoms of pregnancy The most common early symptoms of pregnancy might include: Missed period: Missing a period is often the first clear-cut sign of possible pregnancy. Once implantation has happened, your body produces human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) hormone that helps the body maintain the pregnancy and stops ovulation and the shedding of the uterus lining. However, missing your period can be misleading if you typically have an irregular period. Irregular periods might also be caused by factors such as stress, excessive exercise, dieting or hormone imbalances. Enlarged, tender and swollen breasts: Early in pregnancy the breasts become fuller, swollen and tender due to hormonal changes. The discomfort will lessen after a few weeks when your body gets adjusted to the hormones. Hormones continue to make your breasts grow. The area around the nipple (areola) becomes darker and grows larger. Morning sickness: Though it is called morning sickness, it can occur at any time of the day or night. It often develops as early as 2 weeks into a pregnancy, or it can start a few months after conception and may settle as you enter the second trimester. The symptoms include loss of appetite and nausea with or without vomiting. However, it is possible that a few women may not experience nausea. Fatigue: Fatigue is another most common early symptom of pregnancy. Many women feel overwhelming tiredness in early pregnancy. This is most likely caused by a rapid rise in the hormones during early pregnancy, especially sex hormone called progesterone. It helps maintain the pregnancy and makes the baby grow, but it also slows your metabolism. Try to get enough sleep or rest when you can during early days of your pregnancy. Your energy levels will probably rise again as you enter the second trimester. Another possible cause of tiredness during pregnancy could be anemia, which is most commonly caused by iron deficiency. So eating iron-rich foods and iron supplements is important to prevent iron deficiency anemia during pregnancy. Frequent urination: During pregnancy, you may notice yourself urinating more often than usual. This actually happens because the body’s blood supply increases during pregnancy, causing your kidneys to process more fluid than usual, which leads to more fluid in your bladder. Food cravings and food aversions: When you're pregnant, cravings for certain foods are very common. You might become sensitive to certain odors and may also notice a sudden distaste for foods you previously enjoyed. Spotting: Spotting is also known as implantation bleeding which may be mistaken for a light period. Implantation bleeding occurs when an embryo gets implanted in the endometrium lining of the uterus at blastocyst stage. It is a less common symptom and doesn’t occur for everyone. If it does occur, it usually happens around the time of your regular period or around week 4 of your pregnancy and lasts for a few days to a few weeks. Other less common symptoms of early pregnancy can include metallic taste in your mouth, headaches and dizziness, cramping, mood swings, bloating, constipation, nasal congestion, heartburn, faster heartbeat and high blood pressure. The above symptoms can only give you an idea that you’re pregnant, but they are not a sure sign. Only a test will give a definite result. When should you take a pregnancy test? If you suspect you might be pregnant, the best time to get tested for a home pregnancy urine test is 1 week after you have missed your period. If you take a test earlier than this, you may run the risk of getting a false negative result. This means the test may come up negative, even if you are actually pregnant. A pregnancy test measures a hormone called human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) that is present in the blood and urine of pregnant women. This hormone starts building in your body rapidly in the beginning of your pregnancy, as early as 10 days after conception. Though hCG appears early in the process, you still need to wait (about 3 to 4 weeks from the first day of your last period) for enough hCG to build up in your body for a positive pregnancy test. Early test results may not be the most precise. Unlike at-home urine tests, blood tests can often detect hCG earlier in a pregnancy but it must be done in a clinical setting. Blood tests can sometimes give a positive pregnancy test result as early as 6 to 8 days after ovulation. At-home pregnancy tests are widely available without a prescription in drug stores. It is advised that if you get a negative result on a home pregnancy test, take another test a week later to recheck or contact your doctor if you want a blood test. If you receive a positive result, you can then get started on a prenatal program to safeguard the health of both you and your growing baby. Important Links: To book Triple marker test, click here To book Maternal Serum Screening test, click here
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp