Preventive Healthcare
NIPT Vs First-Trimester Maternal Screening
3423 Views
0
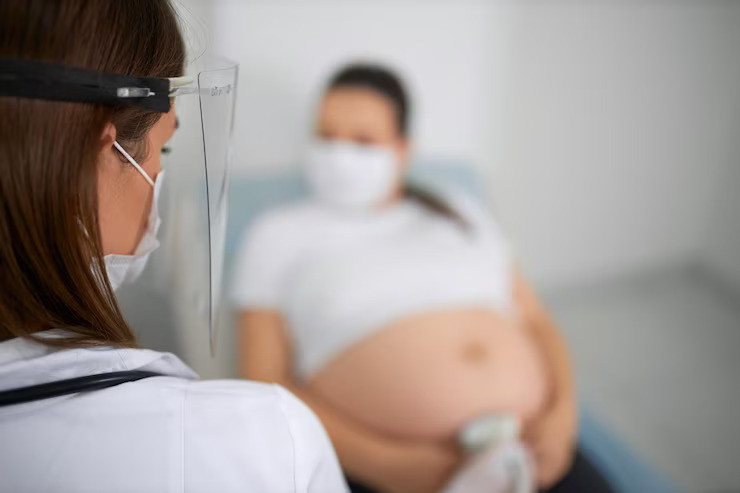

Every new parent and expectant mother needs to figure out the best way to check on the health and well-being of an unborn child. In recent years, non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) and first-trimester maternal screening tests have become popular ways for parents-to-be to learn about their unborn baby's health.
But what are the differences between NIPT and maternal screening tests, and which should you choose?
Overview of Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
NIPT is a safe, non-invasive lab test that can tell you about the genes of your unborn child.
A blood sample is taken 8–14 weeks into your pregnancy and analysed for the presence and types of chromosomes in the fetus. It is a very accurate way to determine if a baby has Down syndrome or another genetic condition. It doesn't have the risks of more invasive tests like amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS).
It is pretty good at telling how likely the condition is to happen for the other conditions, but it is not always a final diagnosis.
Introduction To First-Trimester Maternal Screening
First-trimester screening tests for expecting mothers are very helpful because they can tell a lot about the health of their unborn child. These tests are like an early warning system that lets parents know about possible health problems they may want to test for further in the future. While they are not a diagnosis, they can help guide decisions on further testing and provide peace of mind.
The tests typically occur between the fifth and ninth weeks of pregnancy and are usually done as blood tests. They are designed to assess the risk of certain chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, Trisomy 18, and other conditions. Most importantly, the results should never be considered a final diagnosis since they only show the risk.
These tests are an incredibly important part of the prenatal care process for expecting women.
What Does a First-Trimester Maternal Screening Test Look For?
A simple blood test can check for possible rises in the levels of two hormones—hCG and PAPP-A—during the first trimester. The placenta naturally makes these hormones. The test results, the mother's age, and information from the ultrasound is used to determine how likely the baby will have chromosomal abnormalities.
This test can provide additional information about a baby’s risk for certain chromosomal abnormalities and other birth defects, including Down syndrome, trisomy 18, and trisomy 13, which can help healthcare professionals to plan for the best care for mother and baby. It is important to note that the test is not meant to be used as a diagnostic tool. It is only used to identify potential risks and provide additional information that can be used by healthcare professionals when counselling clients.
Introduction To Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT) is a more advanced form of prenatal screening than traditional first-trimester maternal screening. It gives more accurate results. NIPT typically takes place around 10 weeks into the pregnancy and is based on analyzing the mother's cell-free DNA, or fDNA/cfDNA. It tells mothers about their baby's health, chromosomal conditions, and genetic diseases so that they can learn more about their child's health.
NIPT is an excellent choice for mothers at risk for genetic diseases or wanting to know more about their baby's health. This testing process can provide early answers and peace of mind, making prenatal care less stressful.
What Does The NIPT Examination Look For?
NIPT (Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing) is a test that can detect chromosomal abnormalities in the unborn baby, such as Down Syndrome, Trisomy 18, Turner Syndrome, and many other conditions. It does this by mapping the baby’s DNA from the mother’s blood sample.
NIPT is a highly accurate test that outperforms first-trimester maternal screening. First-trimester screenings are more traditional tests used to detect genetic abnormalities and are less accurate than NIPT.
Even though NIPT is a more reliable and accurate way to find chromosomal abnormalities, not all pregnant women need to take the test every time. However, pregnant women need to discuss all their options with their healthcare provider and decide which testing option is best for them.
NIPT Vs First-Trimester Maternal Screening
First-trimester screening has long been the gold standard for prenatal testing. It has been the best way to check for possible genetic problems in the fetus for a long time. But because of recent improvements in non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), many couples now choose NIPT over first-trimester screening.
NIPT is much more accurate than screening in the first trimester. It can find problems with chromosomes 99% of the time. It is also safe and allows for earlier detection of issues, which can help parents make better decisions about the baby’s future. Additionally, NIPT is considerably less invasive than first-trimester screening and poses no risk to the mother or the baby.
With NIPT, parents can better understand their baby’s health and make informed decisions. It lets couples know that their baby is healthy, giving them peace of mind and improving their pregnancy.
With all of the advantages of NIPT, it is no surprise that many couples are opting for this test over the traditional first-trimester screening.
Conclusion
NIPT and first-trimester maternal screening tests are critical prenatal tests for expectant parents. Knowing their differences is essential for making the right decision for their unborn child’s health.NIPT, or non-invasive prenatal testing, is the most advanced test available. It looks for chromosomal abnormalities in the fetus’s DNA obtained from the mother’s blood sample. It is highly sensitive and can detect the most common chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome, with greater accuracy than traditional methods.
First-trimester maternal screening tests look for more subtle risks associated with birth defects. They are usually done between the 11th and 13th weeks of pregnancy and typically include a blood test, ultrasound, and fetal heart rate monitoring. These tests look for signs of abnormalities in the baby’s development, such as structural issues, growth issues, and genetic disorders.
At Metropolis Healthcare, we understand the importance of being informed and offer comprehensive options when it comes to prenatal tests. We are committed to giving expectant parents the necessary information to make the best decision for their unborn child's health.
Visit us today to learn more.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload













1701259759.webp)









 WhatsApp
WhatsApp