Latest Blogs
Understanding Nasal Polyps: Symptoms, Treatment, Causes & Removal
What are nasal polyps? Nasal polyps are non-cancerous growths that develop in the lining of the nasal passages or sinuses. These soft, painless swellings vary in size and may appear singularly or in clusters. They typically result from chronic inflammation, leading to the enlargement of the mucous membrane that lines the nasal cavity. Nasal polyps may affect one or both nostrils and can obstruct the nasal passages, leading to difficulty breathing and other nasal polyps symptoms. Understanding the nasal polyps types, causes, signs, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition effectively. What are the symptoms of nasal polyps? Nasal polyps can manifest in a variety of ways and may often affect the overall quality of your life. The primary nasal polyps symptoms are: Nasal congestion (stuffy nose) Rhinorrhea (runny nose) Headaches Loss of taste and smell Nosebleeds Postnasal drip (secretions from the nose that drain down into the throat, causing congestion and cough) Sinus pressure Snoring When nasal polyps grow large enough, they can block your nasal passages and sinuses, resulting in: Frequent asthma attacks (in asthma patients). Repeated sinus infections (sinusitis). Sleep disorders What are the causes of nasal polyps? The exact nasal polyps causes are unclear, but they are often associated with chronic inflammation of the nasal passages and sinuses. Common nasal polyps causes include: Allergies Asthma Chronic Sinus Infections Immune system disorders Aspirin sensitivity What are the risk factors of nasal polyps? Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing nasal polyps, such as: Asthma Allergic rhinitis (hay fever) Chronic sinus infections Cystic fibrosis (a genetic disorder causing sticky, thick mucus build-up in organs, including the lungs and the pancreas) Hypersensitivity to certain NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) such as aspirin, ibuprofen, etc. Genetic issues that may impact the reaction of nasal tissues to inflammation. What are the complications of nasal polyps? Nasal polyps, if left untreated or poorly managed, can lead to several complications, impacting both nasal health and overall well-being: Chronic Sinus Infections: Nasal polyps can obstruct sinus drainage, leading to recurrent sinus infections (sinusitis) that may be difficult to treat Breathing Difficulties: Large nasal polyps can block your nasal passages, causing breathing problems, particularly during sleep. Severe obstruction may lead to sleep apnea. Reduced Sense of Smell and Taste: As nasal polyps obstruct the nasal passages, they can impair your sense of smell (anosmia) and taste (dysgeusia) Asthma Exacerbation: Nasal polyps can worsen your asthma symptoms by exacerbating nasal congestion and inflammation, leading to more frequent asthma attacks. Spread of Infection: Infections associated with nasal polyps can spread to nearby structures, such as your eyes or brain, causing serious complications such as meningitis (brain and spine infection) and abscesses (pus in tissues or organs) if left untreated. Challenges in Nasal Polyps Treatment: Recurrent or persistent nasal polyps may pose challenges in treatment, requiring more aggressive management strategies or surgical intervention. How do doctors diagnose nasal polyps? Diagnosing nasal polyps typically starts with a physical examination and medical history review. During the examination, doctors inspect the nasal passages using a nasal speculum. They may use a lighted instrument called an endoscope to identify characteristic nasal polyps symptoms such as nasal congestion and diminished sense of smell. Imaging tests like CT scans may be employed to visualise the extent and location of the nasal polyps. Allergy testing might also be recommended to identify potential triggers. Through these methods, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose nasal polyps and develop a tailored nasal polyps treatment plan for their patients. What tests are used to diagnose nasal polyps? Several tests are employed to diagnose nasal polyps accurately. Nasal Endoscopy: A nasal endoscope is used to examine the nasal passages closely, allowing doctors to view any nasal polyps present. Imaging Studies: Computed tomography (CT) scans provide detailed images of the sinuses, helping identify the size, location, and extent of nasal polyps. Allergy Testing: Allergy tests may be conducted to determine if allergies contribute to nasal inflammation and nasal polyps formation. How are nasal polyps treated? Nasal polyps are typically managed through a combination of medication and, in some cases, surgery. Medication Medication is often the first-line nasal polyps treatment. Corticosteroids, either in nasal spray or oral form, can help reduce inflammation and shrink nasal polyps. Antihistamines (anti-allergics) and decongestants may also be prescribed to alleviate symptoms such as congestion and runny nose. Surgery for nasal polyps When medication fails to provide relief or if nasal polyps are large and obstructive, surgery may be recommended, especially in cases of nasal polyps in childhood. Endoscopic sinus surgery involves nasal polyps removal and improving sinus drainage. This minimally invasive procedure helps restore nasal airflow and alleviate symptoms. Can nasal polyps be prevented? While it is not always possible to prevent nasal polyps, the following certain measures may help reduce the risk of their development or recurrence. Manage Allergies: Taking steps to control allergies can help prevent nasal inflammation, a common precursor to nasal polyps formation. Avoid Irritants: Minimise exposure to airborne irritants like cigarette smoke and pollution, which can exacerbate nasal inflammation. Treat Sinus Infections Promptly: Treating sinus infections promptly can prevent chronic inflammation that may lead to nasal polyps development. Use a Nasal Rinse: Washing the inside of the nose with saltwater sprays or nasal washes helps remove irritants from the passage. Maintain Good Nasal Hygiene: Regular nasal irrigation can help keep nasal passages clear and reduce the risk of nasal polyps formation. Using clean humidifiers prevents the nose from getting stuffy and irritated. What can I expect if I have nasal polyps? If you have nasal polyps, you can have nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, facial swelling, snoring, and reduced taste and smell. Nasal polyps treatment can effectively eliminate these swellings and improve nasal breathing. For those experiencing loss of taste and smell, some may not get it back entirely, even after nasal polyps are treated. Conclusion In conclusion, nasal polyps can significantly impact one's quality of life, causing stuffy nose, loss of crucial senses like taste and smell and facial pain. However, with proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals can find relief from these nasal polyps symptoms. Experience comfort from nasal polyps with Metropolis Healthcare. Our expert team offers comprehensive diagnosis and personalised treatment plans to help you breathe easier. Schedule your appointment now and take the first step towards healthier sinuses.
How To Increase Sperm Count Naturally: Ways & Best Foods To Boost Male Fertility
Overview Sperm count refers to the average number of male reproductive cells present in the semen or seminal fluid (a greyish-white fluid secreted by males). According to the World Health Organization, 15 million per ml or a minimum of 39 million per ejaculate sample (the semen released from a penis after sexual intercourse) is considered a healthy sperm count. Fertility experts believe that a sperm count below this level may cause infertility issues in males. Additionally, sperm health is also a major aspect. It relies on different factors, such as the structure and motility of the sperm. Stress, along with health conditions like infections, genetic medical conditions, and tumours, are likely to affect your sperm count and strength. Are you looking for natural remedies on how to increase sperm count? By modifying your lifestyle preferences, you may boost your sperm count naturally. Additionally, here is a look into the best ways to enhance the quality of your sperm. Best Ways To Increase Sperm Count Quit Smoking According to various studies, people who are moderate to heavy smokers are likely to have a lower sperm quantity and quality than people who smoke tobacco lightly or do not smoke at all. So, it is advisable to quit smoking to ensure sperm health. Exercise Exercising gets your heart pumping, which helps you in multiple ways. It allows you to maintain a healthy weight and ensure proper blood circulation. When you have a healthy body, it will eventually boost your reproductive health. Various studies show that exercises like running, jogging, and weight-lifting help improve your sperm health. Manage Stress Stress can considerably reduce the number of sperm in your semen. Most importantly, these sperm are likely to have motility (movement) and shape-related issues that may lead to fertility problems. Therefore, you should manage your stress level to improve the quantity as well as the quality of your sperm. Take your Vitamins Some of the vitamins that help with sperm production include Vitamin B12, Vitamin C, Vitamin D, Vitamin E, Zinc, Folate, and Selenium. You can add these to your diet by eating vitamin-rich foods or taking them in the form of supplements. However, before taking any health supplements, consult with your doctor first. Take Ashwagandha Ashwagandha is a powerful herbal remedy that can help alleviate stress and infertility. It is very effective in improving blood circulation in the body and also naturally enhancing sperm quality. According to some studies, Ashwagandha's root extracts improve sperm concentration, ejaculate volume, and serum testosterone levels in infertile men. Avoid Substance Abuse People with a history of alcoholism and usage of recreational drugs such as cocaine, heroin, marijuana and cannabis are likely to have low sperm counts and unhealthy sperm. In fact, studies also confirm that excessive amounts of anabolic steroids taken to achieve a muscular physique can lead to poor male reproductive functions, including diminished sexual urge and deficient production and health of sperm. Therefore, it is advisable to quit drugs and avoid any substance abuse in order to maintain your reproductive health. Wear Loose Clothes According to a 2018 study conducted by Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health, males who wore loose-fitting underwear like boxers had considerably higher sperm counts than men who wore tight clothes. One of the primary reasons behind this finding is that wearing tight undergarments is likely to increase your testicular temperature, affecting sperm health and reducing its viability and motility. Lose Weight Did you know losing weight can significantly improve the volume of your semen, sperm motility, and overall sperm health? Actually, the fat cells in your body secrete an enzyme called aromatase. This enzyme breaks down the male reproductive hormone testosterone into estrogen, which can often decrease testosterone levels while reducing sperm count. So, hit the gym regularly or work out at home and maintain a healthy weight. Keep Your Testicles Cool Increased scrotal or testicular temperature is likely to affect sperm production. Although studies on this topic have produced mixed results, avoiding hot tubs and saunas, reducing your sitting time, and refraining from putting laptops on your lap may help improve your sperm quality. Get Enough Sleep Not getting enough sleep can not only affect your reproductive health and impact sperm count but also your health and well-being as a whole. So, nap well and wake up to a healthy and happy you. Seven to eight hours of sleep per day is good for your overall fitness. Foods to Improve Sperm Count Searching for the answer to how to increase sperm count with a diet plan? Eating a well-balanced diet is the easiest way to increase your sperm count. The following is a list of foods to eat to boost fertility: Fruits and vegetables: Green leafy vegetables, beans, collard greens, and berries are good sources of antioxidants and vitamin B, which help keep your sperm motile and strong while protecting them from cellular damage and abnormalities. Spinach, avocados, broccoli, and mangoes are rich in vitamin E, which helps boost your sperm count. You may find your daily dose of vitamin C in tomatoes, grapefruit, lemon, and oranges. Fatty fish: Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish help improve blood circulation to testicles while maintaining the overall health of sperm. To get omega-3s, add fatty fish, including herring, anchovies, sardines, and salmon, to your diet. Seeds and nuts: Walnuts, pecans, almonds, hazelnuts, and peanuts help enhance sperm health as they are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants. Pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, flaxseed, and sunflower seeds may also provide zinc, vitamin E, antioxidants, and omega-3 fatty acids. Garlic: It is one of the best sources of selenium and allicin. Selenium is an antioxidant that boosts sperm motility, while allicin improves blood flow in reproductive organs and protects sperm from damage. Conclusion Sperm count is an indicator of a man's fertility. These cells must be healthy to be viable and fertilise the female eggs. You can boost your sperm count by changing your food and lifestyle. Apart from learning how to increase semen count naturally, get in touch with your doctor to learn about various treatment options to help you improve your fertility. Additionally, you can also get a complete health check-up at regular intervals. It will help you monitor your parameters and seek medical advice as and when needed. At Metropolis Healthcare, we offer a wide range of tests at affordable prices. Get in touch with us and get tested right away!
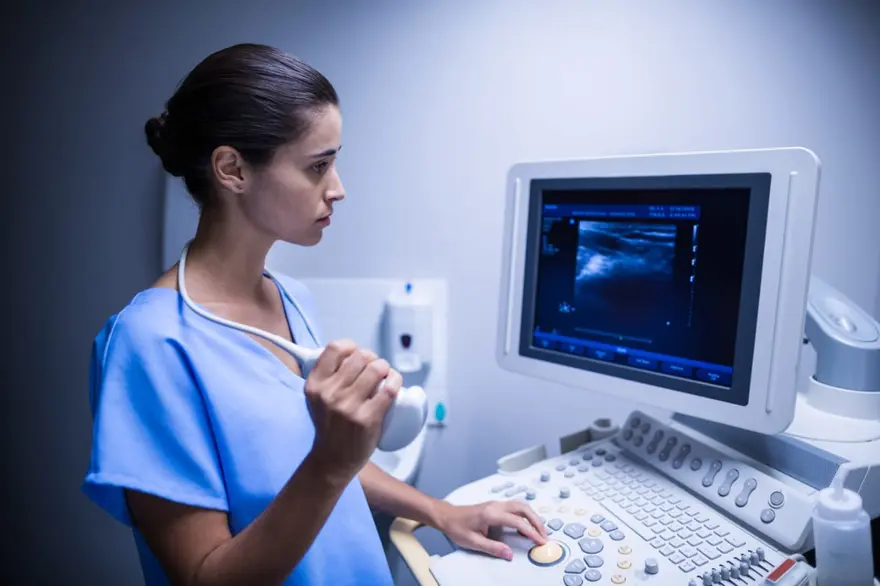
Understanding Transvaginal Ultrasound: Purpose, Preparation, and Results
Introduction Transvaginal ultrasound is a vital diagnostic tool in women's healthcare that offers detailed insights into pelvic health. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of the procedure, its uses, and benefits in ensuring female reproductive well-being. What is a Transvaginal Ultrasound? A transvaginal ultrasound, also known as endovaginal ultrasound, is a medical procedure utilised to examine female reproductive organs, including the uterus, ovaries, cervix, and fallopian tubes. Unlike a traditional abdominal ultrasound, where the ultrasound wand (transducer) is placed on the abdomen's surface, transvaginal ultrasound involves inserting a probe directly into the vagina for a closer view of the pelvic organs. What is the Difference Between an Ultrasound and a Transvaginal Ultrasound? USG, in its full form, stands for Ultrasonography. It is a broad term referring to the medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of internal body structures. It encompasses various types of ultrasound procedures, including abdominal ultrasound and transvaginal ultrasound. While ultrasound uses a non-invasive technique to generate images of internal abdominal structures, transvaginal ultrasound offers superior visualisation and details due to the transducer's proximity to your pelvic organs. When is a Transvaginal Ultrasound Performed? Transvaginal ultrasound is used to investigate the pelvic cavity thoroughly and address various gynaecological concerns such as abnormal bleeding, pelvic pain, and infertility. Another transvaginal ultrasound purpose is to monitor the growth and development of your foetus during pregnancy. When Would a Transvaginal Ultrasound be Needed? The most significant purpose of transvaginal ultrasound is a diagnosis of various gynaecological conditions and reproductive health concerns, like: Endometriosis Evaluation: Endometriosis is a condition where tissue similar to the lining of the uterus may grow outside on your ovaries or other pelvic organs, commonly resulting in chronic pelvic pain or painful periods. A transvaginal ultrasound can help visualise any endometrial implants and adhesions within the pelvic cavity. Ovarian Cyst Assessment: If you suspect ovarian cysts, characterised by pelvic pain or irregular menstruation, you may undergo a transvaginal ultrasound to confirm and assess the size and composition of the cysts. This helps to rule out potential complications such as ovarian rupture, which affects the release and quality of eggs. Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS) Diagnosis: Transvaginal ultrasound plays a crucial role in diagnosing PCOS. It reveals the characteristic appearance of multiple small follicles (fluid-filled sacs containing eggs) within the ovaries, along with other associated findings such as increased ovarian volume and thickened ovarian capsules. Uterine Fibroids Detection: For women experiencing symptoms such as heavy menstrual bleeding, pelvic pressure, or frequent urination, a transvaginal ultrasound can identify the presence, size, and location of uterine fibroids, aiding in treatment planning and management decisions. Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) Evaluation: In cases of suspected PID, which may manifest as lower abdominal pain, abnormal vaginal discharge, or fever, a transvaginal ultrasound can detect signs of inflammation or infection within the reproductive organs. This helps in getting treatment promptly to prevent complications such as tubal scarring (formation of scar tissue in the fallopian tube connecting ovaries to the uterus) or infertility. Fertility Issues: For those struggling with infertility, a transvaginal ultrasound may be a part of the diagnostic process to evaluate the health of reproductive organs, assess ovarian reserve (quantity and quality of eggs available for fertilisation), and identify any anatomical abnormalities that could affect fertility. Early Pregnancy: Transvaginal ultrasound pregnancy assessment is commonly performed during the early stages of conception. This procedure aims to confirm the presence of a gestational sac, assess fetal viability, determine gestational age, and detect potential complications such as ectopic pregnancy (fertilised egg implants outside the uterus) or miscarriage. Fetal Development: Throughout pregnancy, transvaginal ultrasounds may be utilised to monitor the growth and development of your foetus, evaluate its anatomy, and detect any abnormalities or developmental issues that may require medical intervention. Who Performs a Transvaginal Ultrasound? Trained sonographers or radiologists typically conduct transvaginal ultrasounds in a medical facility equipped with ultrasound technology. These professionals possess expertise in operating ultrasound equipment and interpreting the obtained images. How Does a Transvaginal Ultrasound Work? During the procedure, your healthcare provider will gently insert a condom-covered lubricated transducer probe into the vagina. This probe emits high-frequency sound waves that penetrate your pelvic organs and surrounding structures, bouncing back to create real-time clear images on a monitor. How Long Does a Transvaginal Ultrasound Take? The duration of a transvaginal ultrasound varies depending on the specific purpose and complexity of the examination. Generally, the procedure lasts between 15 to 30 minutes, although it may be extended if additional evaluations or measurements are necessary. How Do I Prepare for a Transvaginal Ultrasound? Transvaginal ultrasound preparation takes minimal effort from your side. Your healthcare provider may advise you to drink water and avoid urinating before the procedure to ensure a full bladder, which can aid in obtaining clearer images of the pelvic organs. Additionally, wearing comfortable clothing and informing the healthcare provider of any medical conditions or allergies can be considered as part of transvaginal ultrasound preparation. What Should I Expect During a Transvaginal Ultrasound? During the procedure, you'll be asked to lie on your back on an examination table with your feet placed in stirrups, similar to a pelvic exam. The transducer probe will then be gently inserted into your vagina, causing minimal discomfort. The healthcare provider may turn the probe to capture images from various angles while explaining the process and addressing any concerns you may have. Is a Transvaginal Ultrasound Painful? While some individuals may experience slight discomfort or pressure during the insertion of the transducer probe, the procedure is generally well-tolerated and causes minimal pain. The probe is well-lubricated before the insertion, and it bends around your body. This, coupled with the gentle technique employed by your healthcare provider, helps mitigate discomfort. What Are the Risks of a Transvaginal Ultrasound? Unlike the risk of radiation exposure in X-rays, transvaginal ultrasounds are considered safe with minimal associated threats. Rarely some individuals may experience minor vaginal bleeding or irritation following the procedure. However, serious complications are exceedingly rare. What Type of Results Do You Get After a Transvaginal Ultrasound? Following the procedure, the obtained images are interpreted by a radiologist or healthcare provider who analyses the transvaginal ultrasound result and provides a comprehensive report. Depending on the purpose, your transvaginal ultrasound results may include assessments of pelvic organ health, pregnancy viability, foetal development, or identification of abnormalities requiring further evaluation or treatment. Conclusion: In navigating the realm of women's health, understanding procedures like transvaginal ultrasound is crucial for informed decision-making and proactive healthcare management, especially pelvic wellness and pregnancy care. At Metropolis Lab, we prioritise your health and well-being, offering state-of-the-art diagnostic services. Trust in our commitment to delivering accurate results and personalised care, empowering you to prioritise your reproductive health with confidence.
Protein Rich Food For Vegetarians: Sources, Diet Plan & Food Chart
Overview As a vegetarian, you have chosen a path that is compassionate and incredibly healthy. However, are your nutritional needs, especially protein, really being met? Protein is a nutrient that helps build and repair tissues, supports your immune system, and keeps you feeling full and energised. Women should aim for at least 46 grams of protein per day, while men should target around 56 grams. However, your protein needs may vary depending on your weight and activity level. As meat is the go-to source of protein for many, as vegetarians, you may have heard of concerns about meeting your protein needs, but do not fear! Here, you have a diverse array of protein rich food veg at your fingertips. Let’s look into the veg protein food chart and enrich our knowledge of veg protein sources. Protein Rich Food For Vegetarians Eating a protein rich vegetarian diet offers several health benefits compared to meat-based protein. Plant-based protein is lower in saturated fat and cholesterol, making it a heart-healthier option. They contain more fibre, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which contribute to overall health by helping you reduce your body weight. It also reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Here’s a list of veg protein sources waiting to fuel your journey towards optimal health. Let’s check the protein rich food veg: Lentils Lentils or dals are a staple in every Indian kitchen. With 18 grams of protein per cooked cup (198 grams), they are a very good source of protein and fibre. Legumes Beans, chickpeas, and peas are excellent sources of protein and fibre. Every cooked cup of legumes contains 18 grams of protein. Whether you enjoy them in soups, salads, or curries, legumes are a nutritional addition to any meal. Nuts Almonds, walnuts, and cashews are not only crunchy and delicious but also rich in protein and healthy fats. Every 28 grams of nuts contains 5 to 7 grams of protein based on the variety of nuts. Sprinkle them over the salad or enjoy them as snacks between the meals. Soy Milk Soy milk is a great alternative to dairy milk. It is fortified with calcium and protein, making it a valuable addition to your diet. It contains 6 grams of protein per cup, which is 244 grams of soy milk. Pour it over your morning cereal, or use it in smoothies for an extra protein boost. Green Peas Do not underestimate the nutritional power of these vibrant green gems. They are excellent vegetable protein sources, with around 9 grams of protein per 160 grams of cooked cup of peas. They are a tasty way to sneak in some extra protein. Quinoa Often hailed as a superfood, quinoa is a complete protein, meaning it contains all nine essential amino acids. Quinoa contains 8 to 9 grams of protein per cooked cup (185 grams). Swap out rice or pasta for quinoa in your favourite dishes to up your protein intake. Chia Seeds These tiny seeds are packed with protein, fibre, and omega-3 fatty acids. They contain 5 grams of protein and 10 grams of fibre per 28 grams of chia seeds. Add them to your yoghurt, oatmeal, or smoothies for an extra nutritional boost. Oats Starting your day with a hearty bowl of oatmeal not only provides you with sustained energy but also a good dose of protein. 40 grams of oats contain 5 grams of protein and 4 grams of fibre. Customise your oats with fruits, nuts, and seeds for a nutritious breakfast. High Protein Vegetables Broccoli, spinach, and kale are not only rich in vitamins and minerals but also surprisingly high in protein. It contains 4 to 5 grams of protein per cooked cup. Incorporate them into your meals to add nutritional value and flavour. Fruits While not as protein-dense as other foods on this list, fruits like guava, bananas, and avocados still contribute to your overall protein intake. They contain around 2 to 4 grams of protein per cup. Plus, they’re packed with vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Edamame These young soybeans are not only delicious but also excellent veg protein sources. They contain 10 to 12 grams of protein per 100-gram serving. Enjoy them steamed as a snack or added to salads and stir-fries. Brussels Sprouts These miniature cabbages are not only cute but also nutritious. With approximately 4 to 5 grams of protein per cooked cup, Brussels sprouts are a great addition to any meal. Wild Rice Unlike white rice, wild rice is not stripped of its bran. It is higher in protein and fibre, making it a healthier choice for vegetarians. The cooked cup (approx. 100 grams) of wild rice contains nearly 4 grams of protein. Use it as a base for grain bowls for a satisfying meal. Sweet Corn Bursting with sweetness and flavour, sweet corn is a summertime favourite and a good source of protein. 100 grams of sweet corn contains 3.2 grams of protein. Enjoy it grilled, steamed, or tossed into salads and salsas. Cottage Cheese If you include dairy in your diet, cottage cheese is an excellent source of protein. Every 100 grams of cottage cheese contains around 11 grams of protein. Enjoy it on its own, or mix it with fruits and vegetables. FAQs: How do Vegetarians Get Enough Protein? You can easily meet your protein needs by incorporating a variety of protein rich food veg into your vegetarian diet plan, such as legumes, nuts, seeds, and whole grains. Be sure to include veg protein sources at each meal to ensure adequate intake. Which Fruit Has the Most Protein? While fruits are not typically high in protein compared to other food groups, guava stands out as one of the highest-protein fruits, with approximately 2.6 grams of protein per 100-gram cup. Do Vegetarians Lose Weight Faster? A vegetarian diet plan can be conducive to weight loss due to its high protein content, lower calories, and reduced saturated fat. Veg protein sources can help reduce weight by making you feel satiated, boosting metabolism, preserving muscle mass, regulating appetite hormones, and promoting fat loss. However, weight loss also depends on factors such as overall calorie intake, food choices, and the extent of physical activities to break down fat or calories consumed. Which Dal is High in Protein? Among dals (lentils), moong dal (split green gram) is one of the highest in protein, offering approximately 14 grams of protein per cooked cup. Which Vegetable Has the Most Protein? Spinach and broccoli are among the vegetables with relatively higher protein content, around 2.9 grams per 100-gram serving. As a Vegetarian, How Can I Get 75 Grams of Protein a Day? Your vegetarian diet plan should include a variety of protein rich food veg options, such as lentils, legumes, tofu, nuts, seeds, quinoa, and dairy alternatives. What is the Best Source of Protein for Vegetarians? Legumes, tofu, tempeh (fermented soybeans), nuts, seeds, quinoa, cottage cheese, whey protein, skim milk, etc. are excellent veg protein sources.
Everything You Need to Know About Bartholin Cysts
What is a Bartholin cyst? A Bartholin cyst is a fairly painless lump that forms near the vagina; it can be found on either side of your labia (lips of the vagina). This cyst is named after two small glands that are present in the area and help produce the fluid required to lubricate your vagina. The Bartholin glands and labia are part of the vulva. A Bartholin cyst is usually present on only one of the two glands. While some are smaller and do not cause much pain, larger Bartholin cysts, especially those that get bacterial infections, may be painful and need medical treatment. What does a Bartholin cyst look like? A Bartholin cyst usually appears as a small round bump under the skin of the labia. If there is an infection, some may turn red, swollen, and tender, and at other times, the Bartholin cyst can fill with fluid or pus. The size of Bartholin cysts can range from small pea-sized bumps to large gold ball-sized cysts that can sometimes make the labia look lopsided and larger on one side. Who gets Bartholin cysts? About 2% of women are believed to have developed a Bartholin cyst at some point in their lives. Bartholin cysts are more common in women of reproductive age, and the chances of developing one can decrease considerably after menopause. What causes a Bartholin cyst? The reason why some women are predisposed to developing Bartholin cysts is still unknown to most healthcare providers; however, commonly known Bartholin cyst causes include: Bacterial infections like E-coli Sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhea and chlamydia Irritation, injury, or growth of extra skin near the vulva region What are the symptoms of a Bartholin cyst? Most Bartholin cysts are small and may not cause many symptoms except minor irritation. However, if these Bartholin cysts grow in size and become infected or form an abscess, the following symptoms may occur: Swelling and tenderness in the area Discomfort and pain during sex, while using a tampon, sitting, walking, or when wiping after using the restroom Redness Fever and chills Changes in the size of the cyst Drainage of fluid/pus from the cyst Is a Bartholin cyst contagious? Most Bartholin cyst cases are minor and do not get infected or spread through skin-to-skin contact. However, one of the leading Bartholin cyst causes is sexually transmitted diseases, which can be contagious. Does an infection cause Bartholin cysts? Bartholin cyst causes include bacterial infections such as E. Coli and sexually transmitted diseases. These infections can clog the Bartholin gland, leading to the formation of the Bartholin cyst. How is a Bartholin cyst diagnosed? Your healthcare provider/gynaecologist will perform a physical examination to check the size of the Bartholin cyst and whether it is showing any signs of infection. If a discharge is oozing out of the cyst, this fluid will also be tested for sexually transmitted infections or other forms of bacterial infections. What tests are done to diagnose Bartholin cysts? Women older than 40 may need to undergo a biopsy on the Bartholin cyst to rule out cases of vulva cancer. For this test, your doctor will take a small tissue sample from the Bartholin cyst and examine it under a microscope. If the Bartholin cyst is found to be cancerous, it may need to be surgically removed. However, the Bartholin cyst rarely develops into cancer, which is often more common after the age of 60. What are the treatments for a Bartholin cyst? Bartholin cyst treatment options vary based on the symptoms you are displaying. Smaller, painless Bartholin cysts may not even need any form of treatment. However, if it starts to grow or the symptoms persist, you may develop an infection or abscess requiring treatment or, in severe cases, Bartholin cyst removal. Bartholin cyst treatment options include: Sitz Baths: For a few days, you will need to sit in a bathtub with a few inches of warm water several times a day to give you comfort from Bartholin cyst symptoms and promote healing. The warm water also aids in bursting and draining the Bartholin cyst. Over-the-counter medication: This helps relieve pain and discomfort caused by the Bartholin cyst. Antibiotics: These may be prescribed to treat any bacterial or sexually transmitted infection that may have that causes the Bartholin cyst. Surgical draining: Bartholin cyst surgery is often performed on large and infected cysts to drain the fluid inside. It is carried out with a small tube known as a catheter inserted into the cyst. Marsupialization: This is another Bartholin cyst procedure in which the cyst is surgically opened and drained. The ends of the cyst walls are then stitched together to form a pocket or pouch that aids in continuous drainage. Bartholin Gland removal: This is a rare Bartholin cyst treatment option in which the glands may need to be surgically removed because other treatments have failed. Do Bartholin cysts go away on their own? In most cases, Bartholin cysts can disappear on their own. Sometimes they can even burst and deflate on their own. As long as you keep the area clean and dry to avoid the spread of the infection and avoid squeezing or draining the Bartholin cyst, you can manage the symptoms with just sitz baths. How long does a Bartholin cyst last? In most cases, a Bartholin cyst infection may be wholly resolved in a few weeks. However, this may also depend upon the size of the Bartholin cyst and the severity of the infection. Conclusion If you notice a lump near your vagina that can be painful, see your doctor to check for an infection and determine if it's a Bartholin cyst. Talking freely about the infection and asking questions will help your doctor diagnose and treat the condition more effectively. Regular diagnostic tests and health check-ups can also help reduce the chances of Bartholin cysts, infections or sexually transmitted diseases causing added complications. Metropolis Labs provides at-home diagnostic tests for their customer's convenience while maintaining the patient's anonymity. Contact us today for more details.
Exploring Rectal Prolapse: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
Rectal prolapse can be uncomfortable to deal with; therefore, understanding the symptoms and complications associated with it is necessary. This guide discusses rectal prolapse in detail, offering insights on treatment options and prevention strategies to help you navigate its challenges effectively. What is rectal prolapse? Rectal prolapse is a condition which occurs when your rectum, the last part of the large intestine, protrudes through your anus. This can lead to discomfort, pain, and difficulty with bowel movements. Rectal prolapse types can include partial, complete, internal, or external, depending on the anatomy of the prolapse. What causes rectal prolapse? Rectal prolapse is primarily caused by weakened pelvic floor muscles and tissues that support your rectum. Chronic straining during bowel movements due to constipation, long-term diarrhoea, ageing, childbirth, or previous pelvic surgery are common rectal prolapse causes. Other factors include neurological conditions, genetic predisposition, and certain connective tissue disorders. What does rectal prolapse look like? Rectal prolapse may look like a reddish or pinkish mass emerging from your anus, typically when exerting pressure during bowel movements. This mass may retract back into the anus or remain visible externally. What are the signs or symptoms of rectal prolapse? Common rectal prolapse symptoms include: The most noticeable rectal prolapse symptom is the protrusion of your rectum through your anus during bowel movements or even when standing or walking. You may experience discomfort, pain, or a feeling of fullness in your rectum or anus. Rectal prolapse can lead to difficulty with your bowel movements, including straining or incomplete evacuation. You may experience leakage of faeces or mucus from the protruding rectum. The exposed rectal tissue can become irritated, leading to itching, burning, or bleeding. You may feel increased pressure or heaviness in your pelvic area, especially when standing or sitting for a long time. How is rectal prolapse diagnosed? Rectal Prolapse diagnosis typically involves: Physical examination: A healthcare provider will perform a physical examination, including a visual inspection of your anus and rectum, to look for signs of prolapse. Digital rectal exam: This involves inserting a gloved, lubricated finger into the rectum to assess the extent of prolapse and check for any abnormalities. Colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy: These procedures allow for a more detailed examination of the rectum and colon to rule out other potential causes of rectal prolapse symptoms. Imaging tests: In some cases, imaging tests such as MRI or defecography may be ordered to evaluate pelvic floor function and assess the severity of prolapse. Anorectal manometry: This test measures pressure and function in the rectum and anal sphincters, helping to assess bowel function and pelvic floor coordination. Will rectal prolapse go away on its own? Rectal prolapse typically does not resolve on its own and often requires medical intervention, lifestyle changes, pelvic floor exercises, or surgery, depending on the severity of the condition. What happens if rectal prolapse is left untreated? If left untreated, rectal prolapse can cause chronic pain, fecal incontinence, and difficulty passing stool. In severe cases, tissue damage, ulceration and even strangulation of prolapsed tissue can occur, requiring emergency surgery to prevent complications such as tissue necrosis. How do you fix rectal prolapse? Rectal prolapse treatments vary depending on the severity of the condition and individual factors. They include: Abdominal approach (Rectopexy) Rectopexy is a surgical procedure commonly used for rectal prolapse treatment, particularly when the prolapse is significant or associated with other pelvic floor disorders. Rectopexy via the abdominal approach, i.e. through an incision in the belly, is often effective in providing long-term relief from rectal prolapse symptoms. Compared to some other surgical techniques, it lowers the risk of recurrence. Rectal Approach (Perineal) The perineal approach, also known as perineal recto sigmoidectomy or Delorme's procedure, is another surgical option for rectal prolapse therapies. Unlike rectopexy, which is performed through an abdominal incision, the perineal approach involves accessing the rectum through the area between the anus and the genitalia (the perineum). The perineal approach is often preferred for patients who are not candidates for abdominal surgery due to factors such as advanced age, poor overall health, or previous abdominal surgeries. Other options for rectal prolapse therapies include: Conservative management Dietary changes to regulate bowel movements. Pelvic floor exercises to strengthen muscles. Medications to alleviate constipation or diarrhoea. Medical procedures Manual reduction: Non-surgical manipulation to push the prolapse back into place. Rubber band ligation: Placing bands around the prolapsed tissue to cut off its blood supply, causing it to shrink and fall off. Injection sclerotherapy: Injecting a chemical solution into the prolapsed tissue to shrink it. Biofeedback therapy: Training to improve bowel control and pelvic floor function. What are the possible risks or complications of rectal prolapse surgery? Infection: Surgical procedures carry a risk of infection at the incision site or within the pelvic cavity. Bleeding: Post-operative bleeding can occur, either externally from the surgical site or internally within the abdomen or pelvis. Anaesthesia complications: Reactions to anaesthesia, though rare, can include respiratory problems, allergic reactions, or adverse drug interactions. Urinary problems: Surgery near the bladder or urethra can lead to urinary retention, incontinence, or urinary tract infections. Bowel dysfunction: Following rectal prolapse surgery, you may experience changes in bowel habits, including constipation or diarrhoea. Recurrence: Despite surgical intervention, rectal prolapse may recur in some cases, necessitating further treatment. How can I prevent rectal prolapse? Obesity can increase the risk of rectal prolapse, so aim to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise Avoid straining during bowel movements Address constipation promptly with dietary changes, fibre supplements, or stool softeners Strengthen pelvic floor muscles with exercises like Kegels to help support the rectum and prevent prolapse If you have a chronic cough, seek treatment to reduce strain on the pelvic floor and rectum Avoid heavy lifting. What is the outlook if I have rectal prolapse? While surgery generally offers favourable outcomes for rectal prolapse, you may experience ongoing symptoms like constipation or incomplete bowel movements. With appropriate medical management or surgery, many people experience significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life, with a low risk of recurrence. Conclusion In conclusion, rectal prolapse is a condition that can significantly impact your daily life. Still, with prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment and lifestyle modifications, you can find relief and achieve improved long-term outcomes. If you or your family members want to protect yourself from rectal prolapse and its associated complications, get your blood and stool regularly tested at Metropolis Healthcare for timely diagnosis. Metropolis Healthcare strives to provide best-in-class diagnostic service that is not only reliable but also pocket-friendly, executed by the best phlebotomists, and trusted by the best doctors across the country. Hurry up and book your test today!
Understanding Tinea Versicolor: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment
What is tinea versicolor? Tinea versicolor, a prevalent skin fungal infection, which disrupts natural skin pigmentation, leading to small, discoloured patches. Tinea versicolor commonly affects the torso and upper arms but can also appear on the face and neck, especially in younger children. The tinea versicolor on face can appear to be white, brown, red, or pink in colour or a dry, flaky, or scaly skin with a flat or slightly raised texture. What does tinea versicolor look like? Tinea versicolor spots can manifest as patches that are either lighter or darker than the surrounding skin, presenting in hues of white, pink, or light brown. These patches may exhibit dryness or scaliness and tend to appear more prominently on the chest and shoulders. Who gets tinea versicolor? Tinea versicolor can affect anyone, but it's more common in adolescents and young adults. Tinea versicolor can affect people worldwide, regardless of geographic location or nationality. However, it may be more commonly reported in regions with warm and humid climates, where the conditions are conducive to fungal growth on the skin. What are the symptoms of tinea versicolor? Most individuals experience mild tinea versicolor symptoms such as: Skin discolouration, typically on the back, chest, and abdomen. Discoloured patches can occur anywhere on the body and vary in shades of pink, yellow, brown, tan, or white. Itching in or around the affected skin areas. Increased sweating. Areas of skin that may become dry and develop scales. Skin patches that fail to darken or tan when exposed to sunlight. What causes tinea versicolor? Major cause of tinea versicolor is an excessive proliferation of yeast on the skin's surface. Flourishing in warm, moist, and oily conditions, this yeast multiplies in small clusters, leading to the characteristic symptoms of the condition. Tinea versicolor causes are as follows: Compromised immune function. High temperatures and humidity. Perspiration. Excessively oily skin. Hormonal fluctuations. How is tinea versicolor diagnosed? Tinea versicolor is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history review and physical examination. The distinctive patches associated with this condition often facilitate its identification during the physical examination. Additionally, healthcare providers may utilise a Woods Lamp, an ultraviolet light, to enhance the visibility of the patches for a clearer diagnosis. How is tinea versicolor treated? The following ways can be considered for tinea versicolor treatment: Over-the-counter antifungal medication For mild cases, over-the-counter antifungal lotions, creams, ointments, or shampoos can be applied as an easily and accessible tinea versicolor treatment options. Prescription antifungal medication Clotrimazole cream or lotion Miconazole cream Selenium sulphide lotion Terbinafine cream or gel Zinc pyrithione soap Other ways of treatment are as follows: Severe or unresponsive cases of tinea versicolor may require prescription-strength medication. Medications may include: Ketoconazole cream, gel, or shampoo Ciclopirox cream, gel, or shampoo Fluconazole tablets or oral solution Itraconazole tablets, capsules, or oral solution Selenium sulphide lotion or shampoo Preventative medication may be necessary once or twice a month for persistent cases. How can I treat tinea versicolor at home? Home Remedies for Tinea Versicolor: Natural Antifungal Agents: Tea tree oil and apple cider vinegar possess antifungal properties that can help combat the fungal infection responsible for tinea versicolor. Tea tree oil can be diluted with carrier oil and applied directly to the affected areas, while apple cider vinegar can be diluted with water and applied as a topical solution. Yogurt and Honey Mixture: Yogurt contains probiotics that can help restore the balance of microorganisms on the skin, while honey has antimicrobial properties. Mixing yoghurt and honey into a paste and applying it to the affected areas can help soothe the skin and inhibit fungal growth. Aloe Vera Gel: Aloe vera gel is known for its soothing and healing properties. Applying pure aloe vera gel on the affected areas can help reduce inflammation, soothe irritated skin, and promote healing. Coconut Oil: Coconut oil has antifungal properties and can help combat the fungal infection causing tinea versicolor. Applying coconut oil to the affected areas can help moisturize the skin, reduce dryness, and prevent fungal growth. Maintain Good Hygiene: Keeping the affected area clean and dry is essential for managing tinea versicolor. Regularly washing the skin with a gentle cleanser and patting it dry can help prevent the growth of fungi and reduce the risk of infection. Remember that it is good to get in touch with the doctor before you follow any remedies at home. How long does tinea versicolor take to go away? Treatment for tinea versicolor typically takes around 1-2 weeks to show improvement. If tinea versicolor recurs, you should consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and management. How can I prevent tinea versicolor? Preventing a recurrence of tinea versicolor can pose challenges. However, if you've been diagnosed with and successfully treated the condition, there are proactive measures you can take to reduce the likelihood of future infections: Avoiding prolonged exposure to excessive heat. Steer clear of tanning or extended periods of sun exposure. Minimise excessive sweating by staying cool and wearing breathable clothing. Utilise prescription-strength skin treatments during periods of increased susceptibility to tinea versicolor. What are the risk factors for developing tinea versicolor? Several environmental and biological factors can elevate your susceptibility to this condition, including: A familial predisposition to tinea versicolor. Excessive perspiration. Residence in a humid, warm environment. Weakened immune function. Use of immunosuppressive medications. Certain types of cancer. Can tinea versicolor come back? Yes, it can return even after successful tinea versicolor treatment. Tinea versicolor can recur due to factors like dormant fungal spores, warm and humid environments, individual susceptibility, incomplete treatment, weakened immune function, and lifestyle habits. What are the complications of tinea versicolor? Complications of tinea versicolor are generally minimal but may include: Persistent changes in skin pigmentation, lead to uneven skin tone. Recurrence of the infection, requiring further treatment. Emotional distress or self-esteem issues due to changes in appearance. Conclusion Tinea versicolor is a prevalent fungal skin infection characterised by discoloured patches and mild tinea versicolor symptoms like itching and increased perspiration. Diagnosis involves physical examination and tinea versicolor treatment. Options range from prescription medications to over-the-counter remedies. Recurrences are possible, underscoring the importance of preventive measures such as avoiding excessive heat and sun exposure. While complications are usually minor, changes in skin pigmentation and emotional distress can occur.
 Home Visit
Home Visit Upload
Upload
















 WhatsApp
WhatsApp